Python语法快速入门指南
Python语言与Perl,C和Java等语言有许多相似之处。但是,也存在一些差异。
在本章中我们将来学习Python的基础语法,让你快速学会Python编程。
第一个Python程序
交互式编程
交互式编程不需要创建脚本文件,是通过 Python 解释器的交互模式进来编写代码。
linux上你只需要在命令行中输入 Python 命令即可启动交互式编程,提示窗口如下:
$ python Python 2.7.6 (default, Sep 9 2014, 15:04:36) [GCC 4.2.1 Compatible Apple LLVM 6.0 (clang-600.0.39)] on darwin Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information. >>>
Window上在安装Python时已经已经安装了默认的交互式编程客户端,提示窗口如下:
在 python 提示符中输入以下文本信息,然后按 Enter 键查看运行效果:
>>> print "Hello, Python!";
在 Python 2.7.6 版本中,以上事例输出结果如下:
Hello, Python!
如果您运行的是新版本的Python,那么你就需要在print语句中使用括号如:
>>> print ("Hello, Python!");
脚本式编程
通过脚本参数调用解释器开始执行脚本,直到脚本执行完毕。当脚本执行完成后,解释器不再有效。
让我们写一个简单的Python脚本程序。所有Python文件将以.py为扩展名。将以下的源代码拷贝至test.py文件中。
print "Hello, Python!";
这里,假设你已经设置了Python解释器PATH变量。使用以下命令运行程序:
$ python test.py
输出结果:
Hello, Python!
让我们尝试另一种方式来执行Python脚本。修改test.py文件,如下所示:
#!/usr/bin/python print "Hello, Python!";
这里,假定您的Python解释器在/usr/bin目录中,使用以下命令执行脚本:
$ chmod +x test.py # 脚本文件添加可执行权限 $./test.py
输出结果:
Hello, Python!
Python 标识符
在python里,标识符有字母、数字、下划线组成。
在python中,所有标识符可以包括英文、数字以及下划线(_),但不能以数字开头。
python中的标识符是区分大小写的。
以下划线开头的标识符是有特殊意义的。以单下划线开头(_foo)的代表不能直接访问的类属性,需通过类提供的接口进行访问,不能用"from xxx import *"而导入;
以双下划线开头的(__foo)代表类的私有成员;以双下划线开头和结尾的(__foo__)代表python里特殊方法专用的标识,如__init__()代表类的构造函数。
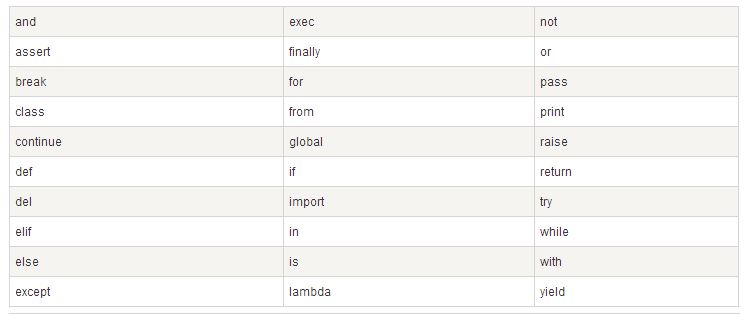
Python保留字符
下面的列表显示了在Python中的保留字。这些保留字不能用作常数或变数,或任何其他标识符名称。
所有Python的关键字只包含小写字母。
行和缩进
学习Python与其他语言最大的区别就是,Python的代码块不使用大括号({})来控制类,函数以及其他逻辑判断。python最具特色的就是用缩进来写模块。
缩进的空白数量是可变的,但是所有代码块语句必须包含相同的缩进空白数量,这个必须严格执行。如下所示:
if True: print "True" else: print "False"
以下代码将会执行错误:
#!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- # 文件名:test.py if True: print "Answer" print "True" else: print "Answer" # 没有严格缩进,在执行时保持 print "False"
$ python test.py File "test.py", line 5 if True: ^ IndentationError: unexpected indent
IndentationError: unexpected indent 错误是python编译器是在告诉你"Hi,老兄,你的文件里格式不对了,可能是tab和空格没对齐的问题",所有python对格式要求非常严格。
如果是 IndentationError: unindent does not match any outer indentation level错误表明,你使用的缩进方式不一致,有的是 tab 键缩进,有的是空格缩进,改为一致即可。
因此,在Python的代码块中必须使用相同数目的行首缩进空格数。
建议你在每个缩进层次使用 单个制表符 或 两个空格 或 四个空格 , 切记不能混用
多行语句
Python语句中一般以新行作为为语句的结束符。
但是我们可以使用斜杠( \)将一行的语句分为多行显示,如下所示:
total = item_one + \
item_two + \
item_three
语句中包含[], {} 或 () 括号就不需要使用多行连接符。如下实例:
days = ['Monday', 'Tuesday', 'Wednesday',
'Thursday', 'Friday']
Python 引号
Python 接收单引号(' ),双引号(" ),三引号(''' """) 来表示字符串,引号的开始与结束必须的相同类型的。
其中三引号可以由多行组成,编写多行文本的快捷语法,常用语文档字符串,在文件的特定地点,被当做注释。
word = 'word' sentence = "这是一个句子。" paragraph = """这是一个段落。 包含了多个语句"""
Python注释
python中单行注释采用 # 开头。
#!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- # 文件名:test.py # 第一个注释print "Hello, Python!"; # 第二个注释
输出结果:
Hello, Python!
注释可以在语句或表达式行末:
name = "Madisetti" # 这是一个注释
python 中多行注释使用三个单引号(''')或三个单引号(""")。
#!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- # 文件名:test.py ''' 这是多行注释,使用单引号。 这是多行注释,使用单引号。 这是多行注释,使用单引号。 ''' """ 这是多行注释,使用双引号。 这是多行注释,使用双引号。 这是多行注释,使用双引号。 """
Python空行
函数之间或类的方法之间用空行分隔,表示一段新的代码的开始。类和函数入口之间也用一行空行分隔,以突出函数入口的开始。
空行与代码缩进不同,空行并不是Python语法的一部分。书写时不插入空行,Python解释器运行也不会出错。但是空行的作用在于分隔两段不同功能或含义的代码,便于日后代码的维护或重构。
记住:空行也是程序代码的一部分。
等待用户输入
下面的程序在按回车键后就会等待用户输入:
#!/usr/bin/python
raw_input("\n\nPress the enter key to exit.")
以上代码中 ,"\n\n"在结果输出前会输出两个新的空行。一旦用户按下键时,程序将退出。
同一行显示多条语句
Python可以在同一行中使用多条语句,语句之间使用分号(;)分割,以下是一个简单的实例:
import sys; x = 'foo'; sys.stdout.write(x + '\n')
多个语句构成代码组
缩进相同的一组语句构成一个代码块,我们称之代码组。
像if、while、def和class这样的复合语句,首行以关键字开始,以冒号( : )结束,该行之后的一行或多行代码构成代码组。
我们将首行及后面的代码组称为一个子句(clause)。
如下实例:
if expression : suite elif expression : suite else : suite
命令行参数
很多程序可以执行一些操作来查看一些基本信,Python可以使用-h参数查看各参数帮助信息:
$ python -h
usage: python [option] ... [-c cmd | -m mod | file | -] [arg] ... Options and arguments (and corresponding environment variables): -c cmd : program passed in as string (terminates option list) -d : debug output from parser (also PYTHONDEBUG=x) -E : ignore environment variables (such as PYTHONPATH) -h : print this help message and exit [ etc. ]

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to open xml format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:00 PM
How to open xml format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:00 PM
Use most text editors to open XML files; if you need a more intuitive tree display, you can use an XML editor, such as Oxygen XML Editor or XMLSpy; if you process XML data in a program, you need to use a programming language (such as Python) and XML libraries (such as xml.etree.ElementTree) to parse.
 How to beautify the XML format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:57 PM
How to beautify the XML format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:57 PM
XML beautification is essentially improving its readability, including reasonable indentation, line breaks and tag organization. The principle is to traverse the XML tree, add indentation according to the level, and handle empty tags and tags containing text. Python's xml.etree.ElementTree library provides a convenient pretty_xml() function that can implement the above beautification process.
 Does XML modification require programming?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:51 PM
Does XML modification require programming?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:51 PM
Modifying XML content requires programming, because it requires accurate finding of the target nodes to add, delete, modify and check. The programming language has corresponding libraries to process XML and provides APIs to perform safe, efficient and controllable operations like operating databases.
 Is there any mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
Is there any mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
An application that converts XML directly to PDF cannot be found because they are two fundamentally different formats. XML is used to store data, while PDF is used to display documents. To complete the transformation, you can use programming languages and libraries such as Python and ReportLab to parse XML data and generate PDF documents.
 Is there a free XML to PDF tool for mobile phones?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
Is there a free XML to PDF tool for mobile phones?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
There is no simple and direct free XML to PDF tool on mobile. The required data visualization process involves complex data understanding and rendering, and most of the so-called "free" tools on the market have poor experience. It is recommended to use computer-side tools or use cloud services, or develop apps yourself to obtain more reliable conversion effects.
 Is the conversion speed fast when converting XML to PDF on mobile phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
Is the conversion speed fast when converting XML to PDF on mobile phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
The speed of mobile XML to PDF depends on the following factors: the complexity of XML structure. Mobile hardware configuration conversion method (library, algorithm) code quality optimization methods (select efficient libraries, optimize algorithms, cache data, and utilize multi-threading). Overall, there is no absolute answer and it needs to be optimized according to the specific situation.
 How to convert XML to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to convert XML to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
It is not easy to convert XML to PDF directly on your phone, but it can be achieved with the help of cloud services. It is recommended to use a lightweight mobile app to upload XML files and receive generated PDFs, and convert them with cloud APIs. Cloud APIs use serverless computing services, and choosing the right platform is crucial. Complexity, error handling, security, and optimization strategies need to be considered when handling XML parsing and PDF generation. The entire process requires the front-end app and the back-end API to work together, and it requires some understanding of a variety of technologies.
 What is the process of converting XML into images?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
What is the process of converting XML into images?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
To convert XML images, you need to determine the XML data structure first, then select a suitable graphical library (such as Python's matplotlib) and method, select a visualization strategy based on the data structure, consider the data volume and image format, perform batch processing or use efficient libraries, and finally save it as PNG, JPEG, or SVG according to the needs.






