举例讲解Python的Tornado框架实现数据可视化的教程
所用拓展模块
xlrd:
Python语言中,读取Excel的扩展工具。可以实现指定表单、指定单元格的读取。
使用前须安装。
下载地址:https://pypi.python.org/pypi/xlrd
解压后cd到解压目录,执行 python setup.py install 即可
datetime:
Python内置用于操作日期时间的模块
拟实现功能模块
读xls文件并录入数据库
根据年、月、日三个参数获取当天的值班情况
饼状图(当天完成值班任务人数/当天未完成值班任务人数)
瀑布图(当天所有值班人员的值班情况)
根据年、月两个参数获取当月的值班情况
根据年参数获取当年的值班情况
值班制度
每天一共有6班:
8:00 - 9:45
9:45 - 11:20
13:30 - 15:10
15:10 - 17:00
17:00 - 18:35
19:00 - 22:00
每个人每天最多值一班。
仅值班时间及前后半个小时内打卡有效。
上班、下班均须打卡,缺打卡则视为未值班。
分析Excel表格
我的指纹考勤机可以一次导出最多一个月的打卡记录。有一个问题是,这一个月可能横跨两个月,也可能横跨一年。比如:2015年03月21日-2015年04月20日、2014年12月15日-2015年01月05日。所以写处理方法的时候一定要注意这个坑。
导出的表格如图所示:
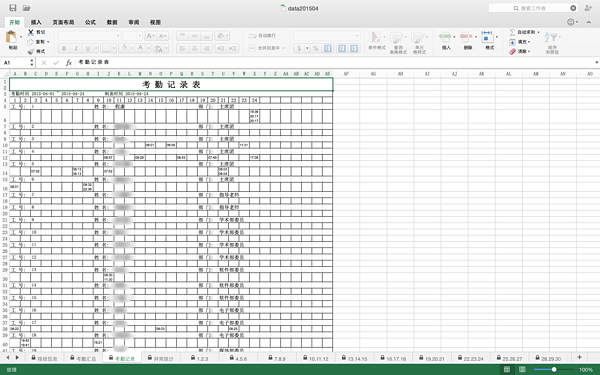
=。=看起来好像基本没人值班,对,就是这样。
大家都好懒T。T
Sign...
简单分析一下,
- 考勤记录表是文件的第三个sheet
- 第三行有起止时间
- 第四行是所有日期的数字
- 接下来每两行:第一行为用户信息;第二行为考勤记录
思路
决定用3个collection分别储存相关信息:
- user:用户信息,包含id、name、dept
- record:考勤记录,包含id(用户id)、y(年)、m(月)、d(日)、check(打卡记录)
- duty:值班安排,包含id(星期数,例:1表示星期一)、list(值班人员id列表)、user_id:["start_time","end_time"](用户值班开始时间和结束时间)
读取xls文件,将新的考勤记录和新的用户存入数据库。
根据年月日参数查询对应record,查询当天的值班安排,匹配获得当天值班同学的考勤记录。将值班同学的打卡时间和值班时间比对,判断是否正常打卡,计算实际值班时长、实际值班百分比。
之后输出json格式数据,用echarts生成图表。
分析当月、当年的考勤记录同理,不过可能稍微复杂一些。
所有的讲解和具体思路都放在源码注释里,请继续往下看源码吧~
源码
main.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import os.path
import tornado.auth
import tornado.escape
import tornado.httpserver
import tornado.ioloop
import tornado.options
import tornado.web
from tornado.options import define, options
import pymongo
import time
import datetime
import xlrd
define("port", default=8007, help="run on the given port", type=int)
class Application(tornado.web.Application):
def __init__(self):
handlers = [
(r"/", MainHandler),
(r"/read", ReadHandler),
(r"/day", DayHandler),
]
settings = dict(
template_path=os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), "templates"),
static_path=os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), "static"),
debug=True,
)
conn = pymongo.Connection("localhost", 27017)
self.db = conn["kaoqin"]
tornado.web.Application.__init__(self, handlers, **settings)
class MainHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self):
pass
class ReadHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self):
#获取collection
coll_record = self.application.db.record
coll_user = self.application.db.user
#读取excel表格
table = xlrd.open_workbook('/Users/ant/Webdev/python/excel/data.xls')
#读取打卡记录sheet
sheet=table.sheet_by_index(2)
#读取打卡月份范围
row3 = sheet.row_values(2)
m1 = int(row3[2][5:7])
m2 = int(row3[2][18:20])
#设置当前年份
y = int(row3[2][0:4])
#设置当前月份为第一个月份
m = m1
#读取打卡日期范围
row4 = sheet.row_values(3)
#初始化上一天
lastday = row4[0]
#遍历第四行中的日期
for d in row4:
#如果日期小于上一个日期
#说明月份增大,则修改当前月份为第二个月份
if d < lastday:
m = m2
#如果当前两个月份分别为12月和1月
#说明跨年了,所以年份 +1
if m1 == 12 and m2 == 1:
y = y + 1
#用n计数,范围为 3 到(总行数/2+1)
#(总行数/2+1)- 3 = 总用户数
#即遍历所有用户
for n in range(3, sheet.nrows/2+1):
#取该用户的第一行,即用户信息行
row_1 = sheet.row_values(n*2-2)
#获取用户id
u_id = row_1[2]
#获取用户姓名
u_name = row_1[10]
#获取用户部门
u_dept = row_1[20]
#查询该用户
user = coll_user.find_one({"id":u_id})
#如果数据库中不存在该用户则创建新用户
if not user:
user = dict()
user['id'] = u_id
user['name'] = u_name
user['dept'] = u_dept
coll_user.insert(user)
#取该用户的第二行,即考勤记录行
row_2 = sheet.row_values(n*2-1)
#获取改当前日期的下标
idx = row4.index(d)
#获取当前用户当前日期的考勤记录
check_data = row_2[idx]
#初始化空考勤记录列表
check = list()
#5个字符一组,遍历考勤记录并存入考勤记录列表
for i in range(0,len(check_data)/5):
check.append(check_data[i*5:i*5+5])
#查询当前用户当天记录
record = coll_record.find_one({"y":y, "m":m, "d":d, "id":user['id']})
#如果记录存在则更新记录
if record:
for item in check:
#将新的考勤记录添加进之前的记录
if item not in record['check']:
record['check'].append(item)
coll_record.save(record)
#如果记录不存在则插入新纪录
else:
record = {"y":y, "m":m, "d":d, "id":user['id'], "check":check}
coll_record.insert(record)
class DayHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self):
#获取年月日参数
y = self.get_argument("y",None)
m = self.get_argument("m",None)
d = self.get_argument("d",None)
#判断参数是否设置齐全
if y and m and d:
#将参数转换为整型数,方便使用
y = int(y)
m = int(m)
d = int(d)
#获取当天所有记录
coll_record = self.application.db.record
record = coll_record.find({"y":y, "m":m, "d":d})
#获取当天为星期几
weekday = datetime.datetime(y,m,d).strftime("%w")
#获取当天值班表
coll_duty = self.application.db.duty
duty = coll_duty.find_one({"id":int(weekday)})
#初始化空目标记录(当天值班人员记录)
target = list()
#遍历当天所有记录
for item in record:
#当该记录的用户当天有值班任务时,计算并存入target数组
if int(item['id']) in duty['list']:
#通过用户id获取该用户值班起止时间
start = duty[item['id']][0]
end = duty[item['id']][1]
#计算值班时长/秒
date1 = datetime.datetime(y,m,d,int(start[:2]),int(start[-2:]))
date2 = datetime.datetime(y,m,d,int(end[:2]),int(end[-2:]))
item['length'] = (date2 - date1).seconds
#初始化实际值班百分比
item['per'] = 0
#初始化上下班打卡时间
item['start'] = 0
item['end'] = 0
#遍历该用户打卡记录
for t in item['check']:
#当比值班时间来得早
if t < start:
#计算时间差
date1 = datetime.datetime(y,m,d,int(start[:2]),int(start[-2:]))
date2 = datetime.datetime(y,m,d,int(t[:2]),int(t[-2:]))
dif = (date1 - date2).seconds
#当打卡时间在值班时间前半小时内
if dif <= 1800:
#上班打卡成功
item['start'] = start
elif t < end:
#如果还没上班打卡
if not item['start']:
#则记录当前时间为上班打卡时间
item['start'] = t
else:
#否则记录当前时间为下班打卡时间
item['end'] = t
else:
#如果已经上班打卡
if item['start']:
#计算时间差
date1 = datetime.datetime(y,m,d,int(end[:2]),int(end[-2:]))
date2 = datetime.datetime(y,m,d,int(t[:2]),int(t[-2:]))
dif = (date1 - date2).seconds
#当打卡时间在值班时间后半小时内
if dif <= 1800:
#下班打卡成功
item['end'] = end
#当上班下班均打卡
if item['start'] and item['end']:
#计算实际值班时长
date1 = datetime.datetime(y,m,d,int(item['start'][:2]),int(item['start'][-2:]))
date2 = datetime.datetime(y,m,d,int(item['end'][:2]),int(item['end'][-2:]))
dif = (date2 - date1).seconds
#计算(实际值班时长/值班时长)百分比
item['per'] = int(dif/float(item['length']) * 100)
else:
#未正常上下班则视为未值班
item['start'] = 0
item['end'] = 0
#将记录添加到target数组中
target.append(item)
#输出数据
self.render("index.html",
target = target
)
def main():
tornado.options.parse_command_line()
http_server = tornado.httpserver.HTTPServer(Application())
http_server.listen(options.port)
tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
index.html
{
{% for item in target %}
{
'id':{{ item['id'] }},
'start':{{ item['start'] }},
'end':{{ item['end'] }},
'length':{{ item['length'] }},
'per':{{ item['per'] }}
}
{% end %}
}
最后
暂时只写到读文件和查询某天值班情况,之后会继续按照之前的计划把这个小应用写完的。
因为涉及到一堆小伙伴的隐私,所以没有把测试文件发上来。不过如果有想实际运行看看的同学可以跟我说,我把文件发给你。
可能用到的一条数据库插入语句:db.duty.insert({"id":5,"list":[1,2],1:["19:00","22:00"],2:["19:00","22:00"]})
希望对像我一样的beginner们有帮助!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1379
1379
 52
52
 PHP and Python: Code Examples and Comparison
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP and Python: Code Examples and Comparison
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP and Python have their own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice depends on project needs and personal preferences. 1.PHP is suitable for rapid development and maintenance of large-scale web applications. 2. Python dominates the field of data science and machine learning.
 How to train PyTorch model on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 03:03 PM
How to train PyTorch model on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 03:03 PM
Efficient training of PyTorch models on CentOS systems requires steps, and this article will provide detailed guides. 1. Environment preparation: Python and dependency installation: CentOS system usually preinstalls Python, but the version may be older. It is recommended to use yum or dnf to install Python 3 and upgrade pip: sudoyumupdatepython3 (or sudodnfupdatepython3), pip3install--upgradepip. CUDA and cuDNN (GPU acceleration): If you use NVIDIAGPU, you need to install CUDATool
 Detailed explanation of docker principle
Apr 14, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Detailed explanation of docker principle
Apr 14, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Docker uses Linux kernel features to provide an efficient and isolated application running environment. Its working principle is as follows: 1. The mirror is used as a read-only template, which contains everything you need to run the application; 2. The Union File System (UnionFS) stacks multiple file systems, only storing the differences, saving space and speeding up; 3. The daemon manages the mirrors and containers, and the client uses them for interaction; 4. Namespaces and cgroups implement container isolation and resource limitations; 5. Multiple network modes support container interconnection. Only by understanding these core concepts can you better utilize Docker.
 How is the GPU support for PyTorch on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:48 PM
How is the GPU support for PyTorch on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:48 PM
Enable PyTorch GPU acceleration on CentOS system requires the installation of CUDA, cuDNN and GPU versions of PyTorch. The following steps will guide you through the process: CUDA and cuDNN installation determine CUDA version compatibility: Use the nvidia-smi command to view the CUDA version supported by your NVIDIA graphics card. For example, your MX450 graphics card may support CUDA11.1 or higher. Download and install CUDAToolkit: Visit the official website of NVIDIACUDAToolkit and download and install the corresponding version according to the highest CUDA version supported by your graphics card. Install cuDNN library:
 Python vs. JavaScript: Community, Libraries, and Resources
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Community, Libraries, and Resources
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Python and JavaScript have their own advantages and disadvantages in terms of community, libraries and resources. 1) The Python community is friendly and suitable for beginners, but the front-end development resources are not as rich as JavaScript. 2) Python is powerful in data science and machine learning libraries, while JavaScript is better in front-end development libraries and frameworks. 3) Both have rich learning resources, but Python is suitable for starting with official documents, while JavaScript is better with MDNWebDocs. The choice should be based on project needs and personal interests.
 How to choose the PyTorch version under CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:51 PM
How to choose the PyTorch version under CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:51 PM
When selecting a PyTorch version under CentOS, the following key factors need to be considered: 1. CUDA version compatibility GPU support: If you have NVIDIA GPU and want to utilize GPU acceleration, you need to choose PyTorch that supports the corresponding CUDA version. You can view the CUDA version supported by running the nvidia-smi command. CPU version: If you don't have a GPU or don't want to use a GPU, you can choose a CPU version of PyTorch. 2. Python version PyTorch
 MiniOpen Centos compatibility
Apr 14, 2025 pm 05:45 PM
MiniOpen Centos compatibility
Apr 14, 2025 pm 05:45 PM
MinIO Object Storage: High-performance deployment under CentOS system MinIO is a high-performance, distributed object storage system developed based on the Go language, compatible with AmazonS3. It supports a variety of client languages, including Java, Python, JavaScript, and Go. This article will briefly introduce the installation and compatibility of MinIO on CentOS systems. CentOS version compatibility MinIO has been verified on multiple CentOS versions, including but not limited to: CentOS7.9: Provides a complete installation guide covering cluster configuration, environment preparation, configuration file settings, disk partitioning, and MinI
 How to install nginx in centos
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:06 PM
How to install nginx in centos
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:06 PM
CentOS Installing Nginx requires following the following steps: Installing dependencies such as development tools, pcre-devel, and openssl-devel. Download the Nginx source code package, unzip it and compile and install it, and specify the installation path as /usr/local/nginx. Create Nginx users and user groups and set permissions. Modify the configuration file nginx.conf, and configure the listening port and domain name/IP address. Start the Nginx service. Common errors need to be paid attention to, such as dependency issues, port conflicts, and configuration file errors. Performance optimization needs to be adjusted according to the specific situation, such as turning on cache and adjusting the number of worker processes.




