 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
 A super detailed introduction to the practical basics of jQuery_jquery
A super detailed introduction to the practical basics of jQuery_jquery
A super detailed introduction to the practical basics of jQuery_jquery
一、jQuery 简介
jQuery 是继 Prototype 之后又一个优秀的 JavaScript 库
jQuery 理念: 写得少, 做得多. 优势如下:
轻量级
强大的选择器
出色的 DOM 操作的封装
可靠的事件处理机制
完善的 Ajax
出色的浏览器兼容性
链式操作方式
……
第一个案例

二、jQuery 对象
jQuery 对象就是通过 jQuery ($()) 包装 DOM 对象后产生的对象
jQuery 对象是 jQuery 独有的. 如果一个对象是 jQuery 对象, 那么它就可以使用 jQuery 里的方法: $(“#persontab”).html();
jQuery 对象无法使用 DOM 对象的任何方法, 同样 DOM 对象也不能使用 jQuery 里的任何方法
约定:如果获取的是 jQuery 对象, 那么要在变量前面加上 $.
var $variable = jQuery 对象
var variable = DOM 对象
三、DOM 对象转成 jQuery 对象
对于一个 DOM 对象, 只需要用 $() 把 DOM 对象包装起来(jQuery 对象就是通过 jQuery 包装 DOM 对象后产生的对象), 就可以获得一个 jQuery 对象.
var dc=document.getElement("aa");
var $dc=$(dc);
转换后就可以使用 jQuery 中的方法了
jQuery 对象转成 DOM 对象
jQuery 对象不能使用 DOM 中的方法, 但如果 jQuery 没有封装想要的方法, 不得不使用 DOM 对象的时候, 有如下两种处理方法:
(1) jQuery 对象是一个数组对象, 可以通过 [index] 的方法得到对应的 DOM对象.
var $dc=$("#dc");
var dc=$dc[0];
(2) 使用 jQuery 中的 get(index) 方法得到相应的 DOM 对象
var $dc=$("#dc");
var dc=$dc.get(0);
四、jQuery 选择器

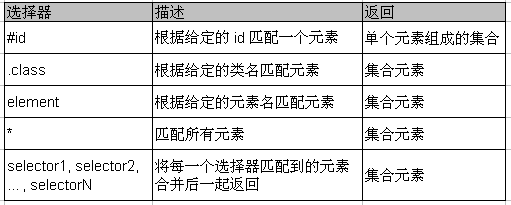
基本选择器
基本选择器是 jQuery 中最常用的选择器, 也是最简单的选择器, 它通过元素 id, class 和标签名来查找 DOM 元素(在网页中 id 只能使用一次, class 允许重复使用).
层次选择器
如果想通过 DOM 元素之间的层次关系来获取特定元素, 例如后代元素, 子元素, 相邻元素, 兄弟元素等, 则需要使用层次选择器.

注意: (“prev ~ div”) 选择器只能选择 “# prev ” 元素后面的同辈元素; 而 jQuery 中的方法 siblings() 与前后位置无关, 只要是同辈节点就可以选取
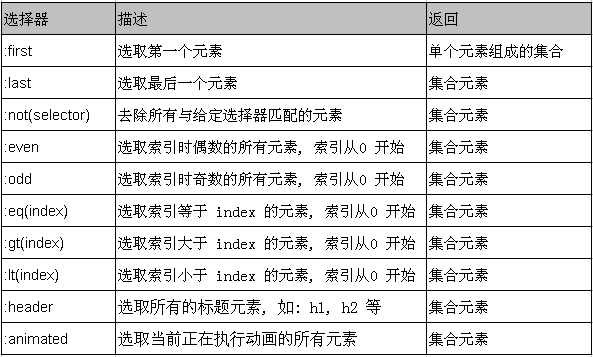
过滤选择器
过滤选择器主要是通过特定的过滤规则来筛选出所需的 DOM 元素, 该选择器都以 “:” 开头
按照不同的过滤规则, 过滤选择器可以分为基本过滤, 内容过滤, 可见性过滤, 属性过滤, 子元素过滤和表单对象属性过滤选择器.
基本过滤选择器
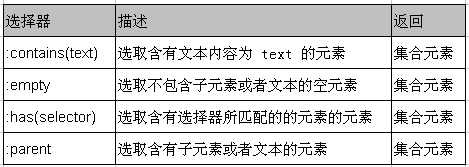
内容过滤选择器
内容过滤选择器的过滤规则主要体现在它所包含的子元素和文本内容上
可见性过滤选择器
可见性过滤选择器是根据元素的可见和不可见状态来选择相应的元素

可见选择器 :hidden 不仅包含样式属性 display 为 none 的元素, 也包含文本隐藏域 ()和 visible:hidden 之类的元素
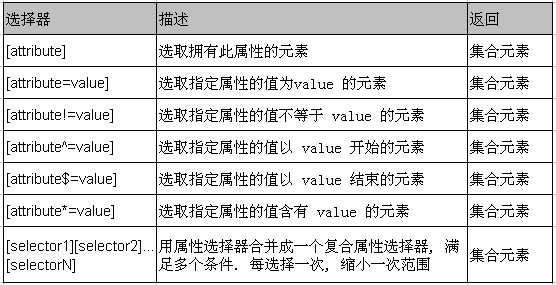
属性过滤选择器
属性过滤选择器的过滤规则是通过元素的属性来获取相应的元素
子元素过滤选择器
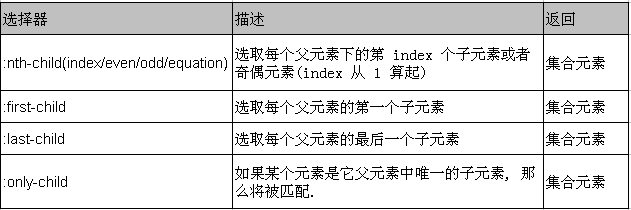
nth-child() 选择器详解如下:
(1) :nth-child(even/odd): 能选取每个父元素下的索引值为偶(奇)数的元素
(2):nth-child(2): 能选取每个父元素下的索引值为 2 的元素
(3):nth-child(3n): 能选取每个父元素下的索引值是 3 的倍数 的元素
(3):nth-child(3n + 1): 能选取每个父元素下的索引值是 3n + 1的元素
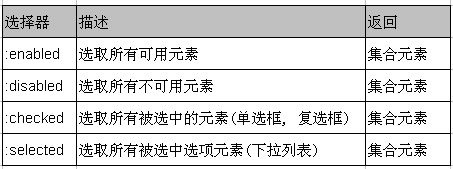
一、表单对象属性过滤选择器
此选择器主要对所选择的表单元素进行过滤
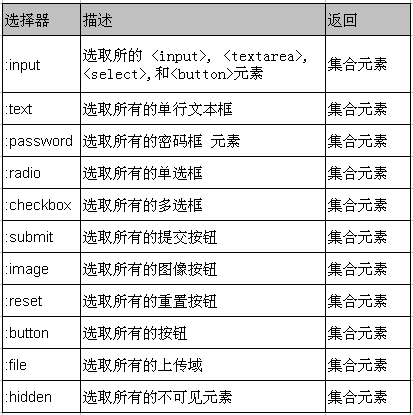
二、表单选择器
三、jQuery 中的 DOM 操作
1、DOM(Document Object Model—文档对象模型):一种与浏览器, 平台, 语言无关的接口, 使用该接口可以轻松地访问页面中所有的标准组件
DOM 操作的分类:
2、DOM Core: DOM Core 并不专属于 JavaScript, 任何一种支持 DOM 的程序设计语言都可以使用它. 它的用途并非仅限于处理网页, 也可以用来处理任何一种是用标记语言编写出来的文档, 例如: XML
HTML DOM: 使用 JavaScript 和 DOM 为 HTML 文件编写脚本时, 有许多专属于 HTML-DOM 的属性
CSS-DOM:针对于 CSS 操作, 在 JavaScript 中, CSS-DOM 主要用于获取和设置 style 对象的各种属性
四、查找节点
查找节点:
查找元素节点: 通过 jQuery 选择器完成.
查找属性节点: 查找到所需要的元素之后, 可以调用 jQuery 对象的 attr() 方法来获取它的各种属性值
五、创建节点
创建节点: 使用 jQuery 的工厂函数 $(): $(html); 会根据传入的 html 标记字符串创建一个 DOM 对象, 并把这个 DOM 对象包装成一个 jQuery 对象返回.
注意:
动态创建的新元素节点不会被自动添加到文档中, 而是需要使用其他方法将其插入到文档中;
当创建单个元素时, 需注意闭合标签和使用标准的 XHTML 格式. 例如创建一个
元素, 可以使用 $(“
”) 或 $(“”), 但不能使用 $(“”) 或 $(“
”)
创建文本节点就是在创建元素节点时直接把文本内容写出来; 创建属性节点也是在创建元素节点时一起创建
六、插入节点(1)
动态创建 HTML 元素并没有实际用处, 还需要将新创建的节点插入到文档中, 即成为文档中某个节点的子节点
七、插入节点(2)

以上方法不但能将新创建的 DOM 元素插入到文档中, 也能对原有的 DOM 元素进行移动.
八、删除节点
1、remove(): 从 DOM 中删除所有匹配的元素, 传入的参数用于根据 jQuery 表达式来筛选元素. 当某个节点用 remove() 方法删除后, 该节点所包含的所有后代节点将被同时删除. 这个方法的返回值是一个指向已被删除的节点的引用.
2、empty(): 清空节点 – 清空元素中的所有后代节点(不包含属性节点).
九、复制节点
1、clone(): 克隆匹配的 DOM 元素, 返回值为克隆后的副本. 但此时复制的新节点不具有任何行为.
2、clone(true): 复制元素的同时也复制元素中的的事件
十、替换节点
1、replaceWith(): 将所有匹配的元素都替换为指定的 HTML 或 DOM 元素
2、replaceAll(): 颠倒了的 replaceWith() 方法.
注意: 若在替换之前, 已经在元素上绑定了事件, 替换后原先绑定的事件会与原先的元素一起消失
十一、包裹节点
wrap(): Wrap the specified node with other tags. This method is very useful for inserting additional structured tags into the document without destroying the semantics of the original document.
wrapAll(): Wrap all The matched element is wrapped with an element. The wrap() method wraps all elements individually.
wrapInner(): wraps the sub-content (including text nodes) of each matched element with other structured tags Get up.
12. Attribute operations
attr(): Get attributes and set attributes
When one parameter is passed to this method, the specified attribute is obtained for an element
When two parameters are passed to this method, it is set for an element Specify the value of the attribute
There are many methods in jQuery that are functions to obtain and set. Such as: attr(), html(), text(), val(), height(), width(), css() etc.
removeAttr(): Remove the specified attribute of the specified element
13. Set and get HTML, text and value
Read and set the HTML content in an element: html(). This method can be used for XHTML, but cannot be used for XML documents
Read and set the text content in an element: text() . This method can be used for both XHTML and XML documents.
Read and set the value in an element: val() --- This method is similar to the value attribute in JavaScript. For text boxes, drop-down lists Box, radio button This method can return the value of the element (multi-select box can only return the first value). If it is a multi-select drop-down list box, it returns an array containing all selected values
14. Commonly used node traversal methods
Get the set of all child elements of the matching element: children(). This method only considers child elements without considering any descendant elements.
Gets the set of sibling elements immediately following the matching element (but there is only one in the set element): next()
Get the set of sibling elements immediately before the matching element (but there is only one element in the set): prev()
Get all the sibling elements before and after the matching element: siblings()
15. Style operation
Getting class and setting class: class is an attribute of the element, so getting class and setting class can be done using the attr() method.
Append style: addClass()
Remove style: removeClass( ) --- Remove all or the specified class from the matched elements
Toggle style: toggleClass() --- Control repeated switching on the style. If the class name exists, delete it, if the class name does not exist, add it .
Determine whether it contains a certain style: hasClass() --- Determine whether the element contains a certain class. If so, return true; otherwise return false

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1359
1359
 52
52
 Detailed introduction to what wapi is
Jan 07, 2024 pm 09:14 PM
Detailed introduction to what wapi is
Jan 07, 2024 pm 09:14 PM
Users may have seen the term wapi when using the Internet, but for some people they definitely don’t know what wapi is. The following is a detailed introduction to help those who don’t know to understand. What is wapi: Answer: wapi is the infrastructure for wireless LAN authentication and confidentiality. This is like functions such as infrared and Bluetooth, which are generally covered near places such as office buildings. Basically they are owned by a small department, so the scope of this function is only a few kilometers. Related introduction to wapi: 1. Wapi is a transmission protocol in wireless LAN. 2. This technology can avoid the problems of narrow-band communication and enable better communication. 3. Only one code is needed to transmit the signal
 Detailed explanation of whether win11 can run PUBG game
Jan 06, 2024 pm 07:17 PM
Detailed explanation of whether win11 can run PUBG game
Jan 06, 2024 pm 07:17 PM
Pubg, also known as PlayerUnknown's Battlegrounds, is a very classic shooting battle royale game that has attracted a lot of players since its popularity in 2016. After the recent launch of win11 system, many players want to play it on win11. Let's follow the editor to see if win11 can play pubg. Can win11 play pubg? Answer: Win11 can play pubg. 1. At the beginning of win11, because win11 needed to enable tpm, many players were banned from pubg. 2. However, based on player feedback, Blue Hole has solved this problem, and now you can play pubg normally in win11. 3. If you meet a pub
 Introduction to Python functions: Introduction and examples of exec function
Nov 03, 2023 pm 02:09 PM
Introduction to Python functions: Introduction and examples of exec function
Nov 03, 2023 pm 02:09 PM
Introduction to Python functions: Introduction and examples of exec function Introduction: In Python, exec is a built-in function that is used to execute Python code stored in a string or file. The exec function provides a way to dynamically execute code, allowing the program to generate, modify, and execute code as needed during runtime. This article will introduce how to use the exec function and give some practical code examples. How to use the exec function: The basic syntax of the exec function is as follows: exec
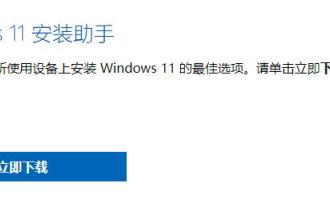 Detailed introduction to whether i5 processor can install win11
Dec 27, 2023 pm 05:03 PM
Detailed introduction to whether i5 processor can install win11
Dec 27, 2023 pm 05:03 PM
i5 is a series of processors owned by Intel. It has various versions of the 11th generation i5, and each generation has different performance. Therefore, whether the i5 processor can install win11 depends on which generation of the processor it is. Let’s follow the editor to learn about it separately. Can i5 processor be installed with win11: Answer: i5 processor can be installed with win11. 1. The eighth-generation and subsequent i51, eighth-generation and subsequent i5 processors can meet Microsoft’s minimum configuration requirements. 2. Therefore, we only need to enter the Microsoft website and download a "Win11 Installation Assistant" 3. After the download is completed, run the installation assistant and follow the prompts to install Win11. 2. i51 before the eighth generation and after the eighth generation
 Introducing the latest Win 11 sound tuning method
Jan 08, 2024 pm 06:41 PM
Introducing the latest Win 11 sound tuning method
Jan 08, 2024 pm 06:41 PM
After updating to the latest win11, many users find that the sound of their system has changed slightly, but they don’t know how to adjust it. So today, this site brings you an introduction to the latest win11 sound adjustment method for your computer. It is not difficult to operate. And the choices are diverse, come and download and try them out. How to adjust the sound of the latest computer system Windows 11 1. First, right-click the sound icon in the lower right corner of the desktop and select "Playback Settings". 2. Then enter settings and click "Speaker" in the playback bar. 3. Then click "Properties" on the lower right. 4. Click the "Enhance" option bar in the properties. 5. At this time, if the √ in front of "Disable all sound effects" is checked, cancel it. 6. After that, you can select the sound effects below to set and click
 Introduction to edge shortcut keys
Jul 12, 2023 pm 05:57 PM
Introduction to edge shortcut keys
Jul 12, 2023 pm 05:57 PM
In today's fast life, in order to improve work efficiency, shortcut keys are an essential work requirement. A shortcut key is a key or key combination that provides an alternative way to perform an action normally performed using a mouse. So what are the edge shortcut keys? What are the functions of edge shortcut keys? The editor below has compiled an introduction to edge shortcut keys. Friends who are interested should come and take a look! Ctrl+D: Add the current page to favorites or reading list Ctrl+E: Perform a search query in the address bar Ctrl+F: Find on the page Ctrl+H: Open the history panel Ctrl+G: Open the reading list panel Ctrl +I: Open the favorites list panel (the test does not seem to work) Ctrl+J: Open
 PyCharm Beginner's Guide: Comprehensive Analysis of Replacement Functions
Feb 25, 2024 am 11:15 AM
PyCharm Beginner's Guide: Comprehensive Analysis of Replacement Functions
Feb 25, 2024 am 11:15 AM
PyCharm is a powerful Python integrated development environment with rich functions and tools that can greatly improve development efficiency. Among them, the replacement function is one of the functions frequently used in the development process, which can help developers quickly modify the code and improve the code quality. This article will introduce PyCharm's replacement function in detail, combined with specific code examples, to help novices better master and use this function. Introduction to the replacement function PyCharm's replacement function can help developers quickly replace specified text in the code
 Detailed information on the location of the printer driver on your computer
Jan 08, 2024 pm 03:29 PM
Detailed information on the location of the printer driver on your computer
Jan 08, 2024 pm 03:29 PM
Many users have printer drivers installed on their computers but don't know how to find them. Therefore, today I bring you a detailed introduction to the location of the printer driver in the computer. For those who don’t know yet, let’s take a look at where to find the printer driver. When rewriting content without changing the original meaning, you need to The language is rewritten to Chinese, and the original sentence does not need to appear. First, it is recommended to use third-party software to search. 2. Find "Toolbox" in the upper right corner. 3. Find and click "Device Manager" below. Rewritten sentence: 3. Find and click "Device Manager" at the bottom 4. Then open "Print Queue" and find your printer device. This time it is your printer name and model. 5. Right-click the printer device and you can update or uninstall it.



