四款mysql 分页存储过程实例
四款mysql 分页存储过程实例 本文章收集了四款mysql 分页存储过程实例代码,有高效的分页存储过程以及入门级的和通用的存储过程分页代码,如果你正在学mysql分页存储过程就进来看看吧。
四款mysql教程 分页存储过程实例
本文章收集了四款mysql 分页存储过程实例代码,有高效的分页存储过程以及入门级的和通用的存储过程分页代码,如果你正在学mysql分页存储过程就进来看看吧。
mysql测试版本:5.0.41-community-nt
/*****************************************************
mysql分页存储过程
吴剑 2009-07-02
*****************************************************/
drop procedure if exists pr_pager;
create procedure pr_pager(
in p_table_name varchar(1024), /*表名*/
in p_fields varchar(1024), /*查询字段*/
in p_page_size int, /*每页记录数*/
in p_page_now int, /*当前页*/
in p_order_string varchar(128), /*排序条件(包含order关键字,可为空)*/
in p_where_string varchar(1024), /*where条件(包含where关键字,可为空)*/
out p_out_rows int /*输出记录总数*/
)
not deterministic
sql security definer
comment '分页存储过程'
begin
/*定义变量*/
declare m_begin_row int default 0;
declare m_limit_string char(64);
/*构造语句*/
set m_begin_row = (p_page_now - 1) * p_page_size;
set m_limit_string = concat(' limit ', m_begin_row, ', ', p_page_size);
set @count_string = concat('select count(*) into @rows_total from ', p_table_name, ' ', p_where_string);
set @main_string = concat('select ', p_fields, ' from ', p_table_name, ' ', p_where_string, ' ', p_order_string, m_limit_string);
/*预处理*/
prepare count_stmt from @count_string;
execute count_stmt;
deallocate prepare count_stmt;
set p_out_rows = @rows_total;
prepare main_stmt from @main_string;
execute main_stmt;
deallocate prepare main_stmt;
end
一款高效的存储过程分页代码
存储过程分页的基本原理:我们先对查找到的记录集(支持输入查找条件_whereclause和排列条件_orderby)的key字段临时存放到临时表,然后构建真正的记录集输出。
create procedure `mysqltestuser_select_pageable`(
_whereclause varchar(2000), -- 查找条件
_orderby varchar(2000), -- 排序条件
_pagesize int , -- 每页记录数
_pageindex int , -- 当前页码
_docount bit -- 标志:统计数据/输出数据
)
not deterministic
sql security definer
comment ' '
begin
-- 定义key字段临时表
drop table if exists _temptable_keyid; -- 删除临时表,如果存在
create temporary table _temptable_keyid
(
userid int
)type=heap;
-- 构建动态的sql,输出关键字key的id集合
-- 查找条件
set @sql = 'select userid from mysqltestuser ';
if (_whereclause is not null) and (_whereclause ' ') then
set @sql= concat(@sql, ' where ' ,_whereclause);
end if;
if (_orderby is not null) and (_orderby ' ') then
set @sql= concat( @sql , ' order by ' , _orderby);
end if;
-- 准备id记录插入到临时表
set @sql=concat( 'insert into _temptable_keyid(userid) ', @sql);
prepare stmt from @sql;
execute stmt ;
deallocate prepare stmt;
-- key的id集合 [end]
-- 下面是输出
if (_docount=1) then -- 统计
begin
select count(*) as recordcount from _temptable_keyid;
end;
else -- 输出记录集
begin
-- 计算记录的起点位置
set @startpoint = ifnull((_pageindex-1)*_pagesize,0);
set @sql= ' select a.*
from mysqltestuser a
inner join _temptable_keyid b
on a.userid =b.userid ';
set @sql=concat(@sql, " limit ",@startpoint, " , ",_pagesize);
prepare stmt from @sql;
execute stmt ;
deallocate prepare stmt;
end;
end if;
drop table _temptable_keyid;
end;
下面是mysqltestuser表的ddl:
create table `mysqltestuser` (
`userid` int(11) not null auto_increment,
`name` varchar(50) default null,
`chinesename` varchar(50) default null,
`registerdatetime` datetime default null,
`jf` decimal(20,2) default null,
`description` longtext,
primary key (`userid`)
) engine=innodb default charset=gb2312;
插入些数据:
insert into `mysqltestuser` (`userid`, `name`, `chinesename`, `registerdatetime`, `jf`, `description`) values
(1, 'xuu1 ', 'www.aimeige.com.cn ', '2007-03-29 12:54:41 ',1.5, 'description1 '),
(2, 'xuu2 ', 'www.bKjia.c0m ', '2007-03-29 12:54:41 ',2.5, 'description2 '),
存储过程调用测试:
-- 方法原型 `mysqltestuser_select_pageable`(条件,排列顺序,每页记录数,第几页,是否统计数据)
-- call `mysqltestuser_select_pageable`(_whereclause ,_orderby ,_pagesize ,_pageindex , _docount)
-- 统计数据
call `mysqltestuser_select_pageable`(null, null, null, null, 1)
-- 输出数据,没条件限制,10条记录/页,第一页
call `mysqltestuser_select_pageable`(null, null, 10, 1,0)
-- 输出数据,条件限制,排列, 10条记录/页,第一页
call `mysqltestuser_select_pageable`( 'chinesename like ' '%飞3% ' ' ', 'userid asc ', 10, 1, 0)
一款mysql .net的方法
mysql + asp教程.net来写网站,既然mysql已经支持存储过程了,那么像分页这么常用的东西,当然要用存储过程啦!
不过在网上找了一些,发现都有一个特点——就是不能传出总记录数,干脆自己研究吧。终于,算是搞出来了,效率可能不是很好,但是我也觉得不错了。贴代码吧直接:也算是对自己学习mysql的一个记录。
create procedure p_pagelist
(
m_pageno int ,
m_perpagecnt int ,
m_column varchar(1000) ,
m_table varchar(1000) ,
m_condition varchar(1000),
m_orderby varchar(200) ,
out m_totalpagecnt int
)
begin
set @pagecnt = 1; -- 总记录数
set @limitstart = (m_pageno - 1)*m_perpagecnt;
set @limitend = m_perpagecnt;
set @sqlcnt = concat('select count(1) into @pagecnt from ',m_table); -- 这条语句很关键,用来得到总数值
set @sql = concat('select ',m_column,' from ',m_table);
if m_condition is not null and m_condition '' then
set @sql = concat(@sql,' where ',m_condition);
set @sqlcnt = concat(@sqlcnt,' where ',m_condition);
end if;
if m_orderby is not null and m_orderby '' then
set @sql = concat(@sql,' order by ',m_orderby);
end if;
set @sql = concat(@sql, ' limit ', @limitstart, ',', @limitend);
prepare s_cnt from @sqlcnt;
execute s_cnt;
deallocate prepare s_cnt;
set m_totalpagecnt = @pagecnt;
prepare record from @sql;
execute record;
deallocate prepare record;
end
方法四
mysql的通用存储过程,本着共享的精神,为大家奉献这段mysql分页查询通用存储过程,假设所用数据库教程为guestbook:
use guestbook;
delimiter $$
drop procedure if exists prc_page_result $$
create procedure prc_page_result (
in currpage int,
in columns varchar(500),
in tablename varchar(500),
in scondition varchar(500),
in order_field varchar(100),
in asc_field int,
in primary_field varchar(100),
in pagesize int
)
begin
declare stemp varchar(1000);
declare ssql varchar(4000);
declare sorder varchar(1000);
if asc_field = 1 then
set sorder = concat( order by , order_field, desc );
set stemp =
else
set sorder = concat( order by , order_field, asc );
set stemp = >(select max;
end if;
if currpage = 1 then
if scondition then
set ssql = concat(select , columns, from , tablename, where );
set ssql = concat(ssql, scondition, sorder, limit ?);
else
set ssql = concat(select , columns, from , tablename, sorder, limit ?);
end if;
else
if scondition then
set ssql = concat(select , columns, from , tablename);
set ssql = concat(ssql, where , scondition, and , primary_field, stemp);
set ssql = concat(ssql, (, primary_field, ), from (select );
set ssql = concat(ssql, , primary_field, from , tablename, sorder);
set ssql = concat(ssql, limit , (currpage-1)*pagesize, ) as tabtemp), sorder);
set ssql = concat(ssql, limit ?);
else
set ssql = concat(select , columns, from , tablename);
set ssql = concat(ssql, where , primary_field, stemp);
set ssql = concat(ssql, (, primary_field, ), from (select );
set ssql = concat(ssql, , primary_field, from , tablename, sorder);
set ssql = concat(ssql, limit , (currpage-1)*pagesize, ) as tabtemp), sorder);
set ssql = concat(ssql, limit ?);
end if;
end if;
set @ipagesize = pagesize;
set @squery = ssql;
prepare stmt from @squery;
execute stmt using @ipagesize;
end;
$$
delimiter;
可以存储为数据库脚本,然后用命令导入:
mysql -u root -p
调用:call prc_page_result(1, "*", "tablename", "", "columnname", 1, "pkid", 25);
*/
?>

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to use MySQL backup and restore in PHP?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 12:19 PM
How to use MySQL backup and restore in PHP?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 12:19 PM
Backing up and restoring a MySQL database in PHP can be achieved by following these steps: Back up the database: Use the mysqldump command to dump the database into a SQL file. Restore database: Use the mysql command to restore the database from SQL files.
 How to optimize MySQL query performance in PHP?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 08:11 PM
How to optimize MySQL query performance in PHP?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 08:11 PM
MySQL query performance can be optimized by building indexes that reduce lookup time from linear complexity to logarithmic complexity. Use PreparedStatements to prevent SQL injection and improve query performance. Limit query results and reduce the amount of data processed by the server. Optimize join queries, including using appropriate join types, creating indexes, and considering using subqueries. Analyze queries to identify bottlenecks; use caching to reduce database load; optimize PHP code to minimize overhead.
 How to insert data into a MySQL table using PHP?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:26 PM
How to insert data into a MySQL table using PHP?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:26 PM
How to insert data into MySQL table? Connect to the database: Use mysqli to establish a connection to the database. Prepare the SQL query: Write an INSERT statement to specify the columns and values to be inserted. Execute query: Use the query() method to execute the insertion query. If successful, a confirmation message will be output.
 How to create a MySQL table using PHP?
Jun 04, 2024 pm 01:57 PM
How to create a MySQL table using PHP?
Jun 04, 2024 pm 01:57 PM
Creating a MySQL table using PHP requires the following steps: Connect to the database. Create the database if it does not exist. Select a database. Create table. Execute the query. Close the connection.
 How to use MySQL stored procedures in PHP?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:13 PM
How to use MySQL stored procedures in PHP?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:13 PM
To use MySQL stored procedures in PHP: Use PDO or the MySQLi extension to connect to a MySQL database. Prepare the statement to call the stored procedure. Execute the stored procedure. Process the result set (if the stored procedure returns results). Close the database connection.
 How to fix mysql_native_password not loaded errors on MySQL 8.4
Dec 09, 2024 am 11:42 AM
How to fix mysql_native_password not loaded errors on MySQL 8.4
Dec 09, 2024 am 11:42 AM
One of the major changes introduced in MySQL 8.4 (the latest LTS release as of 2024) is that the "MySQL Native Password" plugin is no longer enabled by default. Further, MySQL 9.0 removes this plugin completely. This change affects PHP and other app
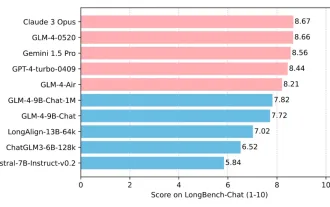 Tsinghua University and Zhipu AI open source GLM-4: launching a new revolution in natural language processing
Jun 12, 2024 pm 08:38 PM
Tsinghua University and Zhipu AI open source GLM-4: launching a new revolution in natural language processing
Jun 12, 2024 pm 08:38 PM
Since the launch of ChatGLM-6B on March 14, 2023, the GLM series models have received widespread attention and recognition. Especially after ChatGLM3-6B was open sourced, developers are full of expectations for the fourth-generation model launched by Zhipu AI. This expectation has finally been fully satisfied with the release of GLM-4-9B. The birth of GLM-4-9B In order to give small models (10B and below) more powerful capabilities, the GLM technical team launched this new fourth-generation GLM series open source model: GLM-4-9B after nearly half a year of exploration. This model greatly compresses the model size while ensuring accuracy, and has faster inference speed and higher efficiency. The GLM technical team’s exploration has not
 The difference between oracle database and mysql
May 10, 2024 am 01:54 AM
The difference between oracle database and mysql
May 10, 2024 am 01:54 AM
Oracle database and MySQL are both databases based on the relational model, but Oracle is superior in terms of compatibility, scalability, data types and security; while MySQL focuses on speed and flexibility and is more suitable for small to medium-sized data sets. . ① Oracle provides a wide range of data types, ② provides advanced security features, ③ is suitable for enterprise-level applications; ① MySQL supports NoSQL data types, ② has fewer security measures, and ③ is suitable for small to medium-sized applications.






