How are arrays stored in memory?
Arrays are stored sequentially in memory, with each element occupying a consecutive address, starting from the first address of the array.

Storage of arrays in memory
Array is a data structure that stores multiple elements of the same data type element. The elements are stored contiguously in memory, just like a list.
Memory layout
Each array occupies a continuous memory address. The elements of the array are stored in these addresses sequentially, starting from the first address of the array.
For example, the following is an array that stores 5 integers:
int[] array = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};In memory, this array may be stored as follows:
| Address | Value | |---|---| | 1000 | 1 | | 1004 | 2 | | 1008 | 3 | | 1012 | 4 | | 1016 | 5 |
Please note that the elements are in memory stored in order. The first element is at the first address (1000), and so on.
Practical case
Consider the following Java code:
int[] nums = new int[5]; nums[0] = 10; nums[1] = 20; nums[2] = 30; nums[3] = 40; nums[4] = 50;
Generate the memory layout of the above code:
| Address | Value | |---|---| | 1000 | 10 | | 1004 | 20 | | 1008 | 30 | | 1012 | 40 | | 1016 | 50 |
Conclusion
Arrays are stored in memory as a continuous sequence of elements. Each element occupies its own memory address, and the elements are stored in order, starting from the first address of the array.
The above is the detailed content of How are arrays stored in memory?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1389
1389
 52
52
 Large memory optimization, what should I do if the computer upgrades to 16g/32g memory speed and there is no change?
Jun 18, 2024 pm 06:51 PM
Large memory optimization, what should I do if the computer upgrades to 16g/32g memory speed and there is no change?
Jun 18, 2024 pm 06:51 PM
For mechanical hard drives or SATA solid-state drives, you will feel the increase in software running speed. If it is an NVME hard drive, you may not feel it. 1. Import the registry into the desktop and create a new text document, copy and paste the following content, save it as 1.reg, then right-click to merge and restart the computer. WindowsRegistryEditorVersion5.00[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SessionManager\MemoryManagement]"DisablePagingExecutive"=d
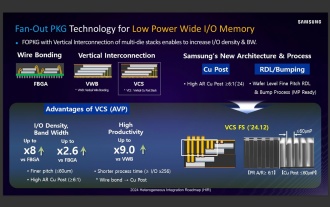 Sources say Samsung Electronics and SK Hynix will commercialize stacked mobile memory after 2026
Sep 03, 2024 pm 02:15 PM
Sources say Samsung Electronics and SK Hynix will commercialize stacked mobile memory after 2026
Sep 03, 2024 pm 02:15 PM
According to news from this website on September 3, Korean media etnews reported yesterday (local time) that Samsung Electronics and SK Hynix’s “HBM-like” stacked structure mobile memory products will be commercialized after 2026. Sources said that the two Korean memory giants regard stacked mobile memory as an important source of future revenue and plan to expand "HBM-like memory" to smartphones, tablets and laptops to provide power for end-side AI. According to previous reports on this site, Samsung Electronics’ product is called LPWide I/O memory, and SK Hynix calls this technology VFO. The two companies have used roughly the same technical route, which is to combine fan-out packaging and vertical channels. Samsung Electronics’ LPWide I/O memory has a bit width of 512
 Lexar launches Ares Wings of War DDR5 7600 16GB x2 memory kit: Hynix A-die particles, 1,299 yuan
May 07, 2024 am 08:13 AM
Lexar launches Ares Wings of War DDR5 7600 16GB x2 memory kit: Hynix A-die particles, 1,299 yuan
May 07, 2024 am 08:13 AM
According to news from this website on May 6, Lexar launched the Ares Wings of War series DDR57600CL36 overclocking memory. The 16GBx2 set will be available for pre-sale at 0:00 on May 7 with a deposit of 50 yuan, and the price is 1,299 yuan. Lexar Wings of War memory uses Hynix A-die memory chips, supports Intel XMP3.0, and provides the following two overclocking presets: 7600MT/s: CL36-46-46-961.4V8000MT/s: CL38-48-49 -1001.45V In terms of heat dissipation, this memory set is equipped with a 1.8mm thick all-aluminum heat dissipation vest and is equipped with PMIC's exclusive thermal conductive silicone grease pad. The memory uses 8 high-brightness LED beads and supports 13 RGB lighting modes.
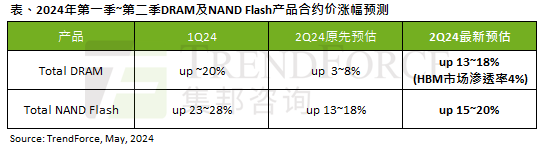 The impact of the AI wave is obvious. TrendForce has revised up its forecast for DRAM memory and NAND flash memory contract price increases this quarter.
May 07, 2024 pm 09:58 PM
The impact of the AI wave is obvious. TrendForce has revised up its forecast for DRAM memory and NAND flash memory contract price increases this quarter.
May 07, 2024 pm 09:58 PM
According to a TrendForce survey report, the AI wave has a significant impact on the DRAM memory and NAND flash memory markets. In this site’s news on May 7, TrendForce said in its latest research report today that the agency has increased the contract price increases for two types of storage products this quarter. Specifically, TrendForce originally estimated that the DRAM memory contract price in the second quarter of 2024 will increase by 3~8%, and now estimates it at 13~18%; in terms of NAND flash memory, the original estimate will increase by 13~18%, and the new estimate is 15%. ~20%, only eMMC/UFS has a lower increase of 10%. ▲Image source TrendForce TrendForce stated that the agency originally expected to continue to
 Kingbang launches new DDR5 8600 memory, offering CAMM2, LPCAMM2 and regular models to choose from
Jun 08, 2024 pm 01:35 PM
Kingbang launches new DDR5 8600 memory, offering CAMM2, LPCAMM2 and regular models to choose from
Jun 08, 2024 pm 01:35 PM
According to news from this site on June 7, GEIL launched its latest DDR5 solution at the 2024 Taipei International Computer Show, and provided SO-DIMM, CUDIMM, CSODIMM, CAMM2 and LPCAMM2 versions to choose from. ▲Picture source: Wccftech As shown in the picture, the CAMM2/LPCAMM2 memory exhibited by Jinbang adopts a very compact design, can provide a maximum capacity of 128GB, and a speed of up to 8533MT/s. Some of these products can even be stable on the AMDAM5 platform Overclocked to 9000MT/s without any auxiliary cooling. According to reports, Jinbang’s 2024 Polaris RGBDDR5 series memory can provide up to 8400
 The Art of PHP Array Deep Copy: Using Different Methods to Achieve a Perfect Copy
May 01, 2024 pm 12:30 PM
The Art of PHP Array Deep Copy: Using Different Methods to Achieve a Perfect Copy
May 01, 2024 pm 12:30 PM
Methods for deep copying arrays in PHP include: JSON encoding and decoding using json_decode and json_encode. Use array_map and clone to make deep copies of keys and values. Use serialize and unserialize for serialization and deserialization.
 PHP array key value flipping: Comparative performance analysis of different methods
May 03, 2024 pm 09:03 PM
PHP array key value flipping: Comparative performance analysis of different methods
May 03, 2024 pm 09:03 PM
The performance comparison of PHP array key value flipping methods shows that the array_flip() function performs better than the for loop in large arrays (more than 1 million elements) and takes less time. The for loop method of manually flipping key values takes a relatively long time.
 Vivo's new X100 series memory, color exposure: all series start at 12+256GB
May 06, 2024 pm 03:58 PM
Vivo's new X100 series memory, color exposure: all series start at 12+256GB
May 06, 2024 pm 03:58 PM
According to news on May 6, vivo officially announced today that the new vivoX100 series will be officially released at 19:00 on May 13. It is understood that this conference is expected to release three models, vivoX100s, vivoX100sPro, and vivoX100Ultra, as well as vivo's self-developed imaging brand BlueImage blueprint imaging technology. Digital blogger "Digital Chat Station" also released the official renderings, memory specifications and color matching of these three models today. Among them, X100s adopts a straight screen design, while X100sPro and X100Ultra have curved screen designs. The blogger revealed that vivoX100s comes in four colors: black, titanium, cyan, and white. The memory specifications




