 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 Holding gauze and grasping needles, NVIDIA cooperates with many universities to develop surgical robots
Holding gauze and grasping needles, NVIDIA cooperates with many universities to develop surgical robots
Holding gauze and grasping needles, NVIDIA cooperates with many universities to develop surgical robots

Editor | X
NVIDIA is working with academic researchers to study surgical robots.
NVIDIA teamed up with researchers from the University of Toronto, UC Berkeley, ETH Zurich, and Georgia Institute of Technology to develop ORBIT-Surgical, a simulation framework for training robots that improves the skills of technical teams while reducing surgical Cognitive load on physicians. ORBIT-Surgical is an artificial intelligence-based simulation framework that achieves highly realistic surgical simulation through a virtual surgical environment and intelligent coaching system. Doctors can interact with this system to simulate the various situations and complexities of real surgeries. This simulation technology can not only help with training
"Inspired by training courses in laparoscopic surgery (also known as minimally invasive surgery), it supports more than a dozen operations, such as grabbing small objects like needles and moving them from one The physics-based framework is built using NVIDIA Isaac Sim, a tool for designing, training and testing AI-based robots. simulation platform.
Researchers trained reinforcement learning and imitation learning algorithms on NVIDIA GPUs and used NVIDIA Omniverse, a platform for developing and deploying advanced 3D applications and pipelines based on the Universal Scene Description (OpenUSD), To achieve photorealistic rendering.
ORBIT-Surgical will be presented at IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) 2024.
 GitHub open source code:
GitHub open source code:
 ORBIT-Surgical is a modular framework for robot learning built on Isaac Orbit. Orbit supports various reinforcement learning and imitation learning libraries, where artificial intelligence agents are trained to imitate real expert demonstrations. By using Orbit, experts can design and optimize surgical procedures and translate them into executable sequences of robotic operations.
The core concept of Isaac Orbit is to transform expert knowledge into robot behaviors that can be executed automatically. The system contains the following components:
1. Data collection: Use experts to perform surgeries and record their operations and decisions to build a training data set.
2. Data preprocessing: Preprocess and specialize the collected data. This surgical framework enables developers to train robots such as the da Vinci Research Kit (dVRK) and is used on NVIDIA RTX Reinforcement learning and imitation learning frameworks running on GPUs to manipulate rigid and soft objects.
ORBIT-Surgical is a modular framework for robot learning built on Isaac Orbit. Orbit supports various reinforcement learning and imitation learning libraries, where artificial intelligence agents are trained to imitate real expert demonstrations. By using Orbit, experts can design and optimize surgical procedures and translate them into executable sequences of robotic operations.
The core concept of Isaac Orbit is to transform expert knowledge into robot behaviors that can be executed automatically. The system contains the following components:
1. Data collection: Use experts to perform surgeries and record their operations and decisions to build a training data set.
2. Data preprocessing: Preprocess and specialize the collected data. This surgical framework enables developers to train robots such as the da Vinci Research Kit (dVRK) and is used on NVIDIA RTX Reinforcement learning and imitation learning frameworks running on GPUs to manipulate rigid and soft objects. ORBIT-Surgical introduces more than a dozen baseline tasks for surgical training, including single-handed tasks such as picking up a piece of gauze, inserting a shunt into a blood vessel, or raising a suture needle to a specific location. It also includes bimanual tasks such as passing a needle from one arm to the other, threading a threaded needle through a looped rod, and reaching both arms into specific locations while avoiding obstacles.
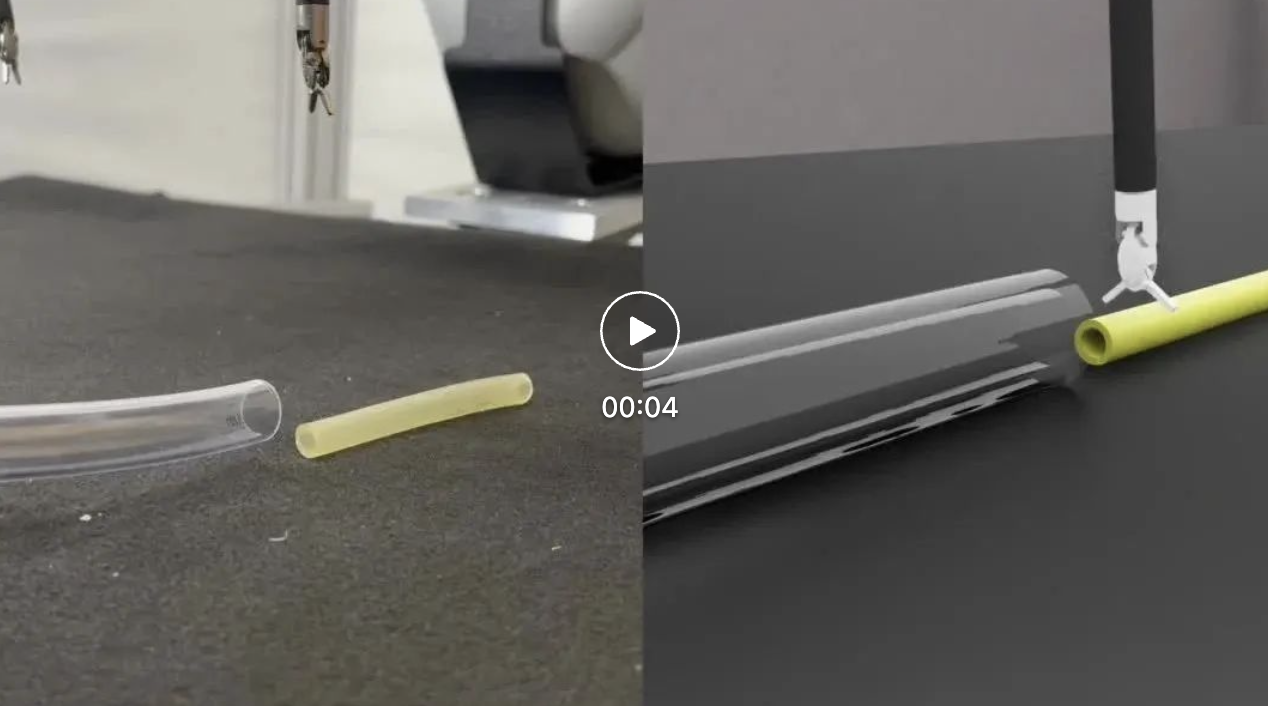

By developing a surgical simulator that leverages GPU acceleration and parallelization, the team was able to increase the robot's learning speed by an order of magnitude over existing surgical frameworks. They found that after training, the robotic digital twin could complete tasks such as inserting a shunt and lifting a suture needle in two hours on a single NVIDIA RTX GPU.
With the visual realism enabled by Omniverse rendering, ORBIT-Surgical also allows researchers to generate high-fidelity synthetic data, which can help train AI models to perform perception tasks, such as segmenting surgeries in real videos captured in the operating room tool.
The team’s proof-of-concept shows that combining simulation and real-world data significantly improves the accuracy of artificial intelligence models in segmenting surgical needles from images, helping to reduce the need for large, expensive training of such models. requirements for realistic data sets.
Reference content: https://blogs.nvidia.com/blog/orbit-surgical-robotics-research-icra/
The above is the detailed content of Holding gauze and grasping needles, NVIDIA cooperates with many universities to develop surgical robots. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1664
1664
 14
14
 1422
1422
 52
52
 1316
1316
 25
25
 1268
1268
 29
29
 1241
1241
 24
24
 DeepMind robot plays table tennis, and its forehand and backhand slip into the air, completely defeating human beginners
Aug 09, 2024 pm 04:01 PM
DeepMind robot plays table tennis, and its forehand and backhand slip into the air, completely defeating human beginners
Aug 09, 2024 pm 04:01 PM
But maybe he can’t defeat the old man in the park? The Paris Olympic Games are in full swing, and table tennis has attracted much attention. At the same time, robots have also made new breakthroughs in playing table tennis. Just now, DeepMind proposed the first learning robot agent that can reach the level of human amateur players in competitive table tennis. Paper address: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2408.03906 How good is the DeepMind robot at playing table tennis? Probably on par with human amateur players: both forehand and backhand: the opponent uses a variety of playing styles, and the robot can also withstand: receiving serves with different spins: However, the intensity of the game does not seem to be as intense as the old man in the park. For robots, table tennis
 The first mechanical claw! Yuanluobao appeared at the 2024 World Robot Conference and released the first chess robot that can enter the home
Aug 21, 2024 pm 07:33 PM
The first mechanical claw! Yuanluobao appeared at the 2024 World Robot Conference and released the first chess robot that can enter the home
Aug 21, 2024 pm 07:33 PM
On August 21, the 2024 World Robot Conference was grandly held in Beijing. SenseTime's home robot brand "Yuanluobot SenseRobot" has unveiled its entire family of products, and recently released the Yuanluobot AI chess-playing robot - Chess Professional Edition (hereinafter referred to as "Yuanluobot SenseRobot"), becoming the world's first A chess robot for the home. As the third chess-playing robot product of Yuanluobo, the new Guoxiang robot has undergone a large number of special technical upgrades and innovations in AI and engineering machinery. For the first time, it has realized the ability to pick up three-dimensional chess pieces through mechanical claws on a home robot, and perform human-machine Functions such as chess playing, everyone playing chess, notation review, etc.
 Claude has become lazy too! Netizen: Learn to give yourself a holiday
Sep 02, 2024 pm 01:56 PM
Claude has become lazy too! Netizen: Learn to give yourself a holiday
Sep 02, 2024 pm 01:56 PM
The start of school is about to begin, and it’s not just the students who are about to start the new semester who should take care of themselves, but also the large AI models. Some time ago, Reddit was filled with netizens complaining that Claude was getting lazy. "Its level has dropped a lot, it often pauses, and even the output becomes very short. In the first week of release, it could translate a full 4-page document at once, but now it can't even output half a page!" https:// www.reddit.com/r/ClaudeAI/comments/1by8rw8/something_just_feels_wrong_with_claude_in_the/ in a post titled "Totally disappointed with Claude", full of
 At the World Robot Conference, this domestic robot carrying 'the hope of future elderly care' was surrounded
Aug 22, 2024 pm 10:35 PM
At the World Robot Conference, this domestic robot carrying 'the hope of future elderly care' was surrounded
Aug 22, 2024 pm 10:35 PM
At the World Robot Conference being held in Beijing, the display of humanoid robots has become the absolute focus of the scene. At the Stardust Intelligent booth, the AI robot assistant S1 performed three major performances of dulcimer, martial arts, and calligraphy in one exhibition area, capable of both literary and martial arts. , attracted a large number of professional audiences and media. The elegant playing on the elastic strings allows the S1 to demonstrate fine operation and absolute control with speed, strength and precision. CCTV News conducted a special report on the imitation learning and intelligent control behind "Calligraphy". Company founder Lai Jie explained that behind the silky movements, the hardware side pursues the best force control and the most human-like body indicators (speed, load) etc.), but on the AI side, the real movement data of people is collected, allowing the robot to become stronger when it encounters a strong situation and learn to evolve quickly. And agile
 ACL 2024 Awards Announced: One of the Best Papers on Oracle Deciphering by HuaTech, GloVe Time Test Award
Aug 15, 2024 pm 04:37 PM
ACL 2024 Awards Announced: One of the Best Papers on Oracle Deciphering by HuaTech, GloVe Time Test Award
Aug 15, 2024 pm 04:37 PM
At this ACL conference, contributors have gained a lot. The six-day ACL2024 is being held in Bangkok, Thailand. ACL is the top international conference in the field of computational linguistics and natural language processing. It is organized by the International Association for Computational Linguistics and is held annually. ACL has always ranked first in academic influence in the field of NLP, and it is also a CCF-A recommended conference. This year's ACL conference is the 62nd and has received more than 400 cutting-edge works in the field of NLP. Yesterday afternoon, the conference announced the best paper and other awards. This time, there are 7 Best Paper Awards (two unpublished), 1 Best Theme Paper Award, and 35 Outstanding Paper Awards. The conference also awarded 3 Resource Paper Awards (ResourceAward) and Social Impact Award (
 Li Feifei's team proposed ReKep to give robots spatial intelligence and integrate GPT-4o
Sep 03, 2024 pm 05:18 PM
Li Feifei's team proposed ReKep to give robots spatial intelligence and integrate GPT-4o
Sep 03, 2024 pm 05:18 PM
Deep integration of vision and robot learning. When two robot hands work together smoothly to fold clothes, pour tea, and pack shoes, coupled with the 1X humanoid robot NEO that has been making headlines recently, you may have a feeling: we seem to be entering the age of robots. In fact, these silky movements are the product of advanced robotic technology + exquisite frame design + multi-modal large models. We know that useful robots often require complex and exquisite interactions with the environment, and the environment can be represented as constraints in the spatial and temporal domains. For example, if you want a robot to pour tea, the robot first needs to grasp the handle of the teapot and keep it upright without spilling the tea, then move it smoothly until the mouth of the pot is aligned with the mouth of the cup, and then tilt the teapot at a certain angle. . this
 Hongmeng Smart Travel S9 and full-scenario new product launch conference, a number of blockbuster new products were released together
Aug 08, 2024 am 07:02 AM
Hongmeng Smart Travel S9 and full-scenario new product launch conference, a number of blockbuster new products were released together
Aug 08, 2024 am 07:02 AM
This afternoon, Hongmeng Zhixing officially welcomed new brands and new cars. On August 6, Huawei held the Hongmeng Smart Xingxing S9 and Huawei full-scenario new product launch conference, bringing the panoramic smart flagship sedan Xiangjie S9, the new M7Pro and Huawei novaFlip, MatePad Pro 12.2 inches, the new MatePad Air, Huawei Bisheng With many new all-scenario smart products including the laser printer X1 series, FreeBuds6i, WATCHFIT3 and smart screen S5Pro, from smart travel, smart office to smart wear, Huawei continues to build a full-scenario smart ecosystem to bring consumers a smart experience of the Internet of Everything. Hongmeng Zhixing: In-depth empowerment to promote the upgrading of the smart car industry Huawei joins hands with Chinese automotive industry partners to provide
 Distributed Artificial Intelligence Conference DAI 2024 Call for Papers: Agent Day, Richard Sutton, the father of reinforcement learning, will attend! Yan Shuicheng, Sergey Levine and DeepMind scientists will give keynote speeches
Aug 22, 2024 pm 08:02 PM
Distributed Artificial Intelligence Conference DAI 2024 Call for Papers: Agent Day, Richard Sutton, the father of reinforcement learning, will attend! Yan Shuicheng, Sergey Levine and DeepMind scientists will give keynote speeches
Aug 22, 2024 pm 08:02 PM
Conference Introduction With the rapid development of science and technology, artificial intelligence has become an important force in promoting social progress. In this era, we are fortunate to witness and participate in the innovation and application of Distributed Artificial Intelligence (DAI). Distributed artificial intelligence is an important branch of the field of artificial intelligence, which has attracted more and more attention in recent years. Agents based on large language models (LLM) have suddenly emerged. By combining the powerful language understanding and generation capabilities of large models, they have shown great potential in natural language interaction, knowledge reasoning, task planning, etc. AIAgent is taking over the big language model and has become a hot topic in the current AI circle. Au



