 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 In just a few seconds, protein dynamics information can be accurately inferred. AI models such as Shandong University and Beijing Institute of Technology RMSF-net are published in Nature sub-journals.
In just a few seconds, protein dynamics information can be accurately inferred. AI models such as Shandong University and Beijing Institute of Technology RMSF-net are published in Nature sub-journals.
In just a few seconds, protein dynamics information can be accurately inferred. AI models such as Shandong University and Beijing Institute of Technology RMSF-net are published in Nature sub-journals.

The dynamics of a protein are crucial to understanding its mechanism. However, computationally predicting protein kinetic information is challenging.
Here, a research team from Shandong University, BioMap, Beijing Institute of Technology, Hubei Medical College, Ningxia Medical University and King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST) proposed a neural network model RMSF -net, which outperforms previous methods and produces the best results in large-scale protein dynamics data sets; the model can accurately infer the dynamics information of a protein in seconds.
By effectively learning from the integration of experimental protein structure data and cryo-EM data, this method is able to accurately identify interactive bidirectional constraints and supervision between cryo-EM images and PDB models to maximize Improve the efficiency of dynamics prediction.
RMSF-net is a free-to-use tool that will play an important role in protein dynamics studies.
The study was titled "Accurate Prediction of Protein Structural Flexibility by Deep Learning Integrating Intricate Atomic Structures and Cryo-EM Density Information" and was published in "Nature Communications" on July 2.

- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-49858-x
RMSF-net GitHub address:
- https://github. com/XintSong/RMSF-net
Protein Dynamics
Protein dynamics are crucial in understanding their mechanisms. Cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) technology can resolve most proteins, where the macromolecular structure is represented by a 3D density map.
Limitations of cryo-electron microscopy
Due to the low resolution and signal-to-noise ratio of the original 2D particle images, cryo-electron microscopy analysis cannot resolve small conformational changes during reconstruction.
Application of deep learning in cryo-electron microscopy
Deep learning methods are widely used in the automatic analysis of cryo-electron microscopy images. Using high-resolution cryo-EM maps, a Protein Data Bank (PDB) model can be constructed from the cryo-EM maps.
RMSF-net Overview
RMSF-net is a neural network model for cryo-electron microscopy density maps. It leverages cryo-EM density and PDB model information to accurately infer protein dynamic information in seconds.
RMSF
RMSF is a widely used measurement method for assessing the flexibility of molecular structures in molecular dynamics (MD) analyses. Its main purpose is to predict the RMSF of local structures (residues, atoms) within a protein.
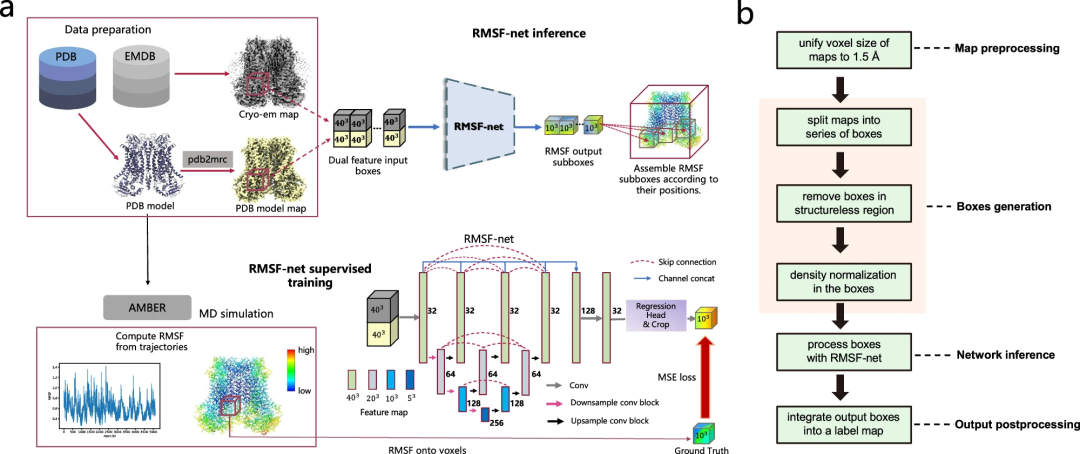
In addition to cryo-EM images, RMSF-net utilizes PDB models as additional input to produce RMSF predictions that are very close to the MD simulation results.
RMSF-net is a three-dimensional convolutional neural network containing two interconnected modules. The main module uses Unet+ (L3) architecture to encode and decode features of input density boxes. Another module utilizes 1x1 convolutions to regress the channels of the feature maps generated by the Unet+backbone. Center clipping is then applied to the regression module output to obtain a centered RMSF subbox, where the voxel value corresponds to the RMSF of the atoms contained within it. Finally, the RMSF subboxes are spatially merged into an RMSF map using a merging algorithm.
In addition, the researchers also constructed a large-scale protein dynamics dataset for training and validation of RMSF-net, in which 335 cryo-EM structural entries with fitted PDB models were selected and corresponding MD simulations were performed. Comprehensive experimental results demonstrate the efficiency and effectiveness of RMSF-net.
Table: Performance of different RMSF prediction methods on the data set. (Source: paper)
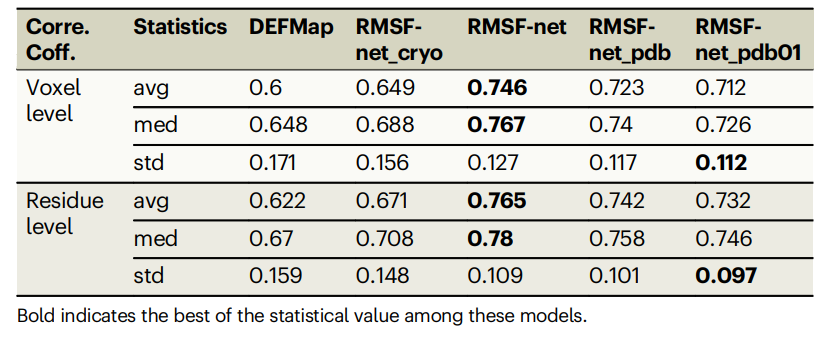
RMSF-net performed well in rigorous 5-fold cross-validation, with a correlation coefficient of 0.746±0.127 with MD simulation results. The correlation coefficient of RMSF-net is improved by 15% compared to DEFMap and by 10% compared to the baseline method.
Interpretability of dynamics predictions
Researchers enhanced the interpretability of RMSF-net dynamics predictions through comparative experiments. They divide the RMSF forecasting process into two steps:
- 結構資訊擷取(Occ2RMSF-net)
- 基於提取的結構資訊進行動力學預測
研究表明,基於低溫電子顯微鏡圖譜的模型(例如DEFMap 或RMSF-net_cryo)的動力學預測主要透過解讀蛋白質結構實現。這突顯了蛋白質拓樸結構與動力學之間的聯繫,符合結構-功能關係的第一原理。
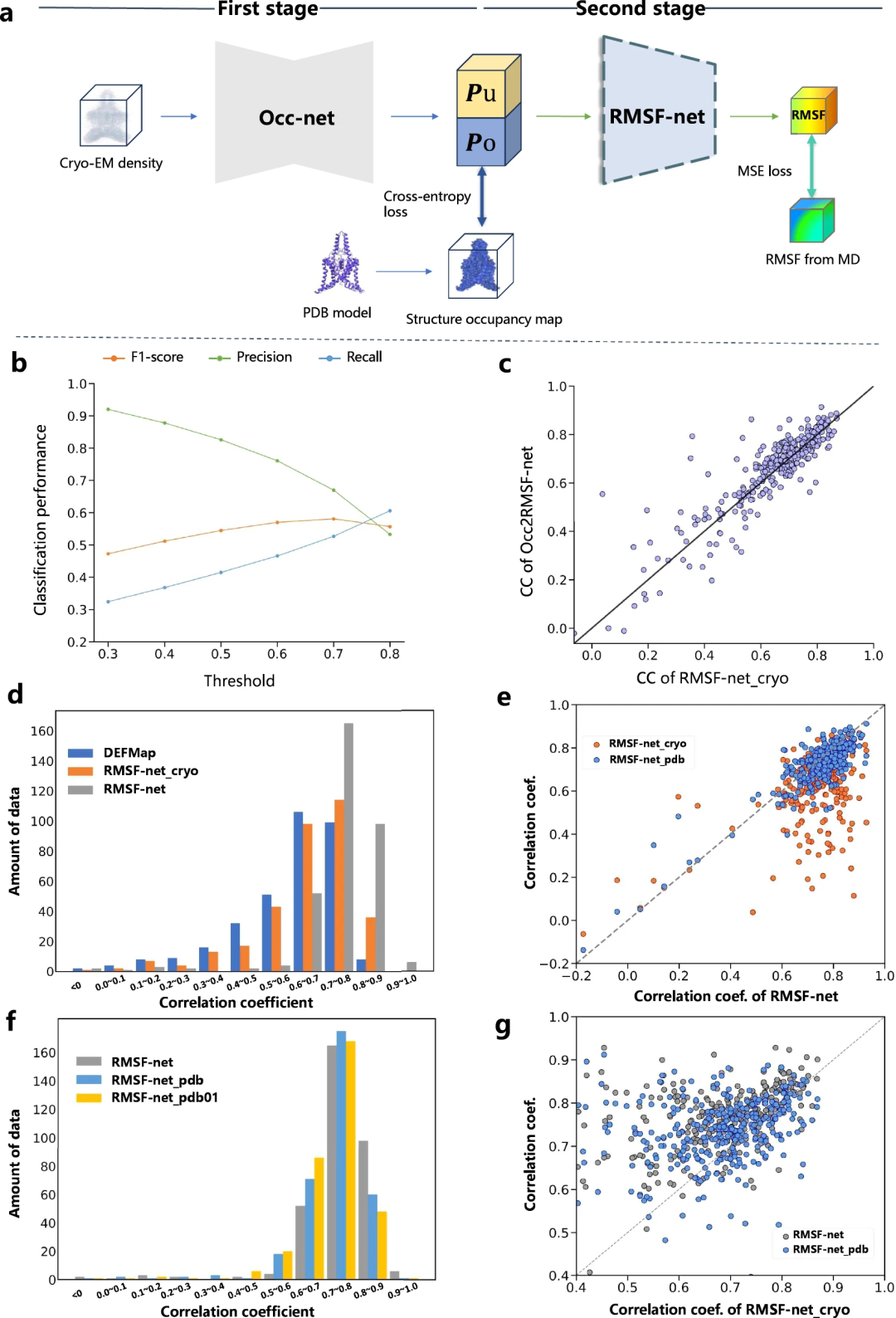
此外,透過對RMSF-net_cryo、RMSF-net_pdb 和最終的雙組合RMSF-net 進行全面比較,證明了:一方面,來自PDB 模型的結構資訊在RMSF-net 中起主要作用,其中深度模型從MD 模擬中學習結構拓撲和靈活性之間的模式,另一方面,低溫電子顯微鏡圖譜異質密度分佈中包含的動力學資訊進一步增強了模型。這些結果驗證了低溫電子顯微鏡圖和 PDB 模型的資訊對 RMSF-net 中的蛋白質動力學預測的互補作用。
局限性與未來方向
不可否認的是,RMSF-net 主要限於預測純蛋白質及其複合物在溶液中的柔韌性。對於蛋白質在與小分子配體結合或在膜環境中的動力學特性,該方法在某些局部區域可能會表現出不準確性。
RMSF-net 的卓越性能揭示了進一步研究該方向的可行性。該研究還沒有擴展到核酸和蛋白質-核酸複合物。綜合表徵大分子動力學的各個方面,包括多構象預測和轉變分析,在未來需要進一步進行廣泛而深入的研究。
儘管如此,作為預測蛋白質動力學的工具,RMSF-net 由於其優越的性能和超快的處理速度,在蛋白質結構和動力學研究中仍有很大的應用前景。
註:封面來自網路
The above is the detailed content of In just a few seconds, protein dynamics information can be accurately inferred. AI models such as Shandong University and Beijing Institute of Technology RMSF-net are published in Nature sub-journals.. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1384
1384
 52
52
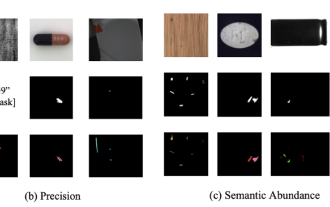 Breaking through the boundaries of traditional defect detection, 'Defect Spectrum' achieves ultra-high-precision and rich semantic industrial defect detection for the first time.
Jul 26, 2024 pm 05:38 PM
Breaking through the boundaries of traditional defect detection, 'Defect Spectrum' achieves ultra-high-precision and rich semantic industrial defect detection for the first time.
Jul 26, 2024 pm 05:38 PM
In modern manufacturing, accurate defect detection is not only the key to ensuring product quality, but also the core of improving production efficiency. However, existing defect detection datasets often lack the accuracy and semantic richness required for practical applications, resulting in models unable to identify specific defect categories or locations. In order to solve this problem, a top research team composed of Hong Kong University of Science and Technology Guangzhou and Simou Technology innovatively developed the "DefectSpectrum" data set, which provides detailed and semantically rich large-scale annotation of industrial defects. As shown in Table 1, compared with other industrial data sets, the "DefectSpectrum" data set provides the most defect annotations (5438 defect samples) and the most detailed defect classification (125 defect categories
 NVIDIA dialogue model ChatQA has evolved to version 2.0, with the context length mentioned at 128K
Jul 26, 2024 am 08:40 AM
NVIDIA dialogue model ChatQA has evolved to version 2.0, with the context length mentioned at 128K
Jul 26, 2024 am 08:40 AM
The open LLM community is an era when a hundred flowers bloom and compete. You can see Llama-3-70B-Instruct, QWen2-72B-Instruct, Nemotron-4-340B-Instruct, Mixtral-8x22BInstruct-v0.1 and many other excellent performers. Model. However, compared with proprietary large models represented by GPT-4-Turbo, open models still have significant gaps in many fields. In addition to general models, some open models that specialize in key areas have been developed, such as DeepSeek-Coder-V2 for programming and mathematics, and InternVL for visual-language tasks.
 Training with millions of crystal data to solve the crystallographic phase problem, the deep learning method PhAI is published in Science
Aug 08, 2024 pm 09:22 PM
Training with millions of crystal data to solve the crystallographic phase problem, the deep learning method PhAI is published in Science
Aug 08, 2024 pm 09:22 PM
Editor |KX To this day, the structural detail and precision determined by crystallography, from simple metals to large membrane proteins, are unmatched by any other method. However, the biggest challenge, the so-called phase problem, remains retrieving phase information from experimentally determined amplitudes. Researchers at the University of Copenhagen in Denmark have developed a deep learning method called PhAI to solve crystal phase problems. A deep learning neural network trained using millions of artificial crystal structures and their corresponding synthetic diffraction data can generate accurate electron density maps. The study shows that this deep learning-based ab initio structural solution method can solve the phase problem at a resolution of only 2 Angstroms, which is equivalent to only 10% to 20% of the data available at atomic resolution, while traditional ab initio Calculation
 Google AI won the IMO Mathematical Olympiad silver medal, the mathematical reasoning model AlphaProof was launched, and reinforcement learning is so back
Jul 26, 2024 pm 02:40 PM
Google AI won the IMO Mathematical Olympiad silver medal, the mathematical reasoning model AlphaProof was launched, and reinforcement learning is so back
Jul 26, 2024 pm 02:40 PM
For AI, Mathematical Olympiad is no longer a problem. On Thursday, Google DeepMind's artificial intelligence completed a feat: using AI to solve the real question of this year's International Mathematical Olympiad IMO, and it was just one step away from winning the gold medal. The IMO competition that just ended last week had six questions involving algebra, combinatorics, geometry and number theory. The hybrid AI system proposed by Google got four questions right and scored 28 points, reaching the silver medal level. Earlier this month, UCLA tenured professor Terence Tao had just promoted the AI Mathematical Olympiad (AIMO Progress Award) with a million-dollar prize. Unexpectedly, the level of AI problem solving had improved to this level before July. Do the questions simultaneously on IMO. The most difficult thing to do correctly is IMO, which has the longest history, the largest scale, and the most negative
 Nature's point of view: The testing of artificial intelligence in medicine is in chaos. What should be done?
Aug 22, 2024 pm 04:37 PM
Nature's point of view: The testing of artificial intelligence in medicine is in chaos. What should be done?
Aug 22, 2024 pm 04:37 PM
Editor | ScienceAI Based on limited clinical data, hundreds of medical algorithms have been approved. Scientists are debating who should test the tools and how best to do so. Devin Singh witnessed a pediatric patient in the emergency room suffer cardiac arrest while waiting for treatment for a long time, which prompted him to explore the application of AI to shorten wait times. Using triage data from SickKids emergency rooms, Singh and colleagues built a series of AI models that provide potential diagnoses and recommend tests. One study showed that these models can speed up doctor visits by 22.3%, speeding up the processing of results by nearly 3 hours per patient requiring a medical test. However, the success of artificial intelligence algorithms in research only verifies this
 To provide a new scientific and complex question answering benchmark and evaluation system for large models, UNSW, Argonne, University of Chicago and other institutions jointly launched the SciQAG framework
Jul 25, 2024 am 06:42 AM
To provide a new scientific and complex question answering benchmark and evaluation system for large models, UNSW, Argonne, University of Chicago and other institutions jointly launched the SciQAG framework
Jul 25, 2024 am 06:42 AM
Editor |ScienceAI Question Answering (QA) data set plays a vital role in promoting natural language processing (NLP) research. High-quality QA data sets can not only be used to fine-tune models, but also effectively evaluate the capabilities of large language models (LLM), especially the ability to understand and reason about scientific knowledge. Although there are currently many scientific QA data sets covering medicine, chemistry, biology and other fields, these data sets still have some shortcomings. First, the data form is relatively simple, most of which are multiple-choice questions. They are easy to evaluate, but limit the model's answer selection range and cannot fully test the model's ability to answer scientific questions. In contrast, open-ended Q&A
 PRO | Why are large models based on MoE more worthy of attention?
Aug 07, 2024 pm 07:08 PM
PRO | Why are large models based on MoE more worthy of attention?
Aug 07, 2024 pm 07:08 PM
In 2023, almost every field of AI is evolving at an unprecedented speed. At the same time, AI is constantly pushing the technological boundaries of key tracks such as embodied intelligence and autonomous driving. Under the multi-modal trend, will the situation of Transformer as the mainstream architecture of AI large models be shaken? Why has exploring large models based on MoE (Mixed of Experts) architecture become a new trend in the industry? Can Large Vision Models (LVM) become a new breakthrough in general vision? ...From the 2023 PRO member newsletter of this site released in the past six months, we have selected 10 special interpretations that provide in-depth analysis of technological trends and industrial changes in the above fields to help you achieve your goals in the new year. be prepared. This interpretation comes from Week50 2023
 Automatically identify the best molecules and reduce synthesis costs. MIT develops a molecular design decision-making algorithm framework
Jun 22, 2024 am 06:43 AM
Automatically identify the best molecules and reduce synthesis costs. MIT develops a molecular design decision-making algorithm framework
Jun 22, 2024 am 06:43 AM
Editor | Ziluo AI’s use in streamlining drug discovery is exploding. Screen billions of candidate molecules for those that may have properties needed to develop new drugs. There are so many variables to consider, from material prices to the risk of error, that weighing the costs of synthesizing the best candidate molecules is no easy task, even if scientists use AI. Here, MIT researchers developed SPARROW, a quantitative decision-making algorithm framework, to automatically identify the best molecular candidates, thereby minimizing synthesis costs while maximizing the likelihood that the candidates have the desired properties. The algorithm also determined the materials and experimental steps needed to synthesize these molecules. SPARROW takes into account the cost of synthesizing a batch of molecules at once, since multiple candidate molecules are often available



