How To Use PHP As A Backend Using React For Frontend
Introduction
Developing dynamic and interactive web apps is crucial in the dynamic and ever-changing world of web development. The speed and versatility of React, a JavaScript toolkit for creating user interfaces, have led to its great popularity. However, PHP is still a strong option for server-side programming. This tutorial will show you how to easily combine the functionality of a PHP backend and React front-end to utilize their respective strengths fully.
Understanding the Distinct Roles of PHP and React
What Is PHP
The term PHP is an acronym for Hypertext Preprocessor. It is a server-side scripting language that is used for web development. It can be easily embedded with HTML files. HTML codes can also be written in a PHP file.
Merits Of PHP
Below are a few Merits of PHP
Ease of Learning and Use:
- PHP is known for its straightforward syntax, which is relatively easy for beginners. This simplicity helps new developers start building web applications quickly.
Wide Adoption and Community Support:
- PHP has a large and active community. This means extensive documentation, numerous tutorials, and a wealth of online resources. Community support also translates into a vast pre-written code, frameworks, and plugin library.
Integration Capabilities:
- PHP integrates seamlessly with various databases (such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQLite), web servers (like Apache and Nginx), and other services. This makes it a versatile choice for web development.
Open Source:
- PHP is free to use and distribute. This lowers the cost of development, especially for small businesses and startups.
Cross-Platform Compatibility:
- PHP can run on multiple platforms, including Windows, Linux, and macOS. This flexibility ensures that PHP applications can be deployed in diverse environments without compatibility issues.
Demerits Of PHP
Below are a few Demerits of PHP.
-
Inconsistent Function Naming and Parameter Order:
- One of the common criticisms of PHP is its inconsistent function naming conventions and parameter order. For example, functions may have different naming patterns (str_replace vs. strpos) and parameter orders (array_filter($array, $callback) vs. array_map($callback, $array)). This inconsistency can lead to confusion and errors, especially for new developers.
-
Historical Security Issues:
- PHP has had a history of security vulnerabilities, partly due to its widespread use and partly due to the way it was designed. While modern PHP has significantly improved in terms of security features, legacy codebases and bad practices from earlier versions can still pose security risks.
-
Performance Compared to Other Languages:
- While PHP has made great strides in improving performance (especially with PHP 7 and later), it can still be slower compared to some other languages like Node.js or Go for certain tasks. This can be a drawback for applications requiring extremely high performance and low latency.
-
Weak Typing:
- PHP’s weak typing system, which allows implicit type conversions, can lead to unexpected behavior and bugs that are difficult to track down. For example, comparing a string to a number may yield unexpected results ("123" == 123 is true, but "123" === 123 is false). This can be problematic, especially for large, complex codebases.
-
Over-Reliance on Older, Procedural Code:
- Many PHP applications and tutorials still use older, procedural programming techniques rather than modern, object-oriented, or functional programming practices. This can lead to less maintainable and harder-to-read code. While modern frameworks encourage better practices, the legacy of procedural code can still be a significant issue.
What Is React
React JS is a declarative, efficient, and flexible JavaScript library for building user interfaces. It’s ‘V’ in MVC. ReactJS is an open-source, component-based front-end library, responsible only for the view layer of the application. It is maintained by Facebook.
Merits Of React Js
Below are a few Merits of React Js.
-
Component-Based Architecture:
- React follows a component-based architecture, which allows developers to build reusable UI components. This modularity leads to cleaner, more maintainable, and scalable code. Components can be reused across different parts of an application, reducing redundancy and improving development efficiency.
-
Virtual DOM for Improved Performance:
- React uses a Virtual DOM (Document Object Model) to optimize rendering performance. When the state of an application changes, React updates the Virtual DOM first, which then efficiently updates the actual DOM only where necessary. This minimizes direct manipulation of the DOM, leading to faster and more efficient updates, particularly beneficial for complex applications with frequent UI changes.
-
Declarative UI:
- React's declarative approach to building UIs makes code more predictable and easier to debug. Developers describe what the UI should look like for a given state, and React takes care of updating the actual UI based on state changes. This simplifies the process of developing interactive user interfaces and makes the code more readable.
-
Rich Ecosystem and Community Support:
- React has a vast ecosystem with numerous libraries, tools, and extensions that enhance its functionality. The strong community support ensures that developers have access to extensive resources, tutorials, and third-party components. Additionally, the backing of Facebook and contributions from a large number of developers worldwide ensure React remains up-to-date and continuously improving.
-
Strong Support for JSX:
- React uses JSX (JavaScript XML), a syntax extension that allows HTML to be written within JavaScript. JSX simplifies the process of creating React components and makes the code more readable by visually separating the structure (HTML) from the logic (JavaScript). This tight integration of markup with logic enhances development efficiency and reduces context switching for developers.
Demerits Of React Js
Below are a few Demerits of React Js.
-
Steep Learning Curve:
- React's flexibility and the wide array of tools and libraries in its ecosystem can make the learning curve steep for beginners. Understanding concepts like JSX, components, state management, and the intricacies of the Virtual DOM can be challenging for new developers.
-
Boilerplate and Complexity:
- Setting up a React project often involves considerable boilerplate code and configuration. Tools like Create React App simplify the initial setup, but as projects grow, the complexity can increase, requiring additional configuration and understanding of build tools like Webpack and Babel.
-
Rapidly Changing Environment:
- The React ecosystem evolves quickly, with frequent updates and new tools emerging regularly. Keeping up with the latest best practices, updates, and libraries can be overwhelming for developers. This fast pace of change can also lead to issues with outdated documentation and compatibility between different libraries and versions.
-
Poor SEO:
- By default, React renders applications on the client side, which can lead to poor SEO performance because search engine crawlers might have difficulty indexing the dynamic content. Although solutions like server-side rendering (SSR) with frameworks like Next.js exist, implementing them adds complexity to the project.
-
State Management Complexity:
- Managing state in large React applications can become complex. While React's built-in state management works well for small applications, scaling up requires more sophisticated state management solutions like Redux, MobX, or the Context API. These solutions add another layer of complexity and require additional learning and setup.
The Synergy Between PHP and React in Modern Web Applications
The synergy between PHP and React in modern web applications leverages the strengths of both technologies to create robust, dynamic, and scalable applications. Here’s an in-depth look at how these technologies complement each other and the benefits of combining them:
5 Benefits of using PHP with React
Note: the benefits are more than five but here are the listed few!
1. Full-Stack Versatility
Frontend and backend integration:
Seamless Data Handling: React effectively manages the front end, while PHP can handle server-side logic and data exchanges, resulting in a coherent development environment.
API-Driven Development: By supplying data to the React frontend via GraphQL or RESTful endpoints, PHP may function as a potent backend API, allowing for a clear division of responsibilities.
Efficiency of Development:
Parallel Development: Teams working on front-end and back-end projects simultaneously can speed up development and eliminate bottlenecks.
reused Components: Frontend development is more modular and manageable because of React's component-based design, which guarantees that UI elements are reused.
2. Scalability
Managing a Higher Load:
Effective Backend: PHP frameworks like Laravel are designed to manage massive amounts of data and user requests effectively, handling intricate and scalable backend processes.
Frontend Optimisation: Even with intricate and data-intensive apps, React's virtual DOM and effective diffing technique guarantee quick and responsive UI changes.
Architecture of Microservices:
Modular Approach: Different services can scale independently when PHP is included in a microservices architecture. React facilitates scalability by allowing it to use these services as required.
Burden Distribution: The program as a whole can manage more traffic skillfully by dividing the burden between PHP, which handles server-side operations, and React, which handles client-side interactions.
3. Performance
Quick load times:
Server-Side Rendering (SSR): Initial HTML may be pre-rendered by PHP and sent to the client, thereafter React can hydrate it. This method boosts the user experience and speeds up the initial load time.
Asynchronous Data Fetching: By using React, data may be fetched from the PHP backend asynchronously, maintaining a responsive user interface and effective handling of data changes.
Enhanced Communication:
Effective State Management: React's state management features, such as context and hooks, enable better handling of UI state changes, which minimizes the need for pointless re-renders.
Caching and Optimisation: PHP can use server-side caching techniques to speed up the serving of static material and lower database demand, therefore improving performance.
4. Rich User Interfaces
UIs that are interactive and dynamic:
Component-Based design: React's component-based design enables programmers to create complex, interactive user interfaces that are simple to update and expand.
Real-Time Updates: React is capable of handling dynamic content changes and real-time updates with efficiency, making for a smooth and interesting user experience.
Improved User Experience:
Contemporary UI Libraries: React works nicely with contemporary UI libraries and frameworks (such as Material-UI and Ant Design), enabling programmers to design aesthetically pleasing and intuitive user interfaces.
Building responsive and adaptable user interfaces (UIs) that function effectively on a variety of devices and screen sizes is made simple using React.
5. SEO-Friendly
Better Optimisation for Search Engines:
Server-Side Rendering (SSR): Pre-rendering HTML content using PHP before providing it to the client guarantees better search engine indexing and SEO.
Meta Tags and Dynamic material: Using information from the PHP backend, React can dynamically manage and update meta tags, titles, and other SEO-relevant material.
Better Crawlability:
Static Site Generation (SSG): React may produce static pages at build time, improving the application's SEO while retaining PHP for dynamic content, by utilizing solutions like Next.js, which supports both SSR and SSG.
URL Structure: React can handle routing and navigation, making sure that visitors and search engines can explore the site with ease, while PHP can manage clear, SEO-friendly URL structures.
Developers may construct robust, scalable, and performance-optimized online apps with rich user experiences and search engine optimization by integrating PHP with React. Because of their synergy, frontend and backend technologies may be combined to create a strong and adaptable development process.
Creating a PHP and React Development Environment
At this point, we are about to start an actual project using React.js and PHP as the front end.
Prerequisites
There are things you need to know as a developer or things you need to have to be able to make php work as a backend with React. Here is the essential list!
- Have Basic Knowledge of PHP
- Know your React.Js
- Make Sure Node.js accompanied by npm is installed on your machine.
- Have PHP installed in your system Apache or Nginx
Step By Step Process On How To Use PHP As a Backend Using React As A Front-end
The step to use PHP as a backend alongside React is quite simple and it’s as follows.
Building The Frontend
Step 1: Open your terminal and run the following command below:
npx create-react-app my-react-app
Note: before running this command, you have to cd into the directory where you want your react folder to be! the way to cd to your desired directory is by adding this command to your terminal
cd Documents
After this, you’ll wait for your React app to be created.
Step 2: Navigate to your project folder:
The project you just created needs to be visited in the terminal
cd my-react-app
Step 3: Start the development server:
npm start
Building the PHP Backend
It's time to construct the PHP backend now that your React application is operational:
Step 1: Create a new folder for your PHP files within your React app directory.
to achieve this, run the following command on your terminal
mkdir php_backend
By running this command you’ll see a folder named php_backend

Step 2: Inside the php-backend folder, create a file named index.php.
Note: you’re free to call it any name, in my case I decided to use the index.php.

Step 3: In the index.php you can start defining your PHP endpoints and logic.
Below is what is written in my php-backend/index.php if you’re a PHP developer you’ll be familiar with this syntax.
<?PHP
$serverName="localhost";
$userName="root";
$password="";
$databaseName="react_php";
$conn = mysqli_connect($serverName, $userName, $password, $databaseName);
$recText = $_POST['text'];
$query = ("INSERT INTO react_php (texts) VALUES('$recText')");
if (mysqli_query($conn, $query)) {
echo "Data has been inserted successfully";
}else {
echo "Error";
}
?>
Now the next thing to do is go to the React Code you created earlier and open the folder in your code editor you’ll see a folder like src/App.js and add this syntax below.
import React, { Component } from 'react';
// import logo from './logo.svg';
import axios from 'axios'; //Import Axios
import './App.css';
class App extends Component{
state = {
text : ""
}
handleAdd = async e =>{
await this.setState({
text : e.target.value
})
}
handleSubmit = e =>{
e.preventDefault();
console.log(this.state.text);
let formData = new FormData();
formData.append("text", this.state.text);
const url = "http://localhost:80/react-backend/"
axios.post(url,formData)
.then(res=> console.log(res.data))
.catch(err=> console.log(err))
}
render(){
return(
<div className="App-header">
<input
onChange={this.handleAdd}
className="form-control"
// value={this.state.text}
type="text"
id='text'
placeholder='Enter Some Text!'/>
<br/>
<button
onClick={this.handleSubmit}
className="btn btn-success"
id='submit'> Save</button>
</div>
);
}
}
export default App;
Note: what allows the PHP to work is the **Axios**. Look at the code snippet below you’ll see how we used it!
In the public folder of your project, you’ll see an index.html file in that file I added a bootstrap cdn as a framework I'm using,
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@4.6.2/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css">
So Here’s a little styling.
.App {
text-align: center;
}
.App-logo {
height: 40vmin;
pointer-events: none;
}
@media (prefers-reduced-motion: no-preference) {
.App-logo {
animation: App-logo-spin infinite 20s linear;
}
}
.App-header {
background-color: #282c34;
min-height: 100vh;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
font-size: calc(10px + 2vmin);
color: white;
}
.App-link {
color: #61dafb;
}
@keyframes App-logo-spin {
from {
transform: rotate(0deg);
}
to {
transform: rotate(360deg);
}
}
After trying all these here’s the view it will give to you.
Her is the database controlling the backend. once you fill in the text and click save the text will display in the database automatically.
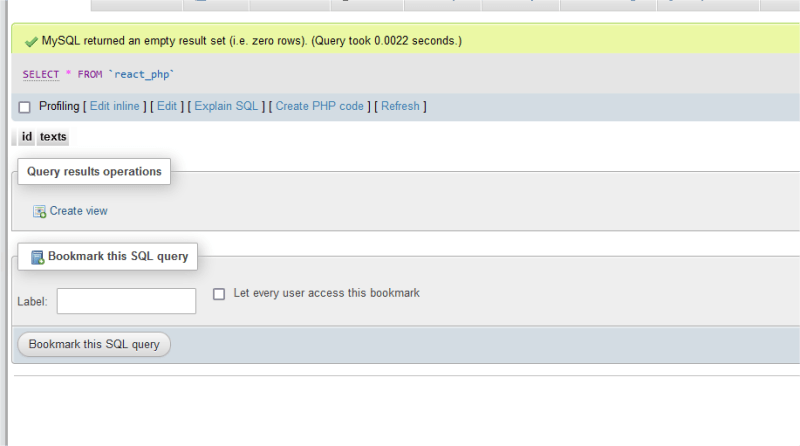
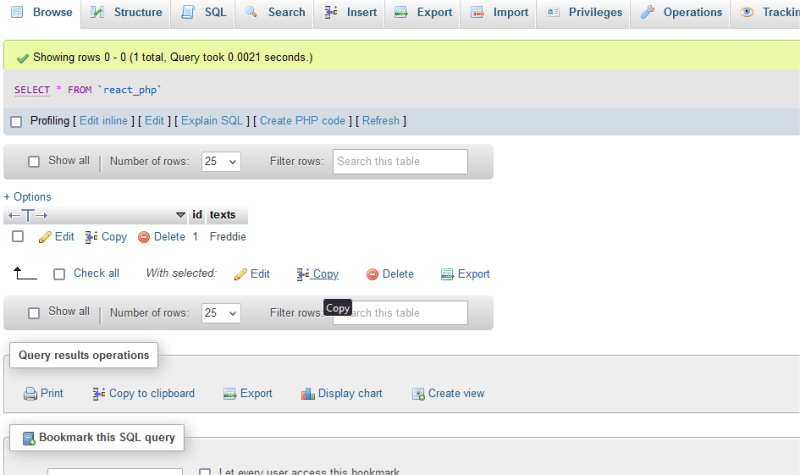
hereafter I wrote **Freddie** and I clicked on Browse, in the top right corner of the image displayed below. Once you see this know that you have done the right thing.
That’s the step I used in React and PHP in a single application.
Conclusion
In conclusion, integrating PHP as a backend with React as a frontend offers a robust and versatile solution for modern web application development. As discussed, this combination leverages the strengths of PHP's server-side capabilities and React's dynamic, component-based architecture to create scalable, high-performance applications. PHP efficiently handles server-side logic, database interactions, and API creation, while React ensures a rich, responsive user interface and seamless data handling.
This synergy between PHP and React not only enhances the development process but also results in web applications that are interactive, engaging, and SEO-friendly. Embracing this powerful integration empowers developers to build comprehensive and user-centric web applications with ease and efficiency.
I hope you found this tutorial incredibly valuable! Until next time, goodbye.
About The Author
Full-stack Laravel developer Emmanuel Okolie has 4+ years of experience in software development. He has developed full-fledged skills by combining software development, writing, and instructing others in what he does.
His stacks include ReactJ, Laravel, PHP, JavaScript, and other languages and frameworks.
As a freelancer, he creates websites for clients and writes technical guides to show people how to do what he does.
If given the chance, Emmanuel Okolie would enjoy speaking with you. Please go to and follow him on his website, Facebook, Github, LinkedIn, and Twitter.
The above is the detailed content of How To Use PHP As A Backend Using React For Frontend. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1664
1664
 14
14
 1423
1423
 52
52
 1317
1317
 25
25
 1268
1268
 29
29
 1246
1246
 24
24
 PHP and Python: Comparing Two Popular Programming Languages
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:13 AM
PHP and Python: Comparing Two Popular Programming Languages
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:13 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages, and choose according to project requirements. 1.PHP is suitable for web development, especially for rapid development and maintenance of websites. 2. Python is suitable for data science, machine learning and artificial intelligence, with concise syntax and suitable for beginners.
 PHP in Action: Real-World Examples and Applications
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP in Action: Real-World Examples and Applications
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP is widely used in e-commerce, content management systems and API development. 1) E-commerce: used for shopping cart function and payment processing. 2) Content management system: used for dynamic content generation and user management. 3) API development: used for RESTful API development and API security. Through performance optimization and best practices, the efficiency and maintainability of PHP applications are improved.
 Explain secure password hashing in PHP (e.g., password_hash, password_verify). Why not use MD5 or SHA1?
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:06 AM
Explain secure password hashing in PHP (e.g., password_hash, password_verify). Why not use MD5 or SHA1?
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:06 AM
In PHP, password_hash and password_verify functions should be used to implement secure password hashing, and MD5 or SHA1 should not be used. 1) password_hash generates a hash containing salt values to enhance security. 2) Password_verify verify password and ensure security by comparing hash values. 3) MD5 and SHA1 are vulnerable and lack salt values, and are not suitable for modern password security.
 PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP is a scripting language widely used on the server side, especially suitable for web development. 1.PHP can embed HTML, process HTTP requests and responses, and supports a variety of databases. 2.PHP is used to generate dynamic web content, process form data, access databases, etc., with strong community support and open source resources. 3. PHP is an interpreted language, and the execution process includes lexical analysis, grammatical analysis, compilation and execution. 4.PHP can be combined with MySQL for advanced applications such as user registration systems. 5. When debugging PHP, you can use functions such as error_reporting() and var_dump(). 6. Optimize PHP code to use caching mechanisms, optimize database queries and use built-in functions. 7
 How does PHP handle file uploads securely?
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:37 AM
How does PHP handle file uploads securely?
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:37 AM
PHP handles file uploads through the $\_FILES variable. The methods to ensure security include: 1. Check upload errors, 2. Verify file type and size, 3. Prevent file overwriting, 4. Move files to a permanent storage location.
 How does PHP type hinting work, including scalar types, return types, union types, and nullable types?
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:25 AM
How does PHP type hinting work, including scalar types, return types, union types, and nullable types?
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP type prompts to improve code quality and readability. 1) Scalar type tips: Since PHP7.0, basic data types are allowed to be specified in function parameters, such as int, float, etc. 2) Return type prompt: Ensure the consistency of the function return value type. 3) Union type prompt: Since PHP8.0, multiple types are allowed to be specified in function parameters or return values. 4) Nullable type prompt: Allows to include null values and handle functions that may return null values.
 The Enduring Relevance of PHP: Is It Still Alive?
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:12 AM
The Enduring Relevance of PHP: Is It Still Alive?
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:12 AM
PHP is still dynamic and still occupies an important position in the field of modern programming. 1) PHP's simplicity and powerful community support make it widely used in web development; 2) Its flexibility and stability make it outstanding in handling web forms, database operations and file processing; 3) PHP is constantly evolving and optimizing, suitable for beginners and experienced developers.
 PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages, and the choice should be based on project requirements. 1.PHP is suitable for web development, with simple syntax and high execution efficiency. 2. Python is suitable for data science and machine learning, with concise syntax and rich libraries.




