 System Tutorial
System Tutorial
 LINUX
LINUX
 How to end a process under Linux: Detailed explanation of normal and abnormal termination
How to end a process under Linux: Detailed explanation of normal and abnormal termination
How to end a process under Linux: Detailed explanation of normal and abnormal termination

In the first two chapters, we learned about creating processes. In this chapter, we will learn how to end the process under Linux.
In Linux, there are 3 ways to end a process normally and 2 ways to terminate abnormally:
1. Normal end:
a. Call return in the main function. This is equivalent to calling exit.
b. Call the exit function. According to the definition of this function in ANSIC, when called, all registered exit handles will be executed, all standard I/O streams will be turned off, and file descriptors and multiple processes (parent processes) will not be processed. (with child processes), jobs, etc., so it is not sound for Linux systems.
c. Call the _exit function. Exit is called linux training by _exit and closes some linux-specific exit handles.
2. Abnormal termination

a. Call abort. This seems to be a special case of the second case, since it forms a SIGABRT signal.
b. The process receives a specific signal. This signal can be generated by the process itself (such as the abort function), or it can come from other processes or the kernel. For example: when a process attempts to access an out-of-bounds memory address or when the divisor is zero, the kernel will generate a signal to interrupt the process.
No matter which method is used to end the process, the same piece of code in the kernel will eventually be executed. This code closes all file descriptors opened by the process, the video memory occupied by private access, etc.
Let’s take a look at the exit and _exit functions
These two functions are in different header files: exit is in stdlib.h, _exit is in unistd.h

Their specific calling methods are as follows:
voidexit(int__status)
void_exit(int__status)
The status parameter is the exit status.
Let’s take a look at the following two pieces of code:

Picture 1

Picture 2


Picture 3

Picture 4
The code in Figure 1 lacks n, resulting in the sentence at the end of the test not being copied. This is because if printf does not add n, the information will not be copied immediately, and _exit will not force the output of the data in the buffer. , that is, the data that has not been written to the device and is still in the buffer caused by calls such as printf/fprintf will be discarded. The copy information will be lost during _exit, but not with exit. If there is n, copy it directly. At this time, there is no difference between exit/_exit
The different order in which the brother and sister processes are terminated will produce different results
1. The parent process terminates before the child process:
This situation is what we call an orphan process. When the parent process exits first, the system will let the init process take over the child process.
2. The child process terminates before the parent process, and the parent process does not call the wait function
In this case, the sub-process enters a zombie state and will remain so until the system is restarted. When the child process is in a zombie state Under Linux, it exits without saving. The kernel only saves some necessary information of the process for the parent process. At this time, the child process still occupies resources, and it also reduces the maximum number of processes that can be created by the system.
What are the zombie states?
A process that has been terminated long ago, but its parent process has not yet dealt with the aftermath (obtaining information about the terminated child process and releasing the resources it still occupies) is called a zombie process (zombie).
3. The child process terminates before the parent processExits without saving under Linux, but the parent process calls the wait function
At this time, the parent process will wait for the child process to end.
The above is the detailed content of How to end a process under Linux: Detailed explanation of normal and abnormal termination. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 Mastering Text Manipulation With the Sed Command
Mar 16, 2025 am 09:48 AM
Mastering Text Manipulation With the Sed Command
Mar 16, 2025 am 09:48 AM
The Linux command line interface provides a wealth of text processing tools, one of the most powerful tools is the sed command. sed is the abbreviation of Stream EDitor, a multi-functional tool that allows complex processing of text files and streams. What is Sed? sed is a non-interactive text editor that operates on pipeline inputs or text files. By providing directives, you can let it modify and process text in a file or stream. The most common use cases of sed include selecting text, replacing text, modifying original files, adding lines to text, or removing lines from text. It can be used from the command line in Bash and other command line shells. Sed command syntax sed
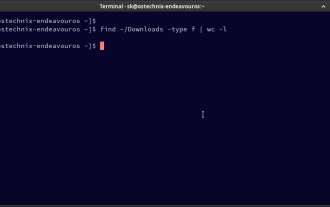 How To Count Files And Directories In Linux: A Beginner's Guide
Mar 19, 2025 am 10:48 AM
How To Count Files And Directories In Linux: A Beginner's Guide
Mar 19, 2025 am 10:48 AM
Efficiently Counting Files and Folders in Linux: A Comprehensive Guide Knowing how to quickly count files and directories in Linux is crucial for system administrators and anyone managing large datasets. This guide demonstrates using simple command-l
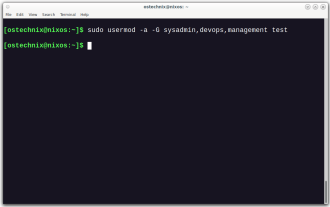 How To Add A User To Multiple Groups In Linux
Mar 18, 2025 am 11:44 AM
How To Add A User To Multiple Groups In Linux
Mar 18, 2025 am 11:44 AM
Efficiently managing user accounts and group memberships is crucial for Linux/Unix system administration. This ensures proper resource and data access control. This tutorial details how to add a user to multiple groups in Linux and Unix systems. We
 Locating Leviathan Files in Linux
Mar 13, 2025 pm 12:11 PM
Locating Leviathan Files in Linux
Mar 13, 2025 pm 12:11 PM
Introduction In the realm of Linux, where the command line is often the compass by which we navigate, the efficient management of disk space is crucial. Whether you’re sailing through personal projects or steering the ship o
 How To List Or Check All Installed Linux Kernels From Commandline
Mar 23, 2025 am 10:43 AM
How To List Or Check All Installed Linux Kernels From Commandline
Mar 23, 2025 am 10:43 AM
Linux Kernel is the core component of a GNU/Linux operating system. Developed by Linus Torvalds in 1991, it is a free, open-source, monolithic, modular, and multitasking Unix-like kernel. In Linux, it is possible to install multiple kernels on a sing
 How To Type Indian Rupee Symbol In Ubuntu Linux
Mar 22, 2025 am 10:39 AM
How To Type Indian Rupee Symbol In Ubuntu Linux
Mar 22, 2025 am 10:39 AM
This brief guide explains how to type Indian Rupee symbol in Linux operating systems. The other day, I wanted to type "Indian Rupee Symbol (₹)" in a word document. My keyboard has a rupee symbol on it, but I don't know how to type it. After
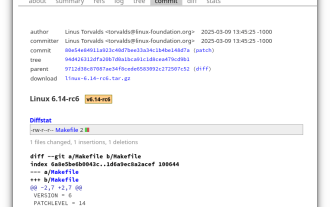 Linux Kernel 6.14 RC6 Released
Mar 24, 2025 am 10:21 AM
Linux Kernel 6.14 RC6 Released
Mar 24, 2025 am 10:21 AM
Linus Torvalds has released Linux Kernel 6.14 Release Candidate 6 (RC6), reporting no significant issues and keeping the release on track. The most notable change in this update addresses an AMD microcode signing issue, while the rest of the updates
 LocalSend - The Open-Source Airdrop Alternative For Secure File Sharing
Mar 24, 2025 am 09:20 AM
LocalSend - The Open-Source Airdrop Alternative For Secure File Sharing
Mar 24, 2025 am 09:20 AM
If you're familiar with AirDrop, you know it's a popular feature developed by Apple Inc. that enables seamless file transfer between supported Macintosh computers and iOS devices using Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. However, if you're using Linux and missing o



