 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 so cool! Old iPhone, iPad, and MacBook devices form a heterogeneous cluster and can run Llama 3
so cool! Old iPhone, iPad, and MacBook devices form a heterogeneous cluster and can run Llama 3
so cool! Old iPhone, iPad, and MacBook devices form a heterogeneous cluster and can run Llama 3
If you have idle equipment, maybe you can give it a try.
This time, the hardware device in your hand can also flex its muscles in the field of AI.
By combining iPhone, iPad, and Macbook, you can assemble a "heterogeneous cluster inference solution" and then run the Llama3 model smoothly.

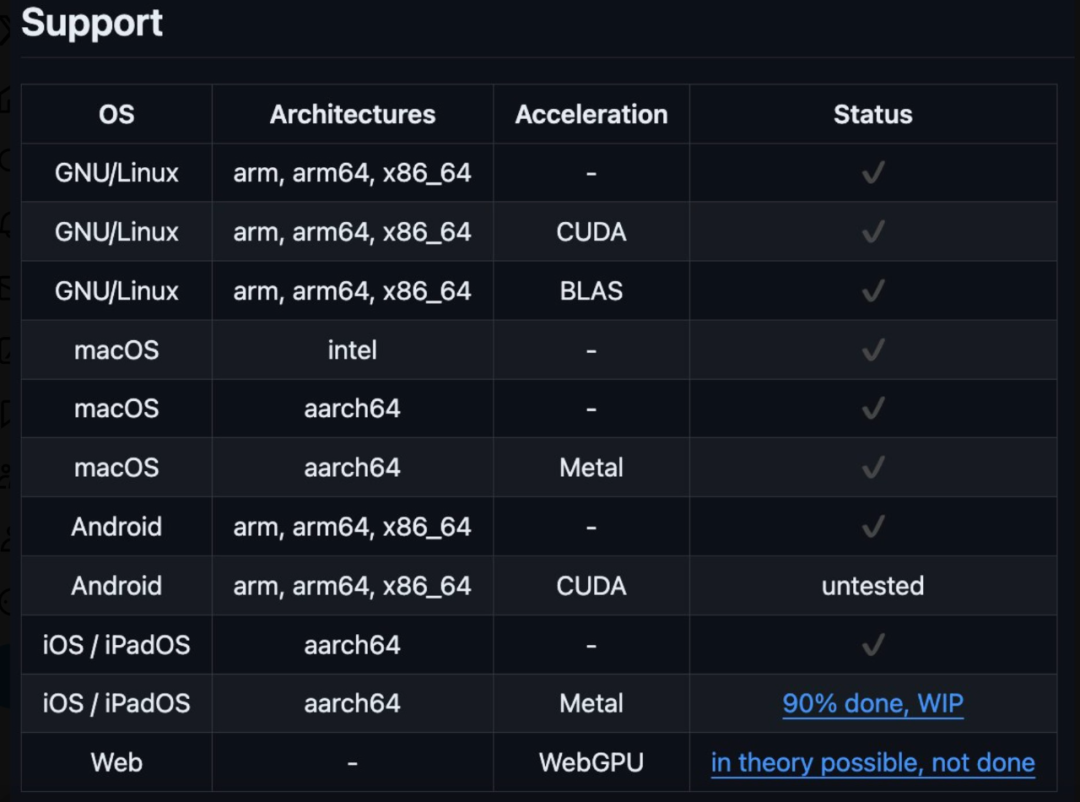
It is worth mentioning that this heterogeneous cluster can be a Windows system, Linux, or iOS system, and support for Android will be coming soon. The heterogeneous cluster is running.
 According to the project author @evilsocket, this heterogeneous cluster includes iPhone 15 Pro Max, iPad Pro, MacBook Pro (M1 Max), NVIDIA GeForce 3080, 2x NVIDIA Titan X Pascal. All code has been uploaded to GitHub. Seeing this, netizens expressed that this old man is indeed not simple.
According to the project author @evilsocket, this heterogeneous cluster includes iPhone 15 Pro Max, iPad Pro, MacBook Pro (M1 Max), NVIDIA GeForce 3080, 2x NVIDIA Titan X Pascal. All code has been uploaded to GitHub. Seeing this, netizens expressed that this old man is indeed not simple.
However, some netizens are beginning to worry about energy consumption. Regardless of speed, the electricity bill cannot be afforded. Moving data back and forth causes too much loss.
Project address: https://github.com/evilsocket/cake
The main idea of Cake is to shard transformer blocks to multiple devices to be able to run inference on models that typically do not fit into the GPU memory of a single device . Inference on consecutive transformer blocks on the same worker thread is done in batches to minimize delays caused by data transfer. 
cargo build --release
make ios
Use
to run the worker node:cake-cli --model /path/to/Meta-Llama-3-8B \ # model path, read below on how to optimize model size for workers --mode worker \# run as worker --name worker0 \ # worker name in topology file --topology topology.yml \# topology --address 0.0.0.0:10128 # bind address
cake-cli --model /path/to/Meta-Llama-3-8B \ --topology topology.yml
linux_server_1:host: 'linux_server.host:10128'description: 'NVIDIA Titan X Pascal (12GB)'layers:- 'model.layers.0-5'linux_server_2:host: 'linux_server2.host:10128'description: 'NVIDIA GeForce 3080 (10GB)'layers:- 'model.layers.6-16'iphone:host: 'iphone.host:10128'description: 'iPhone 15 Pro Max'layers:- 'model.layers.17'ipad:host: 'ipad.host:10128'description: 'iPad'layers:- 'model.layers.18-19'macbook:host: 'macbook.host:10128'description: 'M1 Max'layers: - 'model.layers.20-31'
cake-split-model --model-path path/to/Meta-Llama-3-8B \ # source model to split --topology path/to/topology.yml \# topology file --output output-folder-name
The above is the detailed content of so cool! Old iPhone, iPad, and MacBook devices form a heterogeneous cluster and can run Llama 3. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 The author of ControlNet has another hit! The whole process of generating a painting from a picture, earning 1.4k stars in two days
Jul 17, 2024 am 01:56 AM
The author of ControlNet has another hit! The whole process of generating a painting from a picture, earning 1.4k stars in two days
Jul 17, 2024 am 01:56 AM
It is also a Tusheng video, but PaintsUndo has taken a different route. ControlNet author LvminZhang started to live again! This time I aim at the field of painting. The new project PaintsUndo has received 1.4kstar (still rising crazily) not long after it was launched. Project address: https://github.com/lllyasviel/Paints-UNDO Through this project, the user inputs a static image, and PaintsUndo can automatically help you generate a video of the entire painting process, from line draft to finished product. follow. During the drawing process, the line changes are amazing. The final video result is very similar to the original image: Let’s take a look at a complete drawing.
 Topping the list of open source AI software engineers, UIUC's agent-less solution easily solves SWE-bench real programming problems
Jul 17, 2024 pm 10:02 PM
Topping the list of open source AI software engineers, UIUC's agent-less solution easily solves SWE-bench real programming problems
Jul 17, 2024 pm 10:02 PM
The AIxiv column is a column where this site publishes academic and technical content. In the past few years, the AIxiv column of this site has received more than 2,000 reports, covering top laboratories from major universities and companies around the world, effectively promoting academic exchanges and dissemination. If you have excellent work that you want to share, please feel free to contribute or contact us for reporting. Submission email: liyazhou@jiqizhixin.com; zhaoyunfeng@jiqizhixin.com The authors of this paper are all from the team of teacher Zhang Lingming at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign (UIUC), including: Steven Code repair; Deng Yinlin, fourth-year doctoral student, researcher
 From RLHF to DPO to TDPO, large model alignment algorithms are already 'token-level'
Jun 24, 2024 pm 03:04 PM
From RLHF to DPO to TDPO, large model alignment algorithms are already 'token-level'
Jun 24, 2024 pm 03:04 PM
The AIxiv column is a column where this site publishes academic and technical content. In the past few years, the AIxiv column of this site has received more than 2,000 reports, covering top laboratories from major universities and companies around the world, effectively promoting academic exchanges and dissemination. If you have excellent work that you want to share, please feel free to contribute or contact us for reporting. Submission email: liyazhou@jiqizhixin.com; zhaoyunfeng@jiqizhixin.com In the development process of artificial intelligence, the control and guidance of large language models (LLM) has always been one of the core challenges, aiming to ensure that these models are both powerful and safe serve human society. Early efforts focused on reinforcement learning methods through human feedback (RL
 Posthumous work of the OpenAI Super Alignment Team: Two large models play a game, and the output becomes more understandable
Jul 19, 2024 am 01:29 AM
Posthumous work of the OpenAI Super Alignment Team: Two large models play a game, and the output becomes more understandable
Jul 19, 2024 am 01:29 AM
If the answer given by the AI model is incomprehensible at all, would you dare to use it? As machine learning systems are used in more important areas, it becomes increasingly important to demonstrate why we can trust their output, and when not to trust them. One possible way to gain trust in the output of a complex system is to require the system to produce an interpretation of its output that is readable to a human or another trusted system, that is, fully understandable to the point that any possible errors can be found. For example, to build trust in the judicial system, we require courts to provide clear and readable written opinions that explain and support their decisions. For large language models, we can also adopt a similar approach. However, when taking this approach, ensure that the language model generates
 A significant breakthrough in the Riemann Hypothesis! Tao Zhexuan strongly recommends new papers from MIT and Oxford, and the 37-year-old Fields Medal winner participated
Aug 05, 2024 pm 03:32 PM
A significant breakthrough in the Riemann Hypothesis! Tao Zhexuan strongly recommends new papers from MIT and Oxford, and the 37-year-old Fields Medal winner participated
Aug 05, 2024 pm 03:32 PM
Recently, the Riemann Hypothesis, known as one of the seven major problems of the millennium, has achieved a new breakthrough. The Riemann Hypothesis is a very important unsolved problem in mathematics, related to the precise properties of the distribution of prime numbers (primes are those numbers that are only divisible by 1 and themselves, and they play a fundamental role in number theory). In today's mathematical literature, there are more than a thousand mathematical propositions based on the establishment of the Riemann Hypothesis (or its generalized form). In other words, once the Riemann Hypothesis and its generalized form are proven, these more than a thousand propositions will be established as theorems, which will have a profound impact on the field of mathematics; and if the Riemann Hypothesis is proven wrong, then among these propositions part of it will also lose its effectiveness. New breakthrough comes from MIT mathematics professor Larry Guth and Oxford University
 arXiv papers can be posted as 'barrage', Stanford alphaXiv discussion platform is online, LeCun likes it
Aug 01, 2024 pm 05:18 PM
arXiv papers can be posted as 'barrage', Stanford alphaXiv discussion platform is online, LeCun likes it
Aug 01, 2024 pm 05:18 PM
cheers! What is it like when a paper discussion is down to words? Recently, students at Stanford University created alphaXiv, an open discussion forum for arXiv papers that allows questions and comments to be posted directly on any arXiv paper. Website link: https://alphaxiv.org/ In fact, there is no need to visit this website specifically. Just change arXiv in any URL to alphaXiv to directly open the corresponding paper on the alphaXiv forum: you can accurately locate the paragraphs in the paper, Sentence: In the discussion area on the right, users can post questions to ask the author about the ideas and details of the paper. For example, they can also comment on the content of the paper, such as: "Given to
 The first Mamba-based MLLM is here! Model weights, training code, etc. have all been open source
Jul 17, 2024 am 02:46 AM
The first Mamba-based MLLM is here! Model weights, training code, etc. have all been open source
Jul 17, 2024 am 02:46 AM
The AIxiv column is a column where this site publishes academic and technical content. In the past few years, the AIxiv column of this site has received more than 2,000 reports, covering top laboratories from major universities and companies around the world, effectively promoting academic exchanges and dissemination. If you have excellent work that you want to share, please feel free to contribute or contact us for reporting. Submission email: liyazhou@jiqizhixin.com; zhaoyunfeng@jiqizhixin.com. Introduction In recent years, the application of multimodal large language models (MLLM) in various fields has achieved remarkable success. However, as the basic model for many downstream tasks, current MLLM consists of the well-known Transformer network, which
 Axiomatic training allows LLM to learn causal reasoning: the 67 million parameter model is comparable to the trillion parameter level GPT-4
Jul 17, 2024 am 10:14 AM
Axiomatic training allows LLM to learn causal reasoning: the 67 million parameter model is comparable to the trillion parameter level GPT-4
Jul 17, 2024 am 10:14 AM
Show the causal chain to LLM and it learns the axioms. AI is already helping mathematicians and scientists conduct research. For example, the famous mathematician Terence Tao has repeatedly shared his research and exploration experience with the help of AI tools such as GPT. For AI to compete in these fields, strong and reliable causal reasoning capabilities are essential. The research to be introduced in this article found that a Transformer model trained on the demonstration of the causal transitivity axiom on small graphs can generalize to the transitive axiom on large graphs. In other words, if the Transformer learns to perform simple causal reasoning, it may be used for more complex causal reasoning. The axiomatic training framework proposed by the team is a new paradigm for learning causal reasoning based on passive data, with only demonstrations





