 System Tutorial
System Tutorial
 Windows Series
Windows Series
 How to Access Your Linux (WSL) Files in Windows 10 and Windows 11
How to Access Your Linux (WSL) Files in Windows 10 and Windows 11
How to Access Your Linux (WSL) Files in Windows 10 and Windows 11
Windows 10's May 2019 Update introduced an easy, safe, and officially supported way to access and work with your Linux files from within File Explorer and other applications. Here's how to get at your Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) files.
Unlike previous methods, this is a safe way to work with Linux files! Windows does some magic in the background, making it possible to edit your Linux files from Windows applications without causing file permission issues. You still shouldn't modify the underlying files at their real location on your system.
It doesn't matter if you use WSL1 or WSL2. These commands all function exactly the same way.
Open WSL Files from Terminal
There are two ways to access your Linux files. First, the easy one. From within the Windows Subsystem for Linux environment you want to browse, run the following command:
explorer.exe .
This will launch File Explorer showing the current Linux directory—you can browse the Linux environment's file system from there.
 Open the WSL Directory in File Explorer Directly
Open the WSL Directory in File Explorer Directly
You can also access them directly at the wsl$ path. In File Explorer or any other Windows application that can browse files, navigate to the following path: wsl$ path. In File Explorer or any other Windows application that can browse files, navigate to the following path:
wsl$
You'll see the folders for all your installed Linux distributions, which are exposed as if they were network shares. For example, Ubuntu 22.04 is usually available at wsl$Ubuntu-22.04
wsl$Ubuntu-22.04. 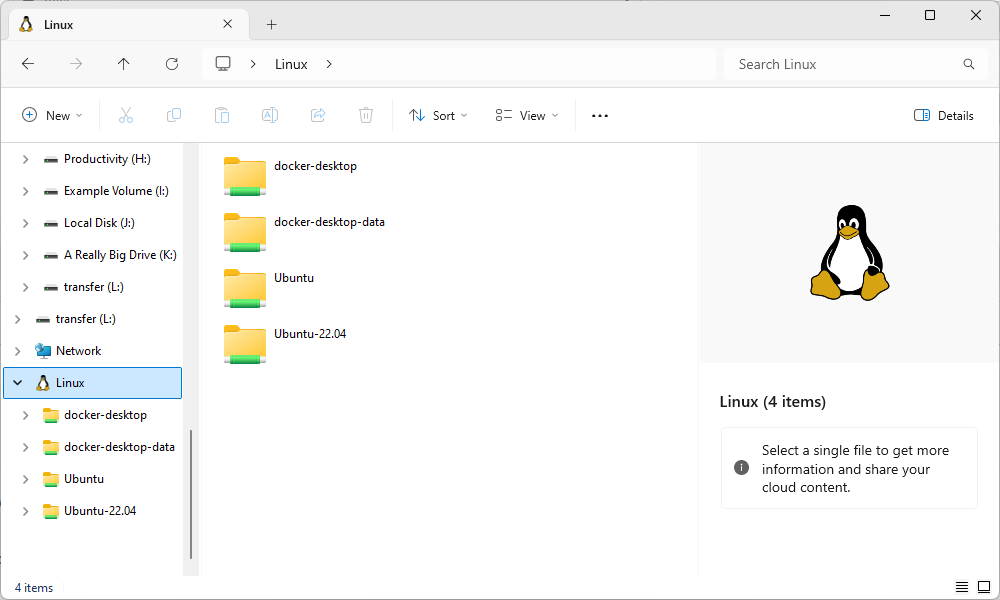
Feel free to create a shortcut to this folder—for example, you could drag it to the Quick Access section in File Explorer's sidebar.
🎜 🎜 Again, you can modify these files normally as if they were any other type of file on your system. Modify files with Windows tools (Notepad even supports Unix line endings!), create new files in the Linux folders, delete files, or do anything else you like. Windows will ensure nothing goes wrong and the file's permissions are updated properly. 🎜The above is the detailed content of How to Access Your Linux (WSL) Files in Windows 10 and Windows 11. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1664
1664
 14
14
 1421
1421
 52
52
 1315
1315
 25
25
 1266
1266
 29
29
 1239
1239
 24
24
 Windows kb5054979 update information Update content list
Apr 15, 2025 pm 05:36 PM
Windows kb5054979 update information Update content list
Apr 15, 2025 pm 05:36 PM
KB5054979 is a cumulative security update released on March 27, 2025, for Windows 11 version 24H2. It targets .NET Framework versions 3.5 and 4.8.1, enhancing security and overall stability. Notably, the update addresses an issue with file and directory operations on UNC shares using System.IO APIs. Two installation methods are provided: one through Windows Settings by checking for updates under Windows Update, and the other via a manual download from the Microsoft Update Catalog.
 Nanoleaf Wants to Change How You Charge Your Tech
Apr 17, 2025 am 01:03 AM
Nanoleaf Wants to Change How You Charge Your Tech
Apr 17, 2025 am 01:03 AM
Nanoleaf's Pegboard Desk Dock: A Stylish and Functional Desk Organizer Tired of the same old charging setup? Nanoleaf's new Pegboard Desk Dock offers a stylish and functional alternative. This multifunctional desk accessory boasts 32 full-color RGB
 Got an AMD CPU and Aren't Using PBO? You're Missing Out
Apr 12, 2025 pm 09:02 PM
Got an AMD CPU and Aren't Using PBO? You're Missing Out
Apr 12, 2025 pm 09:02 PM
Unlocking Ryzen's Potential: A Simple Guide to Precision Boost Overdrive (PBO) Overclocking your new PC can seem daunting. While performance gains might feel elusive, leaving potential untapped is even less appealing. Fortunately, AMD Ryzen processo
 ASUS' ROG Zephyrus G14 OLED Gaming Laptop Is $300 Off
Apr 16, 2025 am 03:01 AM
ASUS' ROG Zephyrus G14 OLED Gaming Laptop Is $300 Off
Apr 16, 2025 am 03:01 AM
ASUS ROG Zephyrus G14 Esports Laptop Special Offer! Buy ASUS ROG Zephyrus G14 Esports Laptop now and enjoy a $300 offer! Original price is $1999, current price is only $1699! Enjoy immersive gaming experience anytime, anywhere, or use it as a reliable portable workstation. Best Buy currently offers offers on this 2024 14-inch ASUS ROG Zephyrus G14 e-sports laptop. Its powerful configuration and performance are impressive. This ASUS ROG Zephyrus G14 e-sports laptop costs 16 on Best Buy
 How to Use Windows 11 as a Bluetooth Audio Receiver
Apr 15, 2025 am 03:01 AM
How to Use Windows 11 as a Bluetooth Audio Receiver
Apr 15, 2025 am 03:01 AM
Turn your Windows 11 PC into a Bluetooth speaker and enjoy your favorite music from your phone! This guide shows you how to easily connect your iPhone or Android device to your computer for audio playback. Step 1: Pair Your Bluetooth Device First, pa
 5 Hidden Windows Features You Should Be Using
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:57 AM
5 Hidden Windows Features You Should Be Using
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:57 AM
Unlock Hidden Windows Features for a Smoother Experience! Discover surprisingly useful Windows functionalities that can significantly enhance your computing experience. Even seasoned Windows users might find some new tricks here. Dynamic Lock: Auto
 Microsoft Might Finally Fix Windows 11's Start Menu
Apr 10, 2025 pm 12:07 PM
Microsoft Might Finally Fix Windows 11's Start Menu
Apr 10, 2025 pm 12:07 PM
Windows 11's Start Menu Gets a Much-Needed Overhaul Microsoft's Windows 11 Start menu, initially criticized for its less-than-intuitive app access, is undergoing a significant redesign. Early testing reveals a vastly improved user experience. The up
 You Can Get The Razer Basilisk V3 Pro Mouse for 39% off
Apr 09, 2025 am 03:01 AM
You Can Get The Razer Basilisk V3 Pro Mouse for 39% off
Apr 09, 2025 am 03:01 AM
##### Razer Basilisk V3 Pro: High-performance wireless gaming mouse The Razer Basilisk V3 Pro is a high-performance wireless gaming mouse with high customization (11 programmable buttons, Chroma RGB) and versatile connectivity. It has excellent sensors, durable switches and extra long battery life. If you are a gamer looking for a high-quality wireless mouse and need excellent customization options, now is a great time to buy the Razer Basilisk V3 Pro. The promotion cuts prices by 39% and has limited promotion periods. This mouse is larger, 5.11 inches long and 2 inches wide



 Open the WSL Directory in File Explorer Directly
Open the WSL Directory in File Explorer Directly 