 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 Changing the rules of the game for future collider experiments, the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Peking University develop AI-driven injection source identification technology
Changing the rules of the game for future collider experiments, the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Peking University develop AI-driven injection source identification technology
Changing the rules of the game for future collider experiments, the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Peking University develop AI-driven injection source identification technology

Editor|Ziluo
Quarks and gluons are elementary particles in the standard model of particle physics. Unlike electrons or photons, quarks and gluons cannot move freely in space and time and can only Can be bound into composite particles such as protons or neutrons.
The high-energy quarks or gluons produced in the collider experiment will be converted into a large number of final particles through complex interactions, which will be ejected at a smaller angle along the direction of motion of the original quarks or gluons. , this phenomenon is called injection.
Recently, Ruan Manqi’s team from the Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Zhou Chen’s team from Peking University, and researcher Qu Huilin from CERN have proposed a jet source identification technology. This technology can significantly enhance the scientific discovery capabilities of high-energy collider experiments.
Combining the original high-performance particle flow reconstruction algorithm Arbor and the advanced artificial intelligence technology ParticleNet, the research team developed an efficient injection source identification technology. By capturing the tiny differences between different types of jets, this technology can simultaneously and efficiently distinguish eleven different jets produced by five types of quarks (up, down, strange, charm, and bottom), five types of antiquarks, and gluons. .
This technology can help scientists accurately measure the interactions between different particles, quarks and gluons, and capture some extremely weak Higgs particle decay signals. This technology can improve the accuracy of key physical measurements on future colliders by an order of magnitude, significantly expanding the scientific discovery capabilities of large scientific devices.
The reviewer evaluated it as "the world's top identification performance", "changed the rules of the game", and "created a new vision for accurate measurement in future collider experiments".
The study was titled "Jet-Origin Identification and Its Application at an Electron-Positron Higgs Factory" and was published in "Physical Review Letters" on May 31, 2024.

Injections can be produced in large quantities in high-energy collision experiments. Accurately identify the origin of the injection, that is, the source of the injection. What kind of quark or gluon is extremely important for discovering and understanding the physical laws behind the collider case. However, the jets produced by different quarks and gluons are very similar in configuration, and it is very difficult to accurately identify the origin of the jets.

Identification of jet origins
Background
In order to enhance the scientific discovery capabilities of high-energy collider experiments, researchers have proposed the concept of jet origin identification and divided jets into the following types :
- Five kinds of quarks: a, b, s, u, d
- Five kinds of antiquarks: a¯, b¯, s¯, u¯, d¯
- gluons
Importance
Successful jet source identification is crucial for experimental particle physics at the energy frontier, such as the Large Hadron Collider, as it can effectively reduce the large background in quantum chromodynamics (QCD) processes.
Methods
Researchers used GEANT4-based simulations (called full simulations) to implement the concept of injection origin identification in physics events at the Electron-Positron Higgs Factory, the future The highest priority for the collider project. Researchers have developed software tools such as Arbor and ParticleNet for particle flow event reconstruction and injection source identification.
Performance
The study demonstrates jet origin discrimination performance using an 11-dimensional confusion matrix (M11), which demonstrates the performance of jet "flavor" markers and jet charge measurements.


Terbitkan had atas untuk tujuh proses ini, antara 10^−3 hingga 10^−4. Dalam Model Standard, nisbah cawangan yang diramalkan untuk proses H → ss¯ ialah 2.3 × 10^−4, dan had atas terbitan adalah bersamaan dengan 3 kali ramalan Model Standard. Nisbah percabangan H → uu¯ dan dd¯ dijangka kurang daripada 10^−6, manakala nisbah percabangan proses FCNC di atas dijangka kurang daripada 10^−7 berdasarkan sumbangan gelung.

Teknologi ini membekalkan para saintis dengan alat baharu yang berkuasa untuk penerokaan saintifik pada masa hadapan, dan juga membuktikan bahawa maklumat kompleks yang terkandung dalam proses penjanaan suntikan boleh difahami dan diproses oleh penggunaan algoritma kecerdasan buatan yang canggih.
Pada masa hadapan, pasukan penyelidik saintifik merancang untuk mengkaji lebih lanjut aplikasi teknologi kecerdasan buatan dalam isu saintifik yang lebih luas dan mendalam.
Pautan kertas: https://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevLett.132.221802
Kandungan rujukan:
https://phys.org/news/2024-powered-jetai -identification-technology.html
https://www.ccnta.cn/article/17151.html
The above is the detailed content of Changing the rules of the game for future collider experiments, the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Peking University develop AI-driven injection source identification technology. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1664
1664
 14
14
 1423
1423
 52
52
 1317
1317
 25
25
 1268
1268
 29
29
 1242
1242
 24
24
 Bytedance Cutting launches SVIP super membership: 499 yuan for continuous annual subscription, providing a variety of AI functions
Jun 28, 2024 am 03:51 AM
Bytedance Cutting launches SVIP super membership: 499 yuan for continuous annual subscription, providing a variety of AI functions
Jun 28, 2024 am 03:51 AM
This site reported on June 27 that Jianying is a video editing software developed by FaceMeng Technology, a subsidiary of ByteDance. It relies on the Douyin platform and basically produces short video content for users of the platform. It is compatible with iOS, Android, and Windows. , MacOS and other operating systems. Jianying officially announced the upgrade of its membership system and launched a new SVIP, which includes a variety of AI black technologies, such as intelligent translation, intelligent highlighting, intelligent packaging, digital human synthesis, etc. In terms of price, the monthly fee for clipping SVIP is 79 yuan, the annual fee is 599 yuan (note on this site: equivalent to 49.9 yuan per month), the continuous monthly subscription is 59 yuan per month, and the continuous annual subscription is 499 yuan per year (equivalent to 41.6 yuan per month) . In addition, the cut official also stated that in order to improve the user experience, those who have subscribed to the original VIP
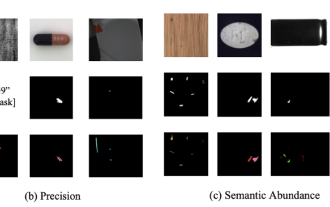 Breaking through the boundaries of traditional defect detection, 'Defect Spectrum' achieves ultra-high-precision and rich semantic industrial defect detection for the first time.
Jul 26, 2024 pm 05:38 PM
Breaking through the boundaries of traditional defect detection, 'Defect Spectrum' achieves ultra-high-precision and rich semantic industrial defect detection for the first time.
Jul 26, 2024 pm 05:38 PM
In modern manufacturing, accurate defect detection is not only the key to ensuring product quality, but also the core of improving production efficiency. However, existing defect detection datasets often lack the accuracy and semantic richness required for practical applications, resulting in models unable to identify specific defect categories or locations. In order to solve this problem, a top research team composed of Hong Kong University of Science and Technology Guangzhou and Simou Technology innovatively developed the "DefectSpectrum" data set, which provides detailed and semantically rich large-scale annotation of industrial defects. As shown in Table 1, compared with other industrial data sets, the "DefectSpectrum" data set provides the most defect annotations (5438 defect samples) and the most detailed defect classification (125 defect categories
 Training with millions of crystal data to solve the crystallographic phase problem, the deep learning method PhAI is published in Science
Aug 08, 2024 pm 09:22 PM
Training with millions of crystal data to solve the crystallographic phase problem, the deep learning method PhAI is published in Science
Aug 08, 2024 pm 09:22 PM
Editor |KX To this day, the structural detail and precision determined by crystallography, from simple metals to large membrane proteins, are unmatched by any other method. However, the biggest challenge, the so-called phase problem, remains retrieving phase information from experimentally determined amplitudes. Researchers at the University of Copenhagen in Denmark have developed a deep learning method called PhAI to solve crystal phase problems. A deep learning neural network trained using millions of artificial crystal structures and their corresponding synthetic diffraction data can generate accurate electron density maps. The study shows that this deep learning-based ab initio structural solution method can solve the phase problem at a resolution of only 2 Angstroms, which is equivalent to only 10% to 20% of the data available at atomic resolution, while traditional ab initio Calculation
 NVIDIA dialogue model ChatQA has evolved to version 2.0, with the context length mentioned at 128K
Jul 26, 2024 am 08:40 AM
NVIDIA dialogue model ChatQA has evolved to version 2.0, with the context length mentioned at 128K
Jul 26, 2024 am 08:40 AM
The open LLM community is an era when a hundred flowers bloom and compete. You can see Llama-3-70B-Instruct, QWen2-72B-Instruct, Nemotron-4-340B-Instruct, Mixtral-8x22BInstruct-v0.1 and many other excellent performers. Model. However, compared with proprietary large models represented by GPT-4-Turbo, open models still have significant gaps in many fields. In addition to general models, some open models that specialize in key areas have been developed, such as DeepSeek-Coder-V2 for programming and mathematics, and InternVL for visual-language tasks.
 Google AI won the IMO Mathematical Olympiad silver medal, the mathematical reasoning model AlphaProof was launched, and reinforcement learning is so back
Jul 26, 2024 pm 02:40 PM
Google AI won the IMO Mathematical Olympiad silver medal, the mathematical reasoning model AlphaProof was launched, and reinforcement learning is so back
Jul 26, 2024 pm 02:40 PM
For AI, Mathematical Olympiad is no longer a problem. On Thursday, Google DeepMind's artificial intelligence completed a feat: using AI to solve the real question of this year's International Mathematical Olympiad IMO, and it was just one step away from winning the gold medal. The IMO competition that just ended last week had six questions involving algebra, combinatorics, geometry and number theory. The hybrid AI system proposed by Google got four questions right and scored 28 points, reaching the silver medal level. Earlier this month, UCLA tenured professor Terence Tao had just promoted the AI Mathematical Olympiad (AIMO Progress Award) with a million-dollar prize. Unexpectedly, the level of AI problem solving had improved to this level before July. Do the questions simultaneously on IMO. The most difficult thing to do correctly is IMO, which has the longest history, the largest scale, and the most negative
 PRO | Why are large models based on MoE more worthy of attention?
Aug 07, 2024 pm 07:08 PM
PRO | Why are large models based on MoE more worthy of attention?
Aug 07, 2024 pm 07:08 PM
In 2023, almost every field of AI is evolving at an unprecedented speed. At the same time, AI is constantly pushing the technological boundaries of key tracks such as embodied intelligence and autonomous driving. Under the multi-modal trend, will the situation of Transformer as the mainstream architecture of AI large models be shaken? Why has exploring large models based on MoE (Mixed of Experts) architecture become a new trend in the industry? Can Large Vision Models (LVM) become a new breakthrough in general vision? ...From the 2023 PRO member newsletter of this site released in the past six months, we have selected 10 special interpretations that provide in-depth analysis of technological trends and industrial changes in the above fields to help you achieve your goals in the new year. be prepared. This interpretation comes from Week50 2023
 To provide a new scientific and complex question answering benchmark and evaluation system for large models, UNSW, Argonne, University of Chicago and other institutions jointly launched the SciQAG framework
Jul 25, 2024 am 06:42 AM
To provide a new scientific and complex question answering benchmark and evaluation system for large models, UNSW, Argonne, University of Chicago and other institutions jointly launched the SciQAG framework
Jul 25, 2024 am 06:42 AM
Editor |ScienceAI Question Answering (QA) data set plays a vital role in promoting natural language processing (NLP) research. High-quality QA data sets can not only be used to fine-tune models, but also effectively evaluate the capabilities of large language models (LLM), especially the ability to understand and reason about scientific knowledge. Although there are currently many scientific QA data sets covering medicine, chemistry, biology and other fields, these data sets still have some shortcomings. First, the data form is relatively simple, most of which are multiple-choice questions. They are easy to evaluate, but limit the model's answer selection range and cannot fully test the model's ability to answer scientific questions. In contrast, open-ended Q&A
 The accuracy rate reaches 60.8%. Zhejiang University's chemical retrosynthesis prediction model based on Transformer was published in the Nature sub-journal
Aug 06, 2024 pm 07:34 PM
The accuracy rate reaches 60.8%. Zhejiang University's chemical retrosynthesis prediction model based on Transformer was published in the Nature sub-journal
Aug 06, 2024 pm 07:34 PM
Editor | KX Retrosynthesis is a critical task in drug discovery and organic synthesis, and AI is increasingly used to speed up the process. Existing AI methods have unsatisfactory performance and limited diversity. In practice, chemical reactions often cause local molecular changes, with considerable overlap between reactants and products. Inspired by this, Hou Tingjun's team at Zhejiang University proposed to redefine single-step retrosynthetic prediction as a molecular string editing task, iteratively refining the target molecular string to generate precursor compounds. And an editing-based retrosynthetic model EditRetro is proposed, which can achieve high-quality and diverse predictions. Extensive experiments show that the model achieves excellent performance on the standard benchmark data set USPTO-50 K, with a top-1 accuracy of 60.8%.



