 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 After Li Feifei's 'spatial intelligence”, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Zhiyuan University, Peking University, etc. proposed the large spatial model SpatialBot
After Li Feifei's 'spatial intelligence”, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Zhiyuan University, Peking University, etc. proposed the large spatial model SpatialBot
After Li Feifei's 'spatial intelligence”, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Zhiyuan University, Peking University, etc. proposed the large spatial model SpatialBot

The AIxiv column is a column where this site publishes academic and technical content. In the past few years, the AIxiv column of this site has received more than 2,000 reports, covering top laboratories from major universities and companies around the world, effectively promoting academic exchanges and dissemination. If you have excellent work that you want to share, please feel free to contribute or contact us for reporting. Submission email: liyazhou@jiqizhixin.com; zhaoyunfeng@jiqizhixin.com

Paper title: SpatialBot: Precise Depth Understanding with Vision Language Models Paper link: https://arxiv.org/abs/2406.13642 Project homepage: https://github. com/BAAI-DCAI/SpatialBot
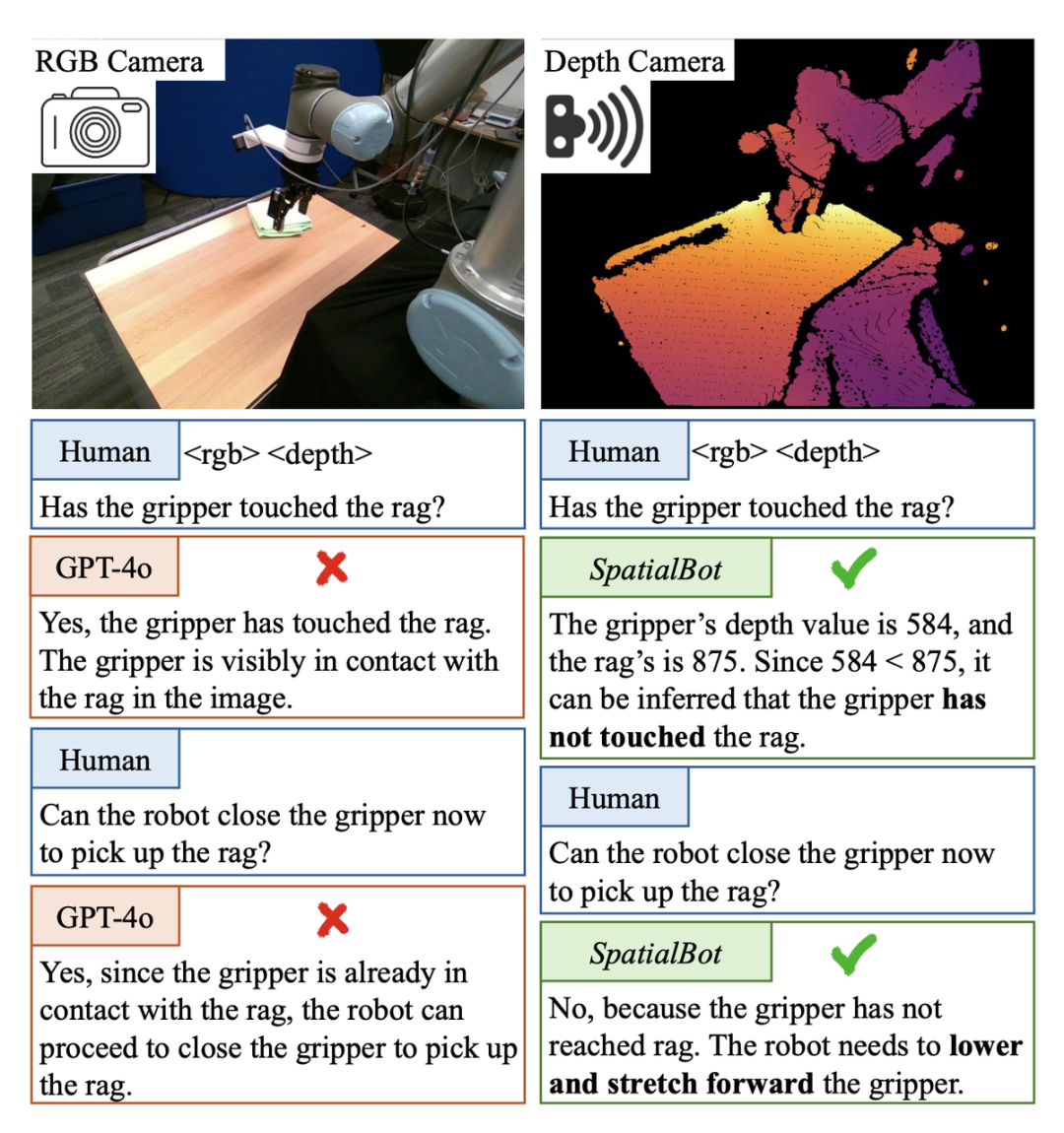
 2. Grab the middle teacup
2. Grab the middle teacup 
Existing models cannot directly understand the depth map input. For example, the image encoder CLIP/SigLIP is trained on RGB images without ever seeing depth maps. Most of the existing large model data sets can be analyzed and answered using only RGB. Therefore, if the existing data is simply changed to RGBD input, the model will not actively index knowledge into the depth map. Specially designed tasks and QA are required to guide the model to understand the depth map and use depth information.

低レベルでは、深度マップを理解するようにモデルをガイドし、深度マップから直接情報をガイドします。
-
中レベルでは、モデルに深度を RGB に合わせます。 高レベルでの複数の深度の設計関連タスクについては、50,000 個のデータに注釈が付けられ、モデルが深度マップの理解に基づいて深度情報を使用してタスクを完了できるようにします。タスクには、空間的な位置関係、オブジェクトのサイズ、オブジェクトが接触しているかどうか、ロボット シーンの理解などが含まれます。 - What dospatialbot contains? でのダイアログの例
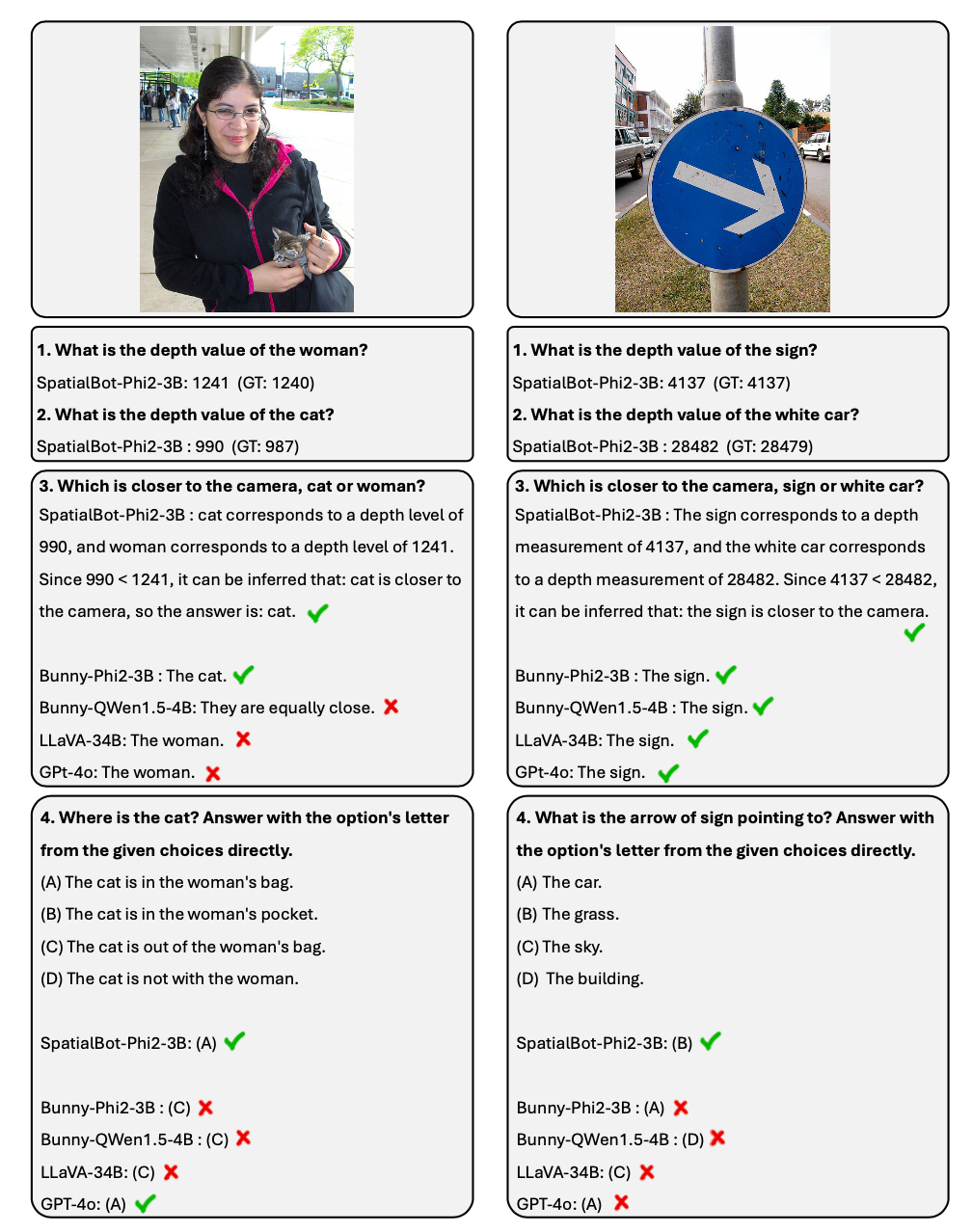
1. モデルの深度マップを入力する: 屋内と屋外のタスクを考慮するために、統合された深度マップのエンコード方法が必要です。屋内のグラブやナビゲーションのタスクでは、ミリメートルレベルの精度が必要な場合があります。屋外のシーンでは、それほど正確である必要はありませんが、100 メートルを超える深度値の範囲が必要な場合があります。 Ordinal Encoding は従来のビジョン タスクのエンコードに使用されますが、Ordinal の値を加算または減算することはできません。すべての深度情報を可能な限り保存するために、SpatialBot は、1 mm から 131 m までの範囲のミリメートル単位の深度を直接使用し、uint24 または 3 チャネル uint8 を使用してこれらの値を保存します。
1. SpatialBot は 3B から 8B までの複数のベース LLM に基づいています。 SpatialQA で空間知識を学習することにより、SpatialBot は、一般的に使用される MLLM データセット (MME、MMBench など) でのパフォーマンスの大幅な向上も実証します。
データをマークするにはどうすればよいですか?
- 空間関係の理解と推論;
- ロボット シーンの理解: Open X 実施形態のシーン、含まれるオブジェクト、および考えられるタスクと、この記事で収集したロボット データを説明し、オブジェクトと境界ボックスに手動でラベルを付けます。ロボットの。

The above is the detailed content of After Li Feifei's 'spatial intelligence”, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Zhiyuan University, Peking University, etc. proposed the large spatial model SpatialBot. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1664
1664
 14
14
 1421
1421
 52
52
 1315
1315
 25
25
 1266
1266
 29
29
 1239
1239
 24
24
 DeepMind robot plays table tennis, and its forehand and backhand slip into the air, completely defeating human beginners
Aug 09, 2024 pm 04:01 PM
DeepMind robot plays table tennis, and its forehand and backhand slip into the air, completely defeating human beginners
Aug 09, 2024 pm 04:01 PM
But maybe he can’t defeat the old man in the park? The Paris Olympic Games are in full swing, and table tennis has attracted much attention. At the same time, robots have also made new breakthroughs in playing table tennis. Just now, DeepMind proposed the first learning robot agent that can reach the level of human amateur players in competitive table tennis. Paper address: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2408.03906 How good is the DeepMind robot at playing table tennis? Probably on par with human amateur players: both forehand and backhand: the opponent uses a variety of playing styles, and the robot can also withstand: receiving serves with different spins: However, the intensity of the game does not seem to be as intense as the old man in the park. For robots, table tennis
 The first mechanical claw! Yuanluobao appeared at the 2024 World Robot Conference and released the first chess robot that can enter the home
Aug 21, 2024 pm 07:33 PM
The first mechanical claw! Yuanluobao appeared at the 2024 World Robot Conference and released the first chess robot that can enter the home
Aug 21, 2024 pm 07:33 PM
On August 21, the 2024 World Robot Conference was grandly held in Beijing. SenseTime's home robot brand "Yuanluobot SenseRobot" has unveiled its entire family of products, and recently released the Yuanluobot AI chess-playing robot - Chess Professional Edition (hereinafter referred to as "Yuanluobot SenseRobot"), becoming the world's first A chess robot for the home. As the third chess-playing robot product of Yuanluobo, the new Guoxiang robot has undergone a large number of special technical upgrades and innovations in AI and engineering machinery. For the first time, it has realized the ability to pick up three-dimensional chess pieces through mechanical claws on a home robot, and perform human-machine Functions such as chess playing, everyone playing chess, notation review, etc.
 Claude has become lazy too! Netizen: Learn to give yourself a holiday
Sep 02, 2024 pm 01:56 PM
Claude has become lazy too! Netizen: Learn to give yourself a holiday
Sep 02, 2024 pm 01:56 PM
The start of school is about to begin, and it’s not just the students who are about to start the new semester who should take care of themselves, but also the large AI models. Some time ago, Reddit was filled with netizens complaining that Claude was getting lazy. "Its level has dropped a lot, it often pauses, and even the output becomes very short. In the first week of release, it could translate a full 4-page document at once, but now it can't even output half a page!" https:// www.reddit.com/r/ClaudeAI/comments/1by8rw8/something_just_feels_wrong_with_claude_in_the/ in a post titled "Totally disappointed with Claude", full of
 At the World Robot Conference, this domestic robot carrying 'the hope of future elderly care' was surrounded
Aug 22, 2024 pm 10:35 PM
At the World Robot Conference, this domestic robot carrying 'the hope of future elderly care' was surrounded
Aug 22, 2024 pm 10:35 PM
At the World Robot Conference being held in Beijing, the display of humanoid robots has become the absolute focus of the scene. At the Stardust Intelligent booth, the AI robot assistant S1 performed three major performances of dulcimer, martial arts, and calligraphy in one exhibition area, capable of both literary and martial arts. , attracted a large number of professional audiences and media. The elegant playing on the elastic strings allows the S1 to demonstrate fine operation and absolute control with speed, strength and precision. CCTV News conducted a special report on the imitation learning and intelligent control behind "Calligraphy". Company founder Lai Jie explained that behind the silky movements, the hardware side pursues the best force control and the most human-like body indicators (speed, load) etc.), but on the AI side, the real movement data of people is collected, allowing the robot to become stronger when it encounters a strong situation and learn to evolve quickly. And agile
 ACL 2024 Awards Announced: One of the Best Papers on Oracle Deciphering by HuaTech, GloVe Time Test Award
Aug 15, 2024 pm 04:37 PM
ACL 2024 Awards Announced: One of the Best Papers on Oracle Deciphering by HuaTech, GloVe Time Test Award
Aug 15, 2024 pm 04:37 PM
At this ACL conference, contributors have gained a lot. The six-day ACL2024 is being held in Bangkok, Thailand. ACL is the top international conference in the field of computational linguistics and natural language processing. It is organized by the International Association for Computational Linguistics and is held annually. ACL has always ranked first in academic influence in the field of NLP, and it is also a CCF-A recommended conference. This year's ACL conference is the 62nd and has received more than 400 cutting-edge works in the field of NLP. Yesterday afternoon, the conference announced the best paper and other awards. This time, there are 7 Best Paper Awards (two unpublished), 1 Best Theme Paper Award, and 35 Outstanding Paper Awards. The conference also awarded 3 Resource Paper Awards (ResourceAward) and Social Impact Award (
 Li Feifei's team proposed ReKep to give robots spatial intelligence and integrate GPT-4o
Sep 03, 2024 pm 05:18 PM
Li Feifei's team proposed ReKep to give robots spatial intelligence and integrate GPT-4o
Sep 03, 2024 pm 05:18 PM
Deep integration of vision and robot learning. When two robot hands work together smoothly to fold clothes, pour tea, and pack shoes, coupled with the 1X humanoid robot NEO that has been making headlines recently, you may have a feeling: we seem to be entering the age of robots. In fact, these silky movements are the product of advanced robotic technology + exquisite frame design + multi-modal large models. We know that useful robots often require complex and exquisite interactions with the environment, and the environment can be represented as constraints in the spatial and temporal domains. For example, if you want a robot to pour tea, the robot first needs to grasp the handle of the teapot and keep it upright without spilling the tea, then move it smoothly until the mouth of the pot is aligned with the mouth of the cup, and then tilt the teapot at a certain angle. . this
 Hongmeng Smart Travel S9 and full-scenario new product launch conference, a number of blockbuster new products were released together
Aug 08, 2024 am 07:02 AM
Hongmeng Smart Travel S9 and full-scenario new product launch conference, a number of blockbuster new products were released together
Aug 08, 2024 am 07:02 AM
This afternoon, Hongmeng Zhixing officially welcomed new brands and new cars. On August 6, Huawei held the Hongmeng Smart Xingxing S9 and Huawei full-scenario new product launch conference, bringing the panoramic smart flagship sedan Xiangjie S9, the new M7Pro and Huawei novaFlip, MatePad Pro 12.2 inches, the new MatePad Air, Huawei Bisheng With many new all-scenario smart products including the laser printer X1 series, FreeBuds6i, WATCHFIT3 and smart screen S5Pro, from smart travel, smart office to smart wear, Huawei continues to build a full-scenario smart ecosystem to bring consumers a smart experience of the Internet of Everything. Hongmeng Zhixing: In-depth empowerment to promote the upgrading of the smart car industry Huawei joins hands with Chinese automotive industry partners to provide
 Distributed Artificial Intelligence Conference DAI 2024 Call for Papers: Agent Day, Richard Sutton, the father of reinforcement learning, will attend! Yan Shuicheng, Sergey Levine and DeepMind scientists will give keynote speeches
Aug 22, 2024 pm 08:02 PM
Distributed Artificial Intelligence Conference DAI 2024 Call for Papers: Agent Day, Richard Sutton, the father of reinforcement learning, will attend! Yan Shuicheng, Sergey Levine and DeepMind scientists will give keynote speeches
Aug 22, 2024 pm 08:02 PM
Conference Introduction With the rapid development of science and technology, artificial intelligence has become an important force in promoting social progress. In this era, we are fortunate to witness and participate in the innovation and application of Distributed Artificial Intelligence (DAI). Distributed artificial intelligence is an important branch of the field of artificial intelligence, which has attracted more and more attention in recent years. Agents based on large language models (LLM) have suddenly emerged. By combining the powerful language understanding and generation capabilities of large models, they have shown great potential in natural language interaction, knowledge reasoning, task planning, etc. AIAgent is taking over the big language model and has become a hot topic in the current AI circle. Au



