 Hardware Tutorial
Hardware Tutorial
 Hardware News
Hardware News
 Introduction to the service life of 'Universal Flash S2' solid state drive
Introduction to the service life of 'Universal Flash S2' solid state drive
Introduction to the service life of 'Universal Flash S2' solid state drive

Universal Flash UNIS SSD S2 series solid state drives provide reliable guarantee in terms of service life, with special emphasis on its durability and long-term stability. The following is key information about the service life of the S2 series solid-state drives
MTBF (mean time between failures)
The mean time between failures of the Unisoc S2 series solid-state drives is nominally 1.5 million hours, which is a high standard in the industry , indicating that it is designed for long-term stable operation and is suitable for application environments that require high reliability.
TBW (Total Bytes Written)
For the 1TB version, the official TBW value is 600TBW, which means that under normal use, the hard drive can withstand 600TB of data writing, which is at the consumer level It is at a higher level among SSDs.
For the 2TB version, although some information mentions the same TBW as the 1TB version, there is also newer information stating that the TBW of the 2TB version can reach 800TBW, which further improves its durability.
Particle selection
Uses original 3D TLC flash memory particles. This type of particles is known for balancing performance and durability. Compared with QLC particles, it has a higher number of writes (P/E cycles), usually 3000 times. left and right, suitable for daily frequent reading and writing usage scenarios.
Warranty Service
Provides a warranty period of up to 5 years, which not only reflects confidence in the product, but also provides users with an extra sense of security, ensuring that if any non-human damage occurs within the normal use period, it will be repaired. Get good service.
To sum up, the Unisoc Flash S2 series solid-state drives are designed to be quite sturdy in terms of service life. They not only use high-quality 3D TLC flash memory at the hardware level, but also optimize data management at the software level to ensure the long-term stability of the hard drive. stability and durability, suitable for users who value data security and long-term storage needs.
The above is the detailed content of Introduction to the service life of 'Universal Flash S2' solid state drive. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1664
1664
 14
14
 1423
1423
 52
52
 1317
1317
 25
25
 1268
1268
 29
29
 1243
1243
 24
24
 The best JRPGs to play in 2025
Apr 11, 2025 am 11:39 AM
The best JRPGs to play in 2025
Apr 11, 2025 am 11:39 AM
The best JRPGs (Japanese role-playing games) in 2025 use theatrical storytelling and vibrant ensemble casts to weave powerful experiences that stay with us long after we put the controller down.Contrary to the name, JRPGs aren't necessarily all from
 Review: Ecovacs' X8 Pro Omni Robot Now Works With HomeKit
Apr 17, 2025 am 06:01 AM
Review: Ecovacs' X8 Pro Omni Robot Now Works With HomeKit
Apr 17, 2025 am 06:01 AM
With iOS 18.4, Apple added support for robot vacuums to HomeKit. There are a few Matter-enabled robot vacuums that can be added to the Home app for use with Siri, including the Deebot X8 Pro Omni from Ecovacs. I've been testing the X8 Pro Omni for th
 Review: Dio Node Aims to Bring Cost-Effective AirPlay Speakers to Your Entire Home
Apr 15, 2025 am 06:12 AM
Review: Dio Node Aims to Bring Cost-Effective AirPlay Speakers to Your Entire Home
Apr 15, 2025 am 06:12 AM
Dio is a small company focused on delivering a single product for the Apple ecosystem: a low-cost AirPlay speaker system known as Dio Node. Initially launched as a crowdfunded Indiegogo campaign back in 2022, the Dio Node began shipping to backers la
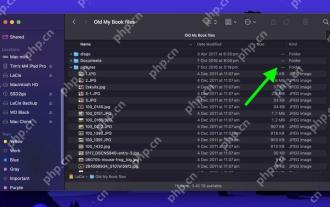 Reveal Hidden Folder Sizes in macOS Finder With These Tricks
Apr 17, 2025 am 01:11 AM
Reveal Hidden Folder Sizes in macOS Finder With These Tricks
Apr 17, 2025 am 01:11 AM
When using macOS Finder in List view, you'll see the sizes of individual files – but not folders.Instead, folders show a pair of dashes (--) in the Size column. macOS skips calculating folder sizes by default to keep List view performance fast, espec
 Best PS5 exclusives 2025 - the top games made for the PlayStation 5
Apr 18, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Best PS5 exclusives 2025 - the top games made for the PlayStation 5
Apr 18, 2025 am 11:37 AM
The best PS5 exclusives are those games that are or were, made exclusively for Sony's latest console. Exclusive games can set the tone and scene for a machine's offering compared to others. This is often the case for PlayStation consoles, with each g
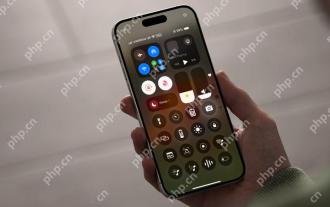 Worried About iPhone Privacy? Do This With Control Center
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:59 AM
Worried About iPhone Privacy? Do This With Control Center
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:59 AM
In iOS, the Control Center can be used to quickly take a picture, jot down a note, turn on the lights, control your Apple TV, and much more. It's useful and convenient because you don't even have to unlock your iPhone or iPad to use it. However, with
 Here's where to pre-order the Nintendo Switch 2 Pro Controller – UK fans can buy the pad, but US gamers have to wait
Apr 11, 2025 am 09:02 AM
Here's where to pre-order the Nintendo Switch 2 Pro Controller – UK fans can buy the pad, but US gamers have to wait
Apr 11, 2025 am 09:02 AM
Alongside the wider Nintendo Switch 2 pre-orders that have gone live in some territories recently, fans where stock is available can also pre-order the new Nintendo Switch 2 Pro Controller.Given how it looks and what it offers to players looking to p
 All the best PS5 controllers we recommend shopping for during Black Friday this week
Apr 12, 2025 am 09:02 AM
All the best PS5 controllers we recommend shopping for during Black Friday this week
Apr 12, 2025 am 09:02 AM
The best PS5 controllers aren't as abundant as other platforms when it comes to overall choice. That's obviously a bit of a shame, but what is available is still absolutely worth a look - especially if you're in the market for a DualSense alternative



