Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 Training with millions of crystal data to solve the crystallographic phase problem, the deep learning method PhAI is published in Science
Training with millions of crystal data to solve the crystallographic phase problem, the deep learning method PhAI is published in Science
Training with millions of crystal data to solve the crystallographic phase problem, the deep learning method PhAI is published in Science

To this day, the structural detail and precision determined by crystallography, from simple metals to large membrane proteins, are unmatched by any other method. However, the biggest challenge, the so-called phase problem, remains retrieving phase information from experimentally determined amplitudes.
Researchers at the University of Copenhagen, Denmark, have developed a deep learning method called PhAI to solve crystal phase problems. A deep learning neural network trained using millions of artificial crystal structures and their corresponding synthetic diffraction data can generate accurate electron density maps. .
Research shows that this deep learning-based ab initio structure solution method can solve the phase problem at a resolution of only 2 Angstroms, which is equivalent to only 10% to 20% of the available data at atomic resolution, while traditional Ab initio methods typically require atomic resolution.
Relevant research was titled "PhAI: A deep-learning approach to solve the crystallographic phase problem" and was published in "Science" on August 1.
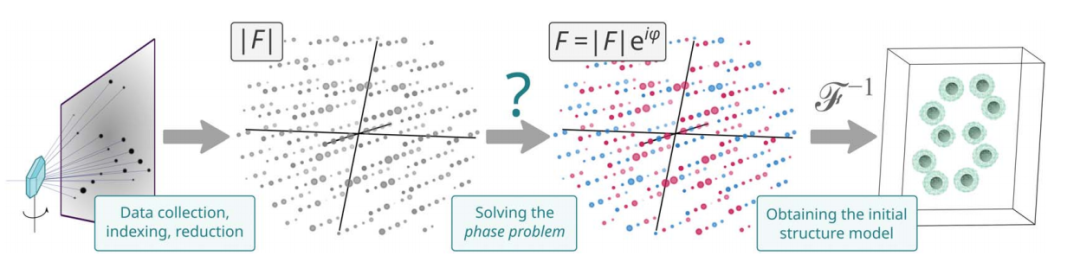
Crystallography is one of the core analytical techniques in natural sciences. X-ray crystallography provides a unique view into the three-dimensional structure of crystals.
In order to reconstruct the electron density map, enough complex structure factors $F$ of the diffraction reflections must be known. In a traditional experiment, only the amplitude $|F|$ is obtained, while the phase $phi$ is lost. This is a crystallographic phase problem.
A major breakthrough came in the 1950s and 1960s, when Karle and Hauptmann** developed so-called direct methods for solving phase problems. But the direct method requires atomic resolution diffraction data. However, the requirement of atomic resolution is an empirical observation.
In recent years, traditional direct methods have been supplemented by dual space methods. The currently available ab initio methods appear to have reached their limits. A general solution to the phase problem remains unknown.
Mathematically speaking, any combination of structure factor amplitude and phase can be subjected to an inverse Fourier transform. However, physical and chemical requirements (such as having an atomically-like electron density distribution) impose rules on the possible combinations of phases consistent with a set of amplitudes. Advances in deep learning allow one to explore this relationship, perhaps in greater depth than current ab initio methods.
Here, researchers from the University of Copenhagen took a data-driven approach, using millions of artificial crystal structures and their corresponding diffraction data, aiming to solve phase problems in crystallography.
Study shows that this deep learning based ab initio structure solution method can be performed at a resolution of only minimum lattice plane distance (dmin) = 2.0 Å using only the data required by the direct method 10% to 20%.
Neural Network Design and Training
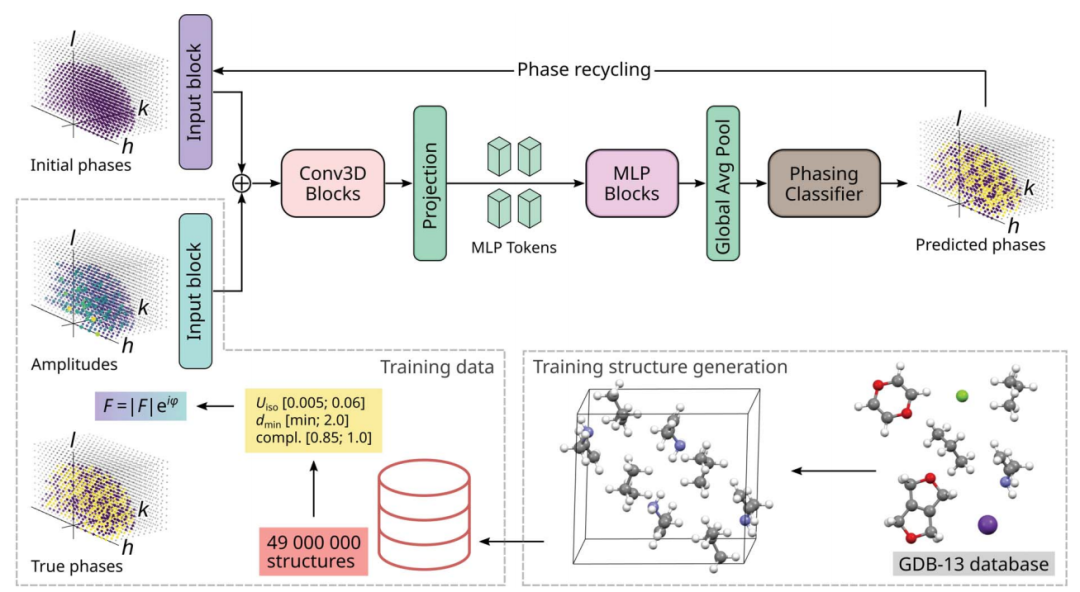
The artificial neural network constructed is called PhAI, which accepts the structure factor amplitude |F| and outputs the corresponding phase value ϕ. The architecture of PhAI is shown in the figure below.
That is, structures restricted to unit cell dimensions of about 10 Å at atomic resolution. Furthermore, the most common centrosymmetric space group P21/c was chosen. Central symmetry limits the possible phase values to zero or π rad.
- Penyelidikan mengenai melatih rangkaian saraf menggunakan struktur kristal buatan yang mengandungi terutamanya molekul organik. Kira-kira 49,000,000 struktur telah dicipta, di mana 94.29% adalah struktur kristal organik, 5.66% adalah struktur kristal logam-organik, dan 0.05% adalah struktur kristal bukan organik.
- Input kepada rangkaian saraf terdiri daripada amplitud dan fasa, yang diproses oleh blok input konvolusi, ditambah dan dimasukkan ke dalam satu siri blok konvolusi (Conv3D), diikuti dengan satu siri blok multilayer perceptron (MLP). Fasa yang diramalkan daripada pengelas linear (pengelas fasa) dikitar melalui rangkaian masa Nc. Data latihan dijana dengan memasukkan atom logam dan molekul organik daripada pangkalan data GDB-13 ke dalam sel unit. Struktur yang terhasil disusun ke dalam data latihan yang daripadanya fasa sebenar dan amplitud faktor struktur pada faktor suhu sampel, resolusi dan integriti boleh dikira.
Selesaikan masalah struktur sebenar - Rangkaian saraf terlatih dijalankan pada komputer standard dengan keperluan pengiraan sederhana. Ia menerima sebagai input senarai indeks hkl dan amplitud faktor struktur yang sepadan. Tiada maklumat input lain diperlukan, malah parameter sel unit struktur. Ini pada asasnya berbeza daripada semua kaedah ab initio moden yang lain. Rangkaian boleh meramalkan dan mengeluarkan nilai fasa dengan cepat.
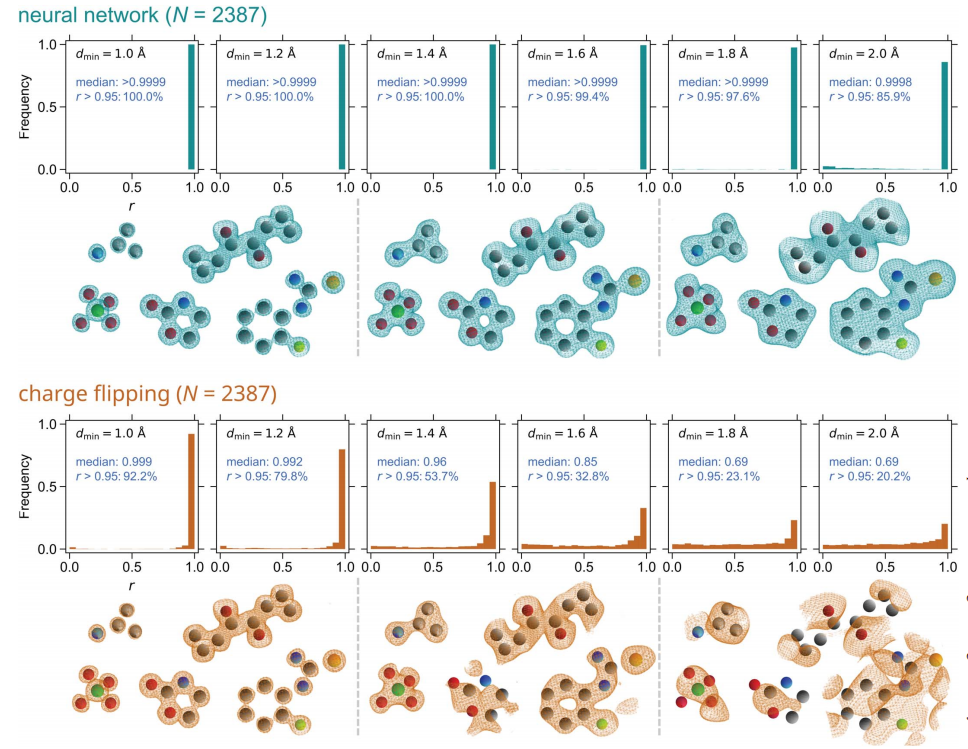
- Para penyelidik menguji prestasi rangkaian saraf menggunakan data pembelauan yang dikira daripada struktur kristal sebenar. Sebanyak 2387 kes ujian diperolehi. Untuk semua struktur yang dikumpul, berbilang nilai resolusi data antara 1.0 hingga 2.0 Å telah dipertimbangkan. Sebagai perbandingan, kaedah caj flip juga digunakan untuk mendapatkan maklumat fasa.
Ilustrasi: Histogram pekali korelasi r antara fasa dan peta ketumpatan elektron sebenar.
(Sumber: kertas)
Rangkaian saraf terlatih berfungsi dengan baik Ia boleh menyelesaikan semua struktur yang diuji (N = 2387) jika data pembelauan yang sepadan mempunyai resolusi yang baik, dan ia lebih baik dalam menyelesaikan struktur daripada resolusi rendah data Prestasi cemerlang. Walaupun rangkaian saraf jarang dilatih mengenai struktur bukan organik, ia boleh menyelesaikan struktur sedemikian dengan sempurna.
Kaedah cas flip berfungsi dengan baik semasa memproses data resolusi tinggi, tetapi keupayaannya untuk menghasilkan penyelesaian yang munasabah betul berkurangan secara beransur-ansur apabila resolusi data berkurangan, bagaimanapun, ia masih menyelesaikan kira-kira 32 piksel pada resolusi 1.6Å % Struktur. Bilangan struktur yang dikenal pasti dengan membalikkan cas boleh dipertingkatkan dengan percubaan selanjutnya dan menukar parameter input seperti ambang membalik.
Dalam pendekatan PhAI, Pengoptimuman meta ini dilakukan semasa latihan dan tidak perlu dilakukan oleh pengguna. Keputusan ini menunjukkan bahawa tanggapan umum dalam kristalografi bahawa data resolusi atom diperlukan untuk mengira fasa ab initio mungkin rosak. PhAI hanya memerlukan 10% hingga 20% data resolusi atom.
Hasil ini jelas menunjukkan bahawa resolusi atom tidak diperlukan untuk kaedah ab initio dan membuka jalan baharu untuk penentuan struktur berasaskan pembelajaran mendalam.
Cabaran pendekatan pembelajaran mendalam ini adalah untuk menskalakan rangkaian saraf, iaitu, data pembelauan untuk sel unit yang lebih besar akan memerlukan sejumlah besar data input dan output serta kos pengiraan semasa latihan. Pada masa hadapan, kajian lanjut diperlukan untuk melanjutkan kaedah ini kepada kes umum.
The above is the detailed content of Training with millions of crystal data to solve the crystallographic phase problem, the deep learning method PhAI is published in Science. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
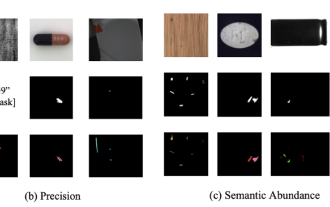 Breaking through the boundaries of traditional defect detection, 'Defect Spectrum' achieves ultra-high-precision and rich semantic industrial defect detection for the first time.
Jul 26, 2024 pm 05:38 PM
Breaking through the boundaries of traditional defect detection, 'Defect Spectrum' achieves ultra-high-precision and rich semantic industrial defect detection for the first time.
Jul 26, 2024 pm 05:38 PM
In modern manufacturing, accurate defect detection is not only the key to ensuring product quality, but also the core of improving production efficiency. However, existing defect detection datasets often lack the accuracy and semantic richness required for practical applications, resulting in models unable to identify specific defect categories or locations. In order to solve this problem, a top research team composed of Hong Kong University of Science and Technology Guangzhou and Simou Technology innovatively developed the "DefectSpectrum" data set, which provides detailed and semantically rich large-scale annotation of industrial defects. As shown in Table 1, compared with other industrial data sets, the "DefectSpectrum" data set provides the most defect annotations (5438 defect samples) and the most detailed defect classification (125 defect categories
 NVIDIA dialogue model ChatQA has evolved to version 2.0, with the context length mentioned at 128K
Jul 26, 2024 am 08:40 AM
NVIDIA dialogue model ChatQA has evolved to version 2.0, with the context length mentioned at 128K
Jul 26, 2024 am 08:40 AM
The open LLM community is an era when a hundred flowers bloom and compete. You can see Llama-3-70B-Instruct, QWen2-72B-Instruct, Nemotron-4-340B-Instruct, Mixtral-8x22BInstruct-v0.1 and many other excellent performers. Model. However, compared with proprietary large models represented by GPT-4-Turbo, open models still have significant gaps in many fields. In addition to general models, some open models that specialize in key areas have been developed, such as DeepSeek-Coder-V2 for programming and mathematics, and InternVL for visual-language tasks.
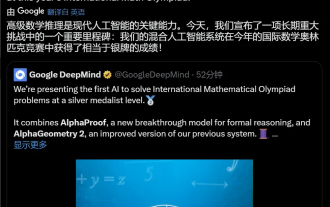 Google AI won the IMO Mathematical Olympiad silver medal, the mathematical reasoning model AlphaProof was launched, and reinforcement learning is so back
Jul 26, 2024 pm 02:40 PM
Google AI won the IMO Mathematical Olympiad silver medal, the mathematical reasoning model AlphaProof was launched, and reinforcement learning is so back
Jul 26, 2024 pm 02:40 PM
For AI, Mathematical Olympiad is no longer a problem. On Thursday, Google DeepMind's artificial intelligence completed a feat: using AI to solve the real question of this year's International Mathematical Olympiad IMO, and it was just one step away from winning the gold medal. The IMO competition that just ended last week had six questions involving algebra, combinatorics, geometry and number theory. The hybrid AI system proposed by Google got four questions right and scored 28 points, reaching the silver medal level. Earlier this month, UCLA tenured professor Terence Tao had just promoted the AI Mathematical Olympiad (AIMO Progress Award) with a million-dollar prize. Unexpectedly, the level of AI problem solving had improved to this level before July. Do the questions simultaneously on IMO. The most difficult thing to do correctly is IMO, which has the longest history, the largest scale, and the most negative
 Training with millions of crystal data to solve the crystallographic phase problem, the deep learning method PhAI is published in Science
Aug 08, 2024 pm 09:22 PM
Training with millions of crystal data to solve the crystallographic phase problem, the deep learning method PhAI is published in Science
Aug 08, 2024 pm 09:22 PM
Editor |KX To this day, the structural detail and precision determined by crystallography, from simple metals to large membrane proteins, are unmatched by any other method. However, the biggest challenge, the so-called phase problem, remains retrieving phase information from experimentally determined amplitudes. Researchers at the University of Copenhagen in Denmark have developed a deep learning method called PhAI to solve crystal phase problems. A deep learning neural network trained using millions of artificial crystal structures and their corresponding synthetic diffraction data can generate accurate electron density maps. The study shows that this deep learning-based ab initio structural solution method can solve the phase problem at a resolution of only 2 Angstroms, which is equivalent to only 10% to 20% of the data available at atomic resolution, while traditional ab initio Calculation
 Nature's point of view: The testing of artificial intelligence in medicine is in chaos. What should be done?
Aug 22, 2024 pm 04:37 PM
Nature's point of view: The testing of artificial intelligence in medicine is in chaos. What should be done?
Aug 22, 2024 pm 04:37 PM
Editor | ScienceAI Based on limited clinical data, hundreds of medical algorithms have been approved. Scientists are debating who should test the tools and how best to do so. Devin Singh witnessed a pediatric patient in the emergency room suffer cardiac arrest while waiting for treatment for a long time, which prompted him to explore the application of AI to shorten wait times. Using triage data from SickKids emergency rooms, Singh and colleagues built a series of AI models that provide potential diagnoses and recommend tests. One study showed that these models can speed up doctor visits by 22.3%, speeding up the processing of results by nearly 3 hours per patient requiring a medical test. However, the success of artificial intelligence algorithms in research only verifies this
 To provide a new scientific and complex question answering benchmark and evaluation system for large models, UNSW, Argonne, University of Chicago and other institutions jointly launched the SciQAG framework
Jul 25, 2024 am 06:42 AM
To provide a new scientific and complex question answering benchmark and evaluation system for large models, UNSW, Argonne, University of Chicago and other institutions jointly launched the SciQAG framework
Jul 25, 2024 am 06:42 AM
Editor |ScienceAI Question Answering (QA) data set plays a vital role in promoting natural language processing (NLP) research. High-quality QA data sets can not only be used to fine-tune models, but also effectively evaluate the capabilities of large language models (LLM), especially the ability to understand and reason about scientific knowledge. Although there are currently many scientific QA data sets covering medicine, chemistry, biology and other fields, these data sets still have some shortcomings. First, the data form is relatively simple, most of which are multiple-choice questions. They are easy to evaluate, but limit the model's answer selection range and cannot fully test the model's ability to answer scientific questions. In contrast, open-ended Q&A
 PRO | Why are large models based on MoE more worthy of attention?
Aug 07, 2024 pm 07:08 PM
PRO | Why are large models based on MoE more worthy of attention?
Aug 07, 2024 pm 07:08 PM
In 2023, almost every field of AI is evolving at an unprecedented speed. At the same time, AI is constantly pushing the technological boundaries of key tracks such as embodied intelligence and autonomous driving. Under the multi-modal trend, will the situation of Transformer as the mainstream architecture of AI large models be shaken? Why has exploring large models based on MoE (Mixed of Experts) architecture become a new trend in the industry? Can Large Vision Models (LVM) become a new breakthrough in general vision? ...From the 2023 PRO member newsletter of this site released in the past six months, we have selected 10 special interpretations that provide in-depth analysis of technological trends and industrial changes in the above fields to help you achieve your goals in the new year. be prepared. This interpretation comes from Week50 2023
 Automatically identify the best molecules and reduce synthesis costs. MIT develops a molecular design decision-making algorithm framework
Jun 22, 2024 am 06:43 AM
Automatically identify the best molecules and reduce synthesis costs. MIT develops a molecular design decision-making algorithm framework
Jun 22, 2024 am 06:43 AM
Editor | Ziluo AI’s use in streamlining drug discovery is exploding. Screen billions of candidate molecules for those that may have properties needed to develop new drugs. There are so many variables to consider, from material prices to the risk of error, that weighing the costs of synthesizing the best candidate molecules is no easy task, even if scientists use AI. Here, MIT researchers developed SPARROW, a quantitative decision-making algorithm framework, to automatically identify the best molecular candidates, thereby minimizing synthesis costs while maximizing the likelihood that the candidates have the desired properties. The algorithm also determined the materials and experimental steps needed to synthesize these molecules. SPARROW takes into account the cost of synthesizing a batch of molecules at once, since multiple candidate molecules are often available