 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 Nature sub-journal | Based on endogenous complexity, the Institute of Automation's new brain-like network builds a bridge between artificial intelligence and neuroscience
Nature sub-journal | Based on endogenous complexity, the Institute of Automation's new brain-like network builds a bridge between artificial intelligence and neuroscience
Nature sub-journal | Based on endogenous complexity, the Institute of Automation's new brain-like network builds a bridge between artificial intelligence and neuroscience

The AIxiv column is a column where this site publishes academic and technical content. In the past few years, the AIxiv column of this site has received more than 2,000 reports, covering top laboratories from major universities and companies around the world, effectively promoting academic exchanges and dissemination. If you have excellent work that you want to share, please feel free to contribute or contact us for reporting. Submission email: liyazhou@jiqizhixin.com; zhaoyunfeng@jiqizhixin.com
This work was published in "Nature Computational Science". The co-corresponding authors are researchers Li Guoqi and Xu Bo from the Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Professor Tian Yonghong from Peking University. . The co-authors are He Linxuan, an undergraduate student in Qian Xuesen's class at Tsinghua University (an intern at the Institute of Automation), Xu Yunhui, an undergraduate student in the basic mathematics and science class (an intern at the Institute of Automation), and He Weihua and Lin Yihan, doctoral students in the Department of Precision Instruments at Tsinghua University.
Enabling models with broader and more general cognitive capabilities is an important goal in the current development of the field of artificial intelligence (AI). The currently popular large model path is based on Scaling Law to build larger, deeper and wider neural networks to improve model performance, which can be called a general intelligence implementation method "based on exogenous complexity". However, this path also faces some insurmountable difficulties, such as high computational resource consumption and energy consumption, and has shortcomings in interpretability.
Artificial intelligence and neuroscience have long been interdependent and developed collaboratively. In order to overcome the dilemma of realizing general intelligence "based on exogenous complexity", the research team of Li Guoqi and Xu Bo from the Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences, together with Tsinghua University, Peking University and others, drew on the complex dynamic characteristics of brain neurons and proposed "based on endogenous complexity". "The brain-like neuron model construction method (Figure 1) improves the computing resource consumption problem caused by the outward expansion of traditional models and provides an example of the effective use of neuroscience to develop artificial intelligence. The journal Nature Computational Science commented on this: "AI research is closer to engineering and applications, while neuroscience research is more exploratory. The research team challenged this traditional view and showed that more detailed and biologically realistic neurons Models can drive greater progress in deep learning ”

Paper link: https://www.nature.com/articles/s43588-024-00674-9
Comment link: https:// /www.nature.com/articles/s43588-024-00677-6
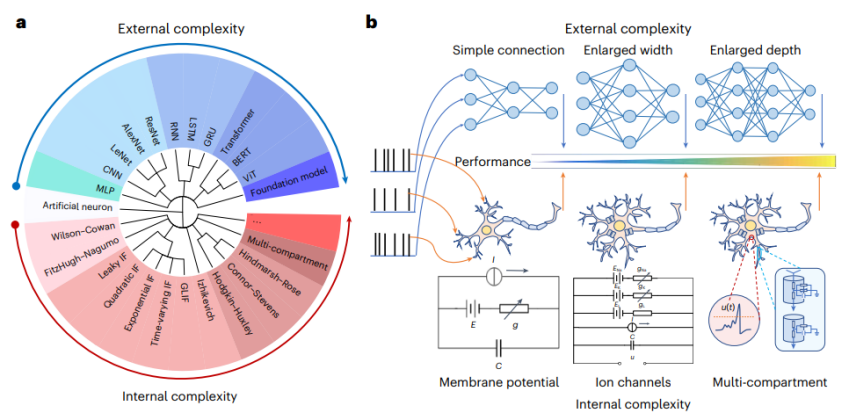
Endogenous complexity refers to internally drawing on the complex dynamic characteristics of brain neurons to construct a neural network primitive model
a small network model with endogenous complexity: inspiration from biological neurons
Biological neurons have complex Internal structures, such as ion channels, synaptic transmission mechanisms, etc., these complex internal structures enable neurons to process complex signals and generate diverse responses. In contrast, current artificial spiking neural network models, such as the classic LIF (Leaky Integrate and Fire) network, usually adopt simple internal structures and are difficult to simulate the complex dynamics and functions of biological neurons.
In this study, the researchers proposed the concept of "small network model with endogenous complexity". The core idea is to introduce complex internal structures into single neurons by simulating the complex dynamics of biological neurons. , thereby building a more efficient AI model. For example, in this study, the researchers used the HH (Hodgkin-Huxley) model in the spiking neural network to replace the traditional LIF model. As a mathematical model that describes the mechanism of neuron action potential generation, the HH model has fine dynamics brought about by complex internal structures and can simulate the response of neurons to various stimuli.
Transformation from exogenous complexity to endogenous complexity
Theoretical dynamics derivation and simulation
研究團隊透過理論證明了HH 模型與LIF 模型在動作電位產生機制上存在某種等效關係,即一個HH 神經元可以和四個時變參數LIF 神經元(tv-LIF)以特定連接方式形成的微結構等效,其中每個LIF 神經元描述HH 模型中的一個離子通道。基於這種等效性,可以透過設計微結構提升計算單元的內生複雜性,使HH 網路模型能夠模擬更大規模LIF 網路模型的動力學特性,在更小的網路結構上實現與之相似的計算功能。
研究團隊透過模擬神經元刺激輸入對比網路輸出對該理論進行了模擬驗證。在相同的輸入刺激下,具有較高外生複雜性的 tv-LIF 網路能夠與 HH 模型產生相同的輸出反應。進一步,團隊將四個tv-LIF 神經元建構的「HH 模型」(tv-LIF2HH)簡化為s-LIF2HH 模型,透過模擬實驗驗證了這種簡化模型仍然保留捕捉HH 模型動力學行為的可能性(圖2)。
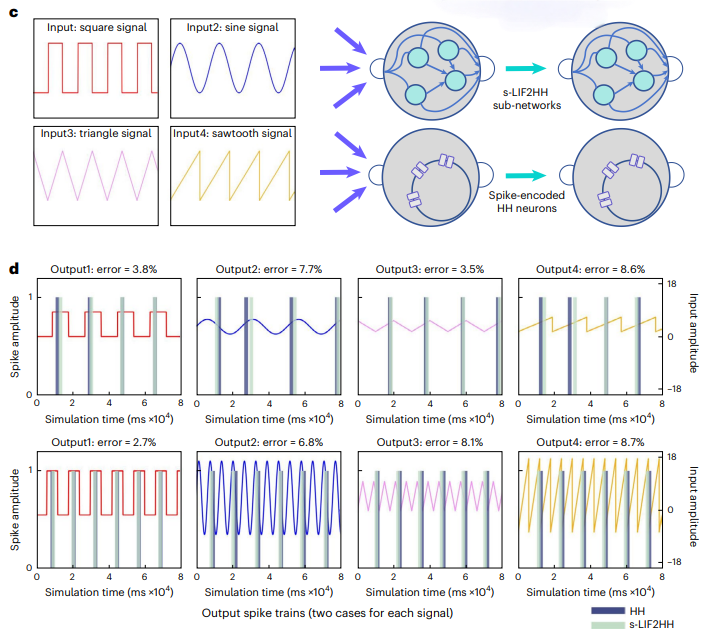
對上生長時保持複雜性的複雜性行為 保持複雜性動力行為
網路學習實驗對比
除了透過模擬研究相同刺激下不同網路的動力學行為,研究者建構了更大規模的HH 網路模型, s-LIF2HH 網路模型,並進行了多任務分類和深度強化學習實驗。結果表明,具有內生複雜性HH 網路模型能夠與更大規模的s-LIF2HH 網路模型在表示能力和穩健性上具有相似的性能,相比更大規模的一般LIF 網路表現出更好的性能。
多任務學習實驗:研究者透過使用Fashion-MNIST 資料集進行多任務學習實驗,結果顯示HH 網路模型能夠與更大規模的s-LIF2HH 網路模型實現相當效能,甚至略優於更大規模的一般LIF 網路(圖3)。
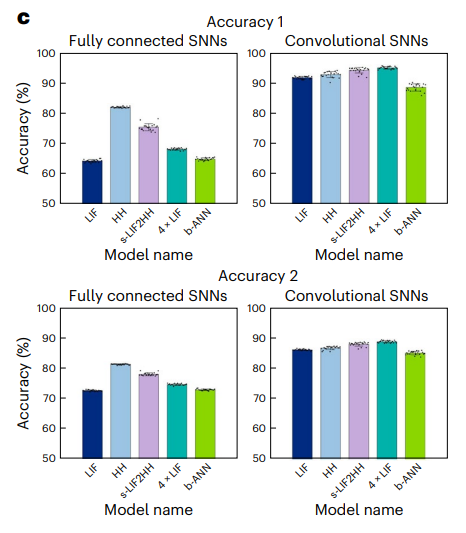
圖3. 內生複雜性的HH 網路模型在多重任務上能與更大規模外生複雜性網路絡性能相當
時序強化學習實驗:研究者在倒立擺(Inverted Pendulum)和倒立雙擺(Inverted Double Pendulum)環境下進行時序強化學習實驗,結果顯示HH 網路模型能夠與更大規模的LIF 網路模型相比,表現出更強的時序資訊擷取能力(圖4)。
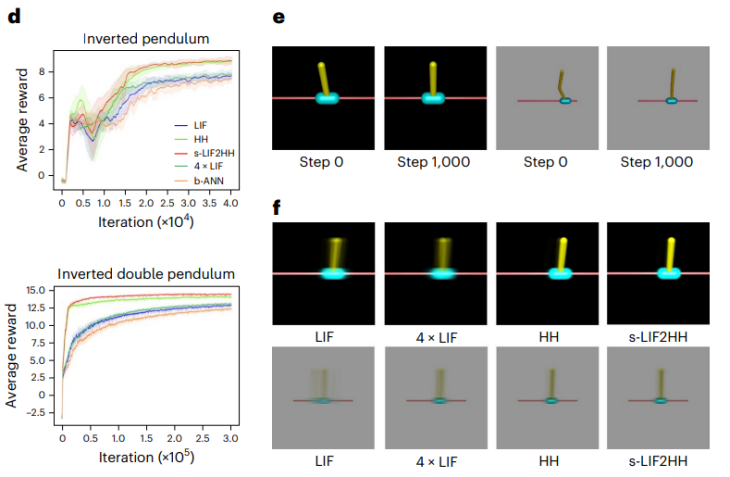
性能相當
魯棒性實驗:研究者在多任務學習和深度強化學習任務中加入高斯噪聲,以評估網路的穩健性。實驗結果顯示,更大規模的一般 LIF 網路模型在噪音影響下效能下降幅度最大,而 HH 網路模型和更大規模的 s-LIF2HH 網路模型則表現出更強的穩健性。在噪音強度增加的情況下,HH 網路模型和 s-LIF2HH 網路模型的獎勵曲線仍然保持接近,並且相比一般 LIF 網路模型受到的影響顯著地更小(圖 5)。
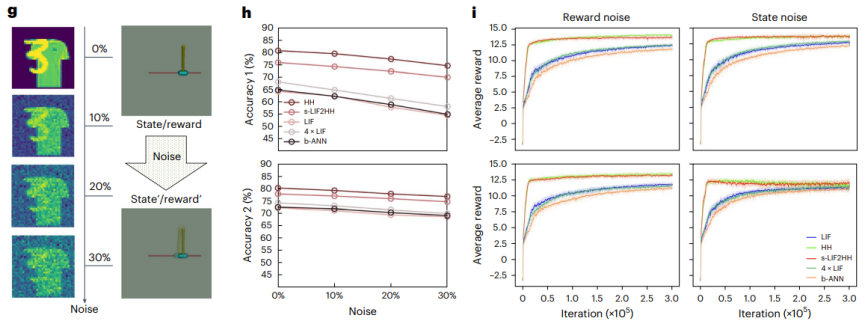
實驗證明了內生複雜性模型在處理複雜任務時的有效性和可靠性。同時,研究發現 HH 網路模型在計算資源消耗上更為高效,顯著減少了記憶體和計算時間的使用,從而提高了整體的運算效率。研究團隊透過資訊瓶頸理論對上述研究結果進行了解釋。除此之外,小規模的模型外部結構相對簡單,更容易理解其決策過程,也提高了模型的可解釋性和安全性。
結語與展望
具有內生複雜性的小型模型為 AI 的發展帶來了新的機遇。透過模擬生物神經元的複雜動力學,優化模型的局部微結構擴展內生複雜性,我們可以建立更有效率、更強大的 AI 模型,並克服外部複雜性大型模型的困境。未來,拓展內生複雜性或將成為 AI 研究的重要方向,並推動 AI 技術走向更廣泛的應用。
本研究為將神經科學的複雜動力學特性融入人工智慧提供了新的方法和理論支持,為實際應用中的 AI 模型優化和性能提升提供了可行的解決方案。目前,研究團隊已進行對更大規模HH 網絡,以及具備更大內生複雜性的多分枝多房室神經元的研究,有望進一步提升大模型計算效率與任務處理能力,實現在實際應用場景中的快速落地。
The above is the detailed content of Nature sub-journal | Based on endogenous complexity, the Institute of Automation's new brain-like network builds a bridge between artificial intelligence and neuroscience. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 The author of ControlNet has another hit! The whole process of generating a painting from a picture, earning 1.4k stars in two days
Jul 17, 2024 am 01:56 AM
The author of ControlNet has another hit! The whole process of generating a painting from a picture, earning 1.4k stars in two days
Jul 17, 2024 am 01:56 AM
It is also a Tusheng video, but PaintsUndo has taken a different route. ControlNet author LvminZhang started to live again! This time I aim at the field of painting. The new project PaintsUndo has received 1.4kstar (still rising crazily) not long after it was launched. Project address: https://github.com/lllyasviel/Paints-UNDO Through this project, the user inputs a static image, and PaintsUndo can automatically help you generate a video of the entire painting process, from line draft to finished product. follow. During the drawing process, the line changes are amazing. The final video result is very similar to the original image: Let’s take a look at a complete drawing.
 Topping the list of open source AI software engineers, UIUC's agent-less solution easily solves SWE-bench real programming problems
Jul 17, 2024 pm 10:02 PM
Topping the list of open source AI software engineers, UIUC's agent-less solution easily solves SWE-bench real programming problems
Jul 17, 2024 pm 10:02 PM
The AIxiv column is a column where this site publishes academic and technical content. In the past few years, the AIxiv column of this site has received more than 2,000 reports, covering top laboratories from major universities and companies around the world, effectively promoting academic exchanges and dissemination. If you have excellent work that you want to share, please feel free to contribute or contact us for reporting. Submission email: liyazhou@jiqizhixin.com; zhaoyunfeng@jiqizhixin.com The authors of this paper are all from the team of teacher Zhang Lingming at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign (UIUC), including: Steven Code repair; Deng Yinlin, fourth-year doctoral student, researcher
 From RLHF to DPO to TDPO, large model alignment algorithms are already 'token-level'
Jun 24, 2024 pm 03:04 PM
From RLHF to DPO to TDPO, large model alignment algorithms are already 'token-level'
Jun 24, 2024 pm 03:04 PM
The AIxiv column is a column where this site publishes academic and technical content. In the past few years, the AIxiv column of this site has received more than 2,000 reports, covering top laboratories from major universities and companies around the world, effectively promoting academic exchanges and dissemination. If you have excellent work that you want to share, please feel free to contribute or contact us for reporting. Submission email: liyazhou@jiqizhixin.com; zhaoyunfeng@jiqizhixin.com In the development process of artificial intelligence, the control and guidance of large language models (LLM) has always been one of the core challenges, aiming to ensure that these models are both powerful and safe serve human society. Early efforts focused on reinforcement learning methods through human feedback (RL
 Posthumous work of the OpenAI Super Alignment Team: Two large models play a game, and the output becomes more understandable
Jul 19, 2024 am 01:29 AM
Posthumous work of the OpenAI Super Alignment Team: Two large models play a game, and the output becomes more understandable
Jul 19, 2024 am 01:29 AM
If the answer given by the AI model is incomprehensible at all, would you dare to use it? As machine learning systems are used in more important areas, it becomes increasingly important to demonstrate why we can trust their output, and when not to trust them. One possible way to gain trust in the output of a complex system is to require the system to produce an interpretation of its output that is readable to a human or another trusted system, that is, fully understandable to the point that any possible errors can be found. For example, to build trust in the judicial system, we require courts to provide clear and readable written opinions that explain and support their decisions. For large language models, we can also adopt a similar approach. However, when taking this approach, ensure that the language model generates
 A significant breakthrough in the Riemann Hypothesis! Tao Zhexuan strongly recommends new papers from MIT and Oxford, and the 37-year-old Fields Medal winner participated
Aug 05, 2024 pm 03:32 PM
A significant breakthrough in the Riemann Hypothesis! Tao Zhexuan strongly recommends new papers from MIT and Oxford, and the 37-year-old Fields Medal winner participated
Aug 05, 2024 pm 03:32 PM
Recently, the Riemann Hypothesis, known as one of the seven major problems of the millennium, has achieved a new breakthrough. The Riemann Hypothesis is a very important unsolved problem in mathematics, related to the precise properties of the distribution of prime numbers (primes are those numbers that are only divisible by 1 and themselves, and they play a fundamental role in number theory). In today's mathematical literature, there are more than a thousand mathematical propositions based on the establishment of the Riemann Hypothesis (or its generalized form). In other words, once the Riemann Hypothesis and its generalized form are proven, these more than a thousand propositions will be established as theorems, which will have a profound impact on the field of mathematics; and if the Riemann Hypothesis is proven wrong, then among these propositions part of it will also lose its effectiveness. New breakthrough comes from MIT mathematics professor Larry Guth and Oxford University
 arXiv papers can be posted as 'barrage', Stanford alphaXiv discussion platform is online, LeCun likes it
Aug 01, 2024 pm 05:18 PM
arXiv papers can be posted as 'barrage', Stanford alphaXiv discussion platform is online, LeCun likes it
Aug 01, 2024 pm 05:18 PM
cheers! What is it like when a paper discussion is down to words? Recently, students at Stanford University created alphaXiv, an open discussion forum for arXiv papers that allows questions and comments to be posted directly on any arXiv paper. Website link: https://alphaxiv.org/ In fact, there is no need to visit this website specifically. Just change arXiv in any URL to alphaXiv to directly open the corresponding paper on the alphaXiv forum: you can accurately locate the paragraphs in the paper, Sentence: In the discussion area on the right, users can post questions to ask the author about the ideas and details of the paper. For example, they can also comment on the content of the paper, such as: "Given to
 The first Mamba-based MLLM is here! Model weights, training code, etc. have all been open source
Jul 17, 2024 am 02:46 AM
The first Mamba-based MLLM is here! Model weights, training code, etc. have all been open source
Jul 17, 2024 am 02:46 AM
The AIxiv column is a column where this site publishes academic and technical content. In the past few years, the AIxiv column of this site has received more than 2,000 reports, covering top laboratories from major universities and companies around the world, effectively promoting academic exchanges and dissemination. If you have excellent work that you want to share, please feel free to contribute or contact us for reporting. Submission email: liyazhou@jiqizhixin.com; zhaoyunfeng@jiqizhixin.com. Introduction In recent years, the application of multimodal large language models (MLLM) in various fields has achieved remarkable success. However, as the basic model for many downstream tasks, current MLLM consists of the well-known Transformer network, which
 Axiomatic training allows LLM to learn causal reasoning: the 67 million parameter model is comparable to the trillion parameter level GPT-4
Jul 17, 2024 am 10:14 AM
Axiomatic training allows LLM to learn causal reasoning: the 67 million parameter model is comparable to the trillion parameter level GPT-4
Jul 17, 2024 am 10:14 AM
Show the causal chain to LLM and it learns the axioms. AI is already helping mathematicians and scientists conduct research. For example, the famous mathematician Terence Tao has repeatedly shared his research and exploration experience with the help of AI tools such as GPT. For AI to compete in these fields, strong and reliable causal reasoning capabilities are essential. The research to be introduced in this article found that a Transformer model trained on the demonstration of the causal transitivity axiom on small graphs can generalize to the transitive axiom on large graphs. In other words, if the Transformer learns to perform simple causal reasoning, it may be used for more complex causal reasoning. The axiomatic training framework proposed by the team is a new paradigm for learning causal reasoning based on passive data, with only demonstrations





