Implement data validation in Go

Data validation is an important part of software development. It makes sure that input data is accurate and meets the requirements before processing or storing it. In Go, data validation is simple and flexible.
This guide will teach you how to use struct tags to validate data and make your apps safe and reliable. From creating validation logic to using built-in validation tags.
Prerequisites
- Go 1.21
Setup project
Setting up the Go project dependencies.
go mod init app go get github.com/gin-gonic/gin
Project structure
├─ main.go ├─ models │ └─ user.go └─ public └─ index.html
Project files
user.go
The User struct is designed for testing validation within the application, incorporating validation tags to enforce specific rules.
package models
type User struct {
Id int `binding:"required" msg:"Required"`
Name string `binding:"max=10" msg:"Maximum length is 10"`
Email string `binding:"email" msg:"Invalid email address"`
Age int `binding:"min=1,max=100" msg:"Must between 1 and 100"`
BirthDate string `binding:"datetime=01/02/2006" msg:"Invalid date format"`
}
Since the default error messages are not user-friendly, we added a custom msg tag to define more meaningful error messages.
main.go
This file is the main entry point for our application. It will create and set up the minimal Go web application.
package main
import (
"app/models"
"net/http"
"reflect"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"github.com/go-playground/validator/v10"
)
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
router.LoadHTMLFiles("public/index.html")
router.GET("/", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.HTML(http.StatusOK, "index.html", nil)
})
router.POST("/", func(c *gin.Context) {
var user models.User
if err := c.ShouldBind(&user); err != nil {
c.HTML(http.StatusOK, "index.html", gin.H{"User": user, "Errors": getErrors(err, user)})
return
}
c.HTML(http.StatusOK, "index.html", gin.H{"Pass": true, "User": user})
})
router.Run()
}
func getErrors(err error, obj any) map[string]string {
messages := getMessages(obj)
errors := map[string]string{}
for _, e := range err.(validator.ValidationErrors) {
errors[e.Field()] = messages[e.Field()]
}
return errors
}
func getMessages(obj any) map[string]string {
t := reflect.TypeOf(obj)
messages := map[string]string{}
for i := 0; i < t.NumField(); i++ {
field := t.Field(i)
messages[field.Name] = field.Tag.Get("msg")
}
return messages
}
- GET method to return the input form.
- POST method for form submission and validation of user input.
- getErrors() returns the error information.
- getMessages() leverages our custom msg tag to retrieve error messages for specific fields.
index.html
The HTML user input form is designed to test the validation rules applied to the User struct. It typically includes fields that correspond to the properties of the User struct.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1">
<link href="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/bootstrap/5.3.3/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet">
<script>
function fill(valid) {
document.getElementById('id').value = (valid ? '1' : '')
document.getElementById('name').value = (valid ? 'foo' : 'my name is foo')
document.getElementById('email').value = (valid ? 'foo@mail.com' : 'mail')
document.getElementById('age').value = (valid ? '10' : '101')
document.getElementById('birthdate').value = (valid ? '01/01/2000' : '01012000')
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="row mt-3">
<form method="post">
<div class="mb-3 col-12">
<label class="form-label" for="id">Id</label>
<input id="id" name="Id" class="form-control form-control-sm" value="{{.User.Id}}" />
{{if .Errors.Id}}<span class="text-danger">{{.Errors.Id}}</span>{{end}}
</div>
<div class="mb-3 col-12">
<label class="form-label" for="name">Name</label>
<input id="name" name="Name" class="form-control form-control-sm" value="{{.User.Name}}" />
{{if .Errors.Name}}<span class="text-danger">{{.Errors.Name}}</span>{{end}}
</div>
<div class="mb-3 col-12">
<label class="form-label" for="email">Email</label>
<input id="email" name="Email" class="form-control form-control-sm" value="{{.User.Email}}" />
{{if .Errors.Email}}<span class="text-danger">{{.Errors.Email}}</span>{{end}}
</div>
<div class="mb-3 col-12">
<label class="form-label" for="age">Age</label>
<input id="age" name="Age" class="form-control form-control-sm" value="{{.User.Age}}" />
{{if .Errors.Age}}<span class="text-danger">{{.Errors.Age}}</span>{{end}}
</div>
<div class="mb-3 col-12">
<label class="form-label" for="birthdate">Birth Date</label>
<input id="birthdate" name="BirthDate" class="form-control form-control-sm" value="{{.User.BirthDate}}" />
{{if .Errors.BirthDate}}<span class="text-danger">{{.Errors.BirthDate}}</span>{{end}}
</div>
<div class="col-12">
<input type="button" class="btn btn-sm btn-danger" onclick="fill(0)" value="Fill invaid data" />
<input type="button" class="btn btn-sm btn-success" onclick="fill(1)" value="Fill vaid data" />
<button class="btn btn-sm btn-primary">Submit</button>
</div>
{{if .Pass}}
<div class="alert alert-success mt-3">
Validation success!
</div>
{{end}}
</form>
</div>
</div>
</body>
We use Go's HTML template syntax, such as {{if .Errors.Id}}, to display error messages to the user.
Run project
go run main.go
Open the web browser and goto http://localhost:8080
You will find this test page.
Testing
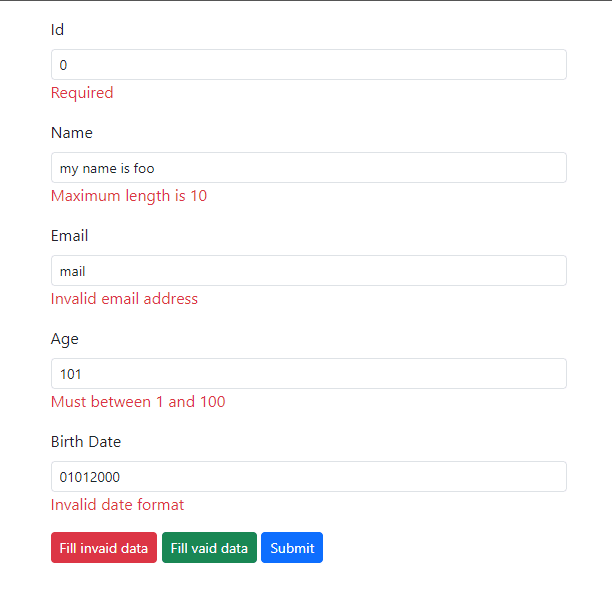
Click "Fill invalid data" and then click "Submit" to see the error messages displayed in the input form.
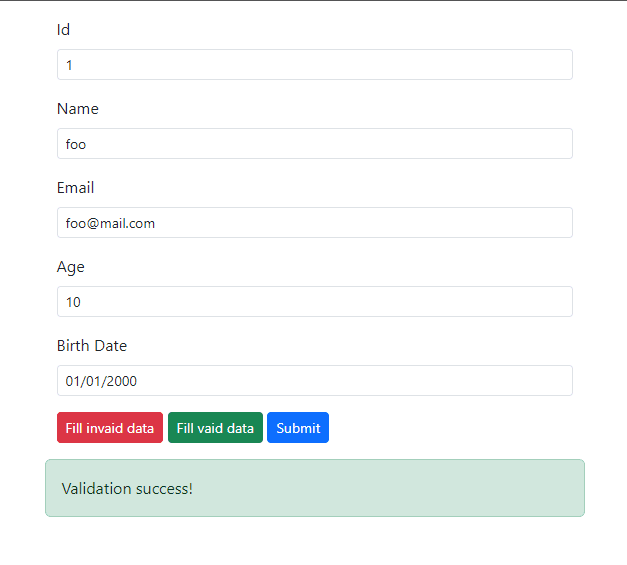
Click "Fill valid data" and then "Submit" again. You should see the validation success message displayed in the input form.
Conclusion
This article has covered implementing the basic data validation, helping you build reliable and user-friendly applications. Apply these practices to enhance both the robustness and usability of your Go web application.
Source code: https://github.com/stackpuz/Example-Validation-Go
Create a CRUD Web App in Minutes: https://stackpuz.com
The above is the detailed content of Implement data validation in Go. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1664
1664
 14
14
 1423
1423
 52
52
 1318
1318
 25
25
 1269
1269
 29
29
 1248
1248
 24
24
 Golang vs. Python: Performance and Scalability
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Golang vs. Python: Performance and Scalability
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Golang is better than Python in terms of performance and scalability. 1) Golang's compilation-type characteristics and efficient concurrency model make it perform well in high concurrency scenarios. 2) Python, as an interpreted language, executes slowly, but can optimize performance through tools such as Cython.
 Golang and C : Concurrency vs. Raw Speed
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Golang and C : Concurrency vs. Raw Speed
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Golang is better than C in concurrency, while C is better than Golang in raw speed. 1) Golang achieves efficient concurrency through goroutine and channel, which is suitable for handling a large number of concurrent tasks. 2)C Through compiler optimization and standard library, it provides high performance close to hardware, suitable for applications that require extreme optimization.
 Golang's Impact: Speed, Efficiency, and Simplicity
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Golang's Impact: Speed, Efficiency, and Simplicity
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Goimpactsdevelopmentpositivelythroughspeed,efficiency,andsimplicity.1)Speed:Gocompilesquicklyandrunsefficiently,idealforlargeprojects.2)Efficiency:Itscomprehensivestandardlibraryreducesexternaldependencies,enhancingdevelopmentefficiency.3)Simplicity:
 Golang vs. Python: Key Differences and Similarities
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Golang vs. Python: Key Differences and Similarities
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Golang and Python each have their own advantages: Golang is suitable for high performance and concurrent programming, while Python is suitable for data science and web development. Golang is known for its concurrency model and efficient performance, while Python is known for its concise syntax and rich library ecosystem.
 Golang vs. C : Performance and Speed Comparison
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:13 AM
Golang vs. C : Performance and Speed Comparison
Apr 21, 2025 am 12:13 AM
Golang is suitable for rapid development and concurrent scenarios, and C is suitable for scenarios where extreme performance and low-level control are required. 1) Golang improves performance through garbage collection and concurrency mechanisms, and is suitable for high-concurrency Web service development. 2) C achieves the ultimate performance through manual memory management and compiler optimization, and is suitable for embedded system development.
 Golang and C : The Trade-offs in Performance
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Golang and C : The Trade-offs in Performance
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:18 AM
The performance differences between Golang and C are mainly reflected in memory management, compilation optimization and runtime efficiency. 1) Golang's garbage collection mechanism is convenient but may affect performance, 2) C's manual memory management and compiler optimization are more efficient in recursive computing.
 Getting Started with Go: A Beginner's Guide
Apr 26, 2025 am 12:21 AM
Getting Started with Go: A Beginner's Guide
Apr 26, 2025 am 12:21 AM
Goisidealforbeginnersandsuitableforcloudandnetworkservicesduetoitssimplicity,efficiency,andconcurrencyfeatures.1)InstallGofromtheofficialwebsiteandverifywith'goversion'.2)Createandrunyourfirstprogramwith'gorunhello.go'.3)Exploreconcurrencyusinggorout
 C and Golang: When Performance is Crucial
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:11 AM
C and Golang: When Performance is Crucial
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:11 AM
C is more suitable for scenarios where direct control of hardware resources and high performance optimization is required, while Golang is more suitable for scenarios where rapid development and high concurrency processing are required. 1.C's advantage lies in its close to hardware characteristics and high optimization capabilities, which are suitable for high-performance needs such as game development. 2.Golang's advantage lies in its concise syntax and natural concurrency support, which is suitable for high concurrency service development.




