
The Java virtual machine memory area is a runtime area that is used for the execution of various programs involved during runtime of a java application, the memory area of JVM is broadly divided into five different parts which are method area, heap area, Stack, Program counter (PC) registers area and Native method area. In this article, we will discuss the different types of memory in java.
ADVERTISEMENT Popular Course in this category JAVA MASTERY - Specialization | 78 Course Series | 15 Mock TestsAs we know that java is an object-oriented language; therefore, all objects created in java are stored in JVM (Java virtual machine). JVM memory is basically divided into the following parts:
All executing threads share this part of the JVM memory area. Class elements like constant pool, class fields, constructor codes, method codes, etc. Method area can be considered as a part of the heap area but stores per-class data only. We can say that the method area is responsible for holding class level information.
Heap Memory in java is used by java runtime to allocate memory to objects and class during a java program’s execution. Whenever an object is created in java, it gets stored into heap memory. A garbage collection process runs on heap memory to free up unnecessary space that is garbage collection removes those objects from the heap area that does not have any references. Heap memory in java is divided into the following parts:
Here are some important points regarding java heap memory:
As the name signifies, stack memory is based on LIFO (last in, first out) principle. Stack memory is used for static memory allocation, and each executing thread in a java program has its own stack memory. Whenever a Java method is called, a new block is created in java stack memory to hold local or intermediate variables and references to other objects in the method. As soon as the execution of the method gets completed, the block of memory in the stack becomes empty and is used by the next method. The size of Stack memory is less as compared to heap memory. Here are some of the important features of stack memory.
The main function of pc registers is to store the address of currently executing the instruction. It also stores the address of threads responsible for executing current instruction. The size of memory allocated to pc registers is very small. Java applications executing in JVM does not have any effect on pc register memory or its contents.
This area is implemented using languages other than java. With the creation of new threads, memory is allocated in this area for each created thread. The size of the native area can be fixed or dynamic.
Now we will see a java example showing how memory is allocated:
Code:
package com.edubca.javademo;
class StudentData {
int rollNumber;
String name;
public StudentData(int rollNumber, String name) {
super();
this.rollNumber = rollNumber;
this.name = name;
}
public int getRollNumber() {
return rollNumber;
}
public void setRollNumber(int rollNumber) {
this.rollNumber = rollNumber;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int id = 11;
String name = "Yash";
StudentData s = null;
s = new StudentData(id, name);
System.out.println("Student Id is " + s.getRollNumber());
System.out.println("Student Name is " + s.getName());
}
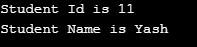
}Output:
Memory Allocation:
Now we will see how memory is allocated in the above program:
The above is the detailed content of Types of Memory in Java. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




