File Handling in Java
File handling refers to working with the file in java. Reading files & writing into java files is known as file handling in java. The FIle is a container that can contain different types of information. The file can contain text, images, videos, tables, etc.
ADVERTISEMENT Popular Course in this category JAVA MASTERY - Specialization | 78 Course Series | 15 Mock TestsStart Your Free Software Development Course
Web development, programming languages, Software testing & others
In java, the File class enables us to work with different types of files. File class is a member of the java.io packages. Java provides various methods to read, write, update & delete files.
Types of Operation
Different types of operation which can be performed on a file is given below:
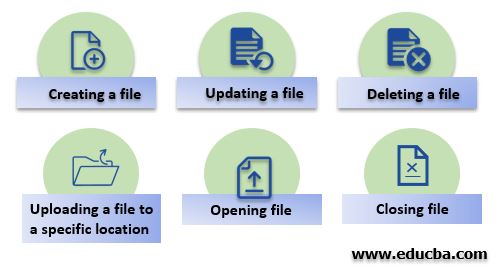
- Creating a file
- Updating a file
- Deleting a file
- Uploading a file to a specific location
- Opening file
- Closing file
Syntax:
To work with files in the program, you need to import the java.io package. Importing this package will provide you with a File class that you can initialize by referencing the file in the constructor of the File class.
//importing file class
import java.io.File;
//File name passed to the object
File fileObj = new File("file.txt");How does file Handling work?
In Java, File handling takes place by streaming concepts. Input/Output operations on a file perform through streaming. Stream refers to a sequence of data.
In java, Stream is of two types:
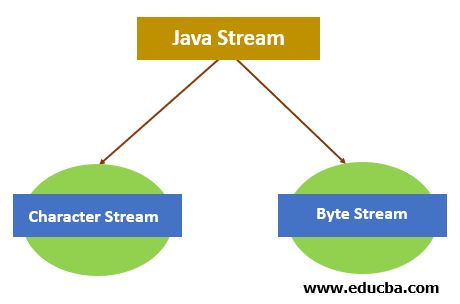
- Character Stream: A character stream refers to a stream that involves the characters. Data processing takes place with the Stream of characters in the files.
- Byte Stream: We call a stream that transfers data in bytes a byte stream. Data processing takes place with the Stream of bytes in the files.
File Handling Methods
Some of the methods are given below for performing different operations in java:
- createNewFile(): createNewFile method is used to create an empty file. It returns the response as a boolean.
- getName(): This method is used to get the file name. It returns the string, i.e., the file’s name in response.
- getAbsolutePath(): It returns the absolute path of the file. The return type of this method is a string.
- canRead(): This method checks whether the file is readable or not. It returns a boolean value.
- canWrite(): This method checks whether the file is writable or not. It returns a boolean value.
- delete(): This method is used in deleting a file. It returns a boolean value.
- exists(): Use this method to check if a file exists. It returns a boolean value.
- length(): This method returns the file size in bytes. The return type of this method is long.
- list(): This method returns an array of the files available in the directory. It returns an array of string values.
- mkdir(): To create a new directory, use this method. It returns a boolean value.
Examples of File Handling in Java
Below are examples of File Handling in Java:
Example #1
In this example, the program uses various methods to get specific details. In this application, different methods are used to get information related to files, such as:
- Retrieving the absolute path of the file.
- Checking whether the file is writable or not.
- Checking whether the file is readable or not.
- Retrieving file name.
- Retrieving file size.
- Obtaining a list of the files that are present in the specified directory, etc.
Code:
Importing io package different classes.
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileHandlingExample2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating an object of a file
File fileObj = new File("D:/Programs/fileHandlingOperations.txt");
if (fileObj.exists()) {
//retrieving the path of the specified file
System.out.println("\nSpecified file path: " + fileObj.getAbsolutePath());
//checking whether the file is writable or not
System.out.println("\nIs the file Writable: " + fileObj.canWrite());
//checking whether the file is Readable or not
System.out.println("\nIs the file Readable " + fileObj.canRead());
//retrieving file name
System.out.println("\nFile name: " + fileObj.getName());
//retrieving file size
System.out.println("\nFile size (in bytes) " + fileObj.length());
File fileDirObj = new File("D:/Programs/");
String[] fileList = fileDirObj.list();
//displaying here the list of files available in the directory
for (int i = 0; i < fileList.length; i++) {
System.out.print("\n" + fileList[i]);
}
System.out.println("\n");
}
else {
System.out.println("Specified file does not exist.");
}
}
}Output:
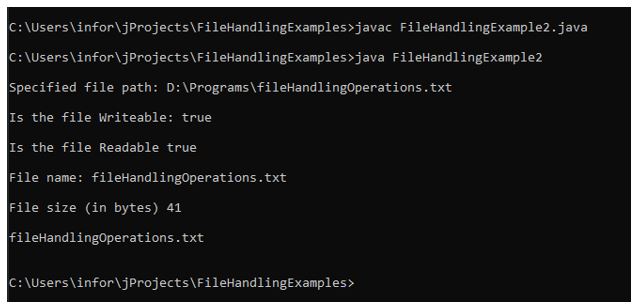
In the above-given example, we can see how different methods provide the information needed to perform the different checks related to files.
Example #2
This example shows how different methods are used in the program for different types of operations. exists() method used in the program to check if a file exists is not; after that, the if..else.. condition is placed.
In the If condition, it checks first whether the existing file is writable or not; if the existing file remains writable, then the code block under the if section uses the FileWriter class method to write content into the existing file.
Code:
Importing io package different classes.
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileHandlingExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
File fileObj = new File("D:/Programs/fileHandlingOperations.txt");
if(fileObj.exists()){
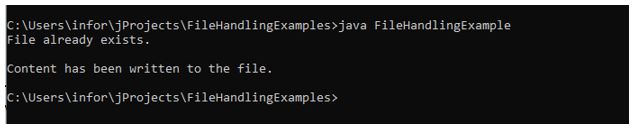
System.out.println("File already exists.");
if(fileObj.canWrite()){
//creating object of FileWriter class to write things on file
FileWriter fwObj = new FileWriter("D:/Programs/fileHandlingOperations.txt");
// Writes this content into the specified file
fwObj.write("It is a basic example of writing in file!");
//closing the files once writing completed
fwObj.close();
System.out.println("\nContent has been written to the file.");
}else{
System.out.println("\nFile is not in writable mode.");
}
;
}else{
if (fileObj.createNewFile()) {
System.out.println("New File created: " + fileObj.getName());
}
}
}
catch (IOException ioError) {
System.out.println("An error occurred.");
ioError.printStackTrace();
}
}
}Output:
In the above-given example, After compilation, running the program the first time will create a file with the specified name in the program.
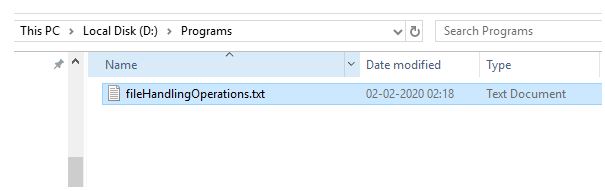
Running the program a second time will write the content in the existing file.
Conclusion
The article above explains what a file is, how to perform operations on it, and how file handling works. It was also demonstrated in the above section about classes & methods that can be used to work with files in java.
The above is the detailed content of File Handling in Java. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Guide to Random Number Generator in Java. Here we discuss Functions in Java with examples and two different Generators with ther examples.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to TimeStamp to Date in Java. Here we also discuss the introduction and how to convert timestamp to date in java along with examples.
 Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Java is a popular programming language that can be learned by both beginners and experienced developers. This tutorial starts with basic concepts and progresses through advanced topics. After installing the Java Development Kit, you can practice programming by creating a simple "Hello, World!" program. After you understand the code, use the command prompt to compile and run the program, and "Hello, World!" will be output on the console. Learning Java starts your programming journey, and as your mastery deepens, you can create more complex applications.




