TreeMap is used with the Abstract Class to deploy the Map and NavigableMap interface in Java. The map is sorted according to the natural sequence of its keys or by a pre-built comparator that depends on the builder. This is an easy way to sort and store the key-value pairs. The order of storage retained by the treemap must be the same as any other classified map, irrespective of the specific comparators.
Start Your Free Software Development Course
Web development, programming languages, Software testing & others
The following are some of the properties of TreeMap.
- It consists of unique elements.
- It cannot have a null key.
- Can have null values multiple times.
- Non-synchronized.
Declaration:
public class TreeMap<Key, Value> extends AbstractMap<Key, Value>implements NavigableMap<Key, Value>, Cloneable, Serializable
Copy after login
Here, Key and Value are the type of keys and mapped values in this map, respectively.
Constructors of TreeMap
The following are the constructors of TreeMap.
-
TreeMap(): A new and empty treemap will be constructed by naturally ordering the keys.
-
TreeMap( Comparator Key> comparator): A new and empty treemap will be constructed by ordering the keys specified in the comparator.
-
TreeMap( MapKey,? Ext Value> m): A new treemap will be constructed with the mappings in map m and naturally order the keys.
-
TreeMap( SortedMap<Key,? extends Value> m): A new treemap will be constructed with the mappings in map m and ordering the keys specified in the comparator.
Methods of TreeMap
TreeMap offers a wide collection of methods that helps in performing different functions. They are:
-
clear(): All the mapping in the map will be removed.
-
clone(): A shallow copy will be returned for the TreeMap instance.
-
containsKey(Objectk): If there is mapping available for the specified key, true will be returned.
-
containsValue(Objectv): If there is mapping available for one or more keys for the value v, true will be returned.
-
ceilingKey(Kkey): Least key which is larger than or equal to the specified key will be returned. If there is no key, then null will be returned.
-
ceilingEntry(Kkey): Key-value pair for the least key, which is larger than or equal to the specified key will be returned. If there is no key, then null will be returned.
-
firstKey(): First or last key in the map will be returned.
-
firstEntry(): Key-value pair for the least or first key in the map will be returned. If there is no key, then null will be returned.
-
floorKey(Kkey): The Largest key, which is less than or equal to the specified key, will be returned. If there is no key, then null will be returned.
-
floorEntry(Kkey): Key-value pair for the largest key, which is less than or equal to the specified key, will be returned. If there is no key, then null will be returned.
-
lastKey(): Highest or last key in the map will be returned.
-
lastEntry(): Key-value pair for the largest key in the map will be returned. If there is no key, then null will be returned.
-
lowerKey(Kkey): The Largest key, which is strictly smaller than the specified key, will be returned. If there is no key, then null will be returned.
-
lowerEntry(Kkey): Key-value pair for the largest key, which is strictly smaller than the specified key, will be returned. If there is no key, then null will be returned.
-
remove(Objectk): Mapping for the specified key in the map will be removed.
-
size(): Count of key-value pairs in the map will be returned.
-
higherEntry(Kkey): Key-value pair for the smallest key, which is strictly larger than the specified key, will be returned. If there is no key, then null will be returned.
-
higherKey(Kkey): The Smallest key, which is strictly higher than the specified key, will be returned. If there is no key, then null will be returned.
-
descendingMap(): Reverse order will be returned for the mappings.
-
entrySet(): Set view will be returned for the mappings.
-
get(Objectk): The value of the specified key will be returned. If the key does not contain any mapping, then null will be returned.
-
keySet(): Set view will be returned for the keys.
-
navigableKeySet(): NavigableSet view will be returned for the keys.
-
pollFirstEntry(): Key-value pair for the least or first key in the map will be removed and returned. If the map is empty, then null will be returned.
-
pollLastEntry(): Key-value pairs for the greatest key in the map will be removed and returned. If the map is empty, then null will be returned.
-
values(): Collection view will be returned for the values in the map.
Example to Implement TreeMap in Java
Now, let us see a sample program to create a treemap and add elements to it.
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class TreeMapExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// Tree Map creation
TreeMap tmap = new TreeMap();
// Add elements to the treemap tmap
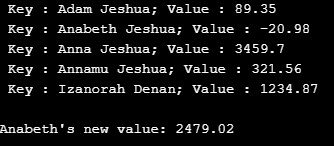
tmap.put("Anna Jeshua", new Double(3459.70));
tmap.put("Annamu Jeshua", new Double(321.56));
tmap.put("Izanorah Denan", new Double(1234.87));
tmap.put("Adam Jeshua", new Double(89.35));
tmap.put("Anabeth Jeshua", new Double(-20.98));
// Retrieve the entry set of treemap
Set set = tmap.entrySet();
// Create an iterator itr
Iterator itr = set.iterator();
// Display the elements in treemap using while loop
while(itr.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry mp = (Map.Entry)itr.next();
System.out.print(" Key : " + mp.getKey() + ";");
System.out.println(" Value : "+ mp.getValue());
}
System.out.println();
// Add 2500 to Anabeth's value
double val = ((Double)tmap.get("Anabeth Jeshua")).doubleValue();
tmap.put("Anabeth Jeshua", new Double(val + 2500));
System.out.println("Anabeth's new value: " + tmap.get("Anabeth Jeshua"));
} }Copy after login
Output:
Keys and corresponding values of the TreeMap will be displayed on executing the code.

Explanation:
- Firstly, create a TreeMap and add elements to it.
- In order to display the elements, an iterator has to be created.
- Using the iterator, all the keys and their corresponding values are displayed.
- To add 2500 to a key’s value, the put() method is also used.
Conclusion
Java TreeMap is an implementation of the Red-Black tree that helps in storing key-value pairs in sorted order. In this document, several details such as declaration, constructors, methods, and sample program of Java TreeMap is discussed in detail.
The above is the detailed content of What is TreeMap in Java?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!