How difficult is it to build a truly humanoid robot? Usually when a robot moves, all its joints will make a clicking sound, but the startup company 1X seen by OpenAI can do something different. They last week The new public humanoid robot NEO can be quiet and practical. If we turn up the volume of the video, we can hear the slight hum of the motor as it bends down to pick up the backpack.  After watching this video, I really want to ask, isn’t this really a human wearing a holster? Today’s industrial robots can move very fast, but they need to slow down to an extremely slow speed before they come into contact with things. To ensure safety, these robots often need to be kept in safety cages, but NEO can gently hug the girl in the video and hand her her schoolbag naturally and smoothly. How is this done? Eric Jang, Vice President of AI at 1X Technologies, wrote a blog exposing the technology behind NEO.
After watching this video, I really want to ask, isn’t this really a human wearing a holster? Today’s industrial robots can move very fast, but they need to slow down to an extremely slow speed before they come into contact with things. To ensure safety, these robots often need to be kept in safety cages, but NEO can gently hug the girl in the video and hand her her schoolbag naturally and smoothly. How is this done? Eric Jang, Vice President of AI at 1X Technologies, wrote a blog exposing the technology behind NEO. 
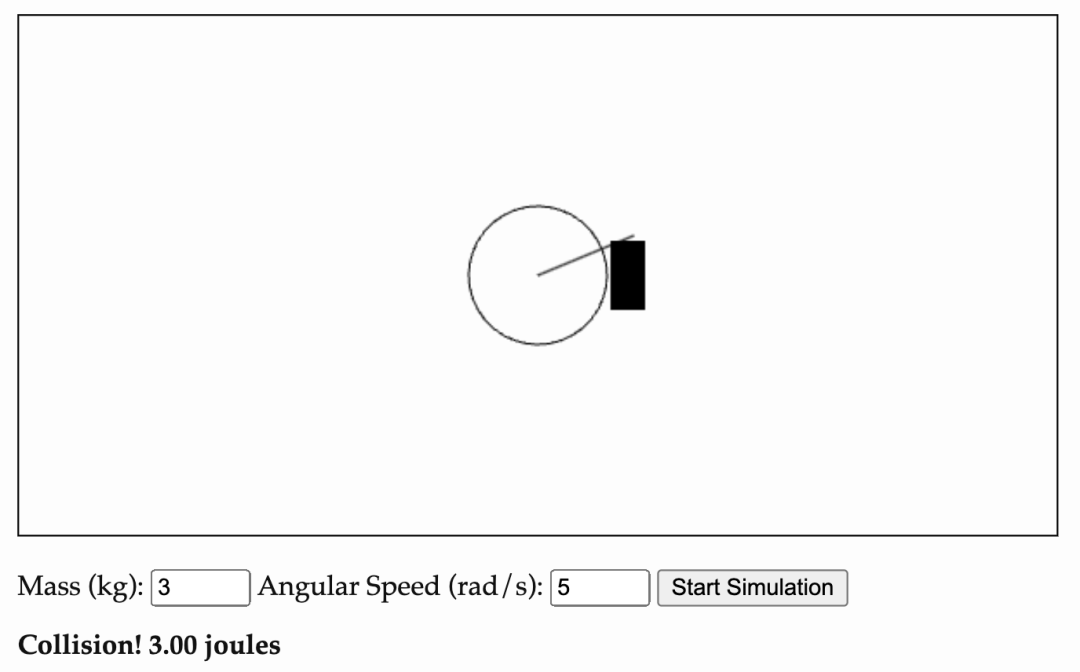
He called this blog a tutorial on motor inertia and gear systems. Before joining 1X Technologies, Eric Jang worked in Google's robotics research department for six years, but he admitted that it was not until joining 1X Technologies that he deeply understood the importance of these concepts. By conducting physical calculations himself, Eric Jang became more convinced that lightweight and high-torque motors are the key to building universal robots with learning capabilities. Is the loud noise due to low joint kinetic energy conversion efficiency? Imagine a wheel weighing 3 kg and having a radius of 0.4 m that rotates at 5 radians per second. Extending from the wheel is a lever that collides with a stationary block. Assume that the collision is completely inelastic, meaning that the wheel will stop spinning after the collision and will not bounce off the block. To simplify the calculations, we assume that the lever arm has no mass and only serves to prevent the rotation of the wheel. According to the rotational kinetic energy formula  , where I is the moment of inertia and ω is the angular velocity. Because the lever is assumed to have no mass, the inertia of the system is equivalent to that of a fixed cylinder:
, where I is the moment of inertia and ω is the angular velocity. Because the lever is assumed to have no mass, the inertia of the system is equivalent to that of a fixed cylinder:  . Plugging in the values gives us I = 0.24 kg⋅m^2. Therefore, the rotational kinetic energy of this system can be further calculated to be 3 Joules. In a real-world inelastic collision, the total momentum of the wheel and the block is conserved, but their total kinetic energy is not. Therefore, the rotational kinetic energy of the system will be less than 3 Joules. Energy is a conserved quantity, so where does the rest of the kinetic energy go? The answer is that part of the kinetic energy is converted into motion, and the remaining kinetic energy is consumed in the form of heat energy, sound and internal material deformation. When you hear a loud noise when a robot is moving, it is because the transmission of kinetic energy is inefficient, converting mechanical work into sound, and energy is wasted. Because the wooden block prevents the movement of the lever, the new speed of the wheel drops to zero, and the corresponding kinetic energy also drops to zero. This means that in order for the wheel to stop spinning, all of the kinetic energy must be converted into some other form of energy. Fortunately, 3 joules is not a lot of energy, it's the equivalent of a puppy trotting into you at 1 m/s and coming to a stop. Collision after adding gear boxSlightly modify the above system: Now we have two wheels, each wheel has a mass of 1.5 kg and a radius of 0.4 meters. The two wheels rotate at 5 rad/s and 50 rad/s respectively (i.e., 10 times the speed of the first wheel) and collide with a fixed block. The second wheel spins 10 times faster than the first wheel and drives the first wheel through a gearing. This setup equates to a 10:1 gear reduction ratio, which reduces the final speed of the lever. The kinetic energy of the system is the sum of the rotational kinetic energy of the two wheels. As in the previous example, the system comes to rest after the collision, and all kinetic energy must be dissipated in the form of heat, noise, and material deformation. Although the lever contacts the block at the same speed as before, the total kinetic energy (150 Joules) is 50 times that of the original single-wheel system! If the gear ratio is increased to 100 by robot gearbox standards, the total kinetic energy that needs to be dissipated is 15,000 joules. This is roughly equivalent to a baseball hitting you at 1,000 miles per hour. At this speed, any object the lever hits will be completely destroyed. Of course, the gear system itself will not be immune. This may be a little counter-intuitive, as gear linkages are often designed for safety. If the final speed of the lever remains unchanged, the total mass of the wheel remains unchanged, and there is no wooden block to prevent the movement of the lever, and the movements of the two sets of devices are recorded and observed separately, then you will not be able to tell the difference just by watching the video. But when it comes to collisions—especially those that are unexpected—the story is very different.The physics of rotating motors are crucial for humanoid robots to safely interact with the world. Most humanoid robotics companies choose to deploy robots in factories rather than homes because they rely on rigid, high-speed gear transmission systems. Just like the "destroying" kinetic energy of the baseball mentioned above, this kind of system is not safe around people, so they need to be surrounded by protective cages. think , if you want the robot to bring a cup of coffee quickly, then the end effector of its limbs needs to move quickly, which means that on the other side of the robot's limbs and gears, there must be a motor whose speed is much faster than that of the end effector. operation. Since kinetic energy is proportional to the square of angular velocity, the robot's movements are actually controlled by the inertia of the high-speed rotating gears, rather than the robot's limb links themselves. Professor Russ Tedrake from MIT gave a wonderful explanation of these counterintuitive robot dynamics phenomena in his class. コースリンク: https://manipulation.csail.mit.edu/robot .html エネルギーを消費し、安全ではないのに、なぜギアボックスを使用するのでしょうか?
. Plugging in the values gives us I = 0.24 kg⋅m^2. Therefore, the rotational kinetic energy of this system can be further calculated to be 3 Joules. In a real-world inelastic collision, the total momentum of the wheel and the block is conserved, but their total kinetic energy is not. Therefore, the rotational kinetic energy of the system will be less than 3 Joules. Energy is a conserved quantity, so where does the rest of the kinetic energy go? The answer is that part of the kinetic energy is converted into motion, and the remaining kinetic energy is consumed in the form of heat energy, sound and internal material deformation. When you hear a loud noise when a robot is moving, it is because the transmission of kinetic energy is inefficient, converting mechanical work into sound, and energy is wasted. Because the wooden block prevents the movement of the lever, the new speed of the wheel drops to zero, and the corresponding kinetic energy also drops to zero. This means that in order for the wheel to stop spinning, all of the kinetic energy must be converted into some other form of energy. Fortunately, 3 joules is not a lot of energy, it's the equivalent of a puppy trotting into you at 1 m/s and coming to a stop. Collision after adding gear boxSlightly modify the above system: Now we have two wheels, each wheel has a mass of 1.5 kg and a radius of 0.4 meters. The two wheels rotate at 5 rad/s and 50 rad/s respectively (i.e., 10 times the speed of the first wheel) and collide with a fixed block. The second wheel spins 10 times faster than the first wheel and drives the first wheel through a gearing. This setup equates to a 10:1 gear reduction ratio, which reduces the final speed of the lever. The kinetic energy of the system is the sum of the rotational kinetic energy of the two wheels. As in the previous example, the system comes to rest after the collision, and all kinetic energy must be dissipated in the form of heat, noise, and material deformation. Although the lever contacts the block at the same speed as before, the total kinetic energy (150 Joules) is 50 times that of the original single-wheel system! If the gear ratio is increased to 100 by robot gearbox standards, the total kinetic energy that needs to be dissipated is 15,000 joules. This is roughly equivalent to a baseball hitting you at 1,000 miles per hour. At this speed, any object the lever hits will be completely destroyed. Of course, the gear system itself will not be immune. This may be a little counter-intuitive, as gear linkages are often designed for safety. If the final speed of the lever remains unchanged, the total mass of the wheel remains unchanged, and there is no wooden block to prevent the movement of the lever, and the movements of the two sets of devices are recorded and observed separately, then you will not be able to tell the difference just by watching the video. But when it comes to collisions—especially those that are unexpected—the story is very different.The physics of rotating motors are crucial for humanoid robots to safely interact with the world. Most humanoid robotics companies choose to deploy robots in factories rather than homes because they rely on rigid, high-speed gear transmission systems. Just like the "destroying" kinetic energy of the baseball mentioned above, this kind of system is not safe around people, so they need to be surrounded by protective cages. think , if you want the robot to bring a cup of coffee quickly, then the end effector of its limbs needs to move quickly, which means that on the other side of the robot's limbs and gears, there must be a motor whose speed is much faster than that of the end effector. operation. Since kinetic energy is proportional to the square of angular velocity, the robot's movements are actually controlled by the inertia of the high-speed rotating gears, rather than the robot's limb links themselves. Professor Russ Tedrake from MIT gave a wonderful explanation of these counterintuitive robot dynamics phenomena in his class. コースリンク: https://manipulation.csail.mit.edu/robot .html エネルギーを消費し、安全ではないのに、なぜギアボックスを使用するのでしょうか?
その理由は、ギアボックスが重要な機械的レバレッジを提供するためです。多くのモーターは単独で動作すると十分なトルクを提供できないため、エンジニアは高速モーターにギアを取り付けます。必要なトルクを犠牲にしています。
この種の歯車システムは「剛性」があり、一度回転し始めると歯車がしっかりと噛み合い、逆駆動することが困難になります。引き返してください。そのため、ギアボックスのもう一方の端では、高速モーターによって生成される回転力に抵抗するために、より多くの力を加える必要があります。
上記の考慮事項に基づいて、1X Technologies は過去 10 年間、トランスミッション システムの安全性を最大限に高めるために高トルク、低速モーターの製造に取り組んできました。 NEO ロボットは、ギア比が小さく軽量なモーターと駆動システムを採用しているため、家庭環境に安全に組み込むことができる初の真の家庭用ロボットとなっています。 ロボットトレーニングにおける実写ビデオの重要性を再定義 に加えてロボットからの収集 研究者は、実際の人間がタスクを実行する一人称視点のビデオを使用してロボットを訓練することもできます。
1.一般的なロボットの進歩がボトルネックになっている。ロボットのハードウェアは高価ですが、かさばるハードウェアを使用してタスクを実行するために人間のリモート オペレーターを雇うのも同様に高価です。さらに、遠隔操作の効率は非常に低く、人間が直接タスクを完了できる速度よりもはるかに遅いです。
2. ヘッドマウント カメラを人々にストラップで固定し、肉を覆う大きなゴム手袋を着用してもらうと、さまざまな雑用を行っている人々の大規模なデータセットをすぐに収集できます。そしてタスク。普通の人は、日常生活の中で無意識のうちにさまざまな動作や操作タスクを実行します。生のモーション出力を直接認識することは困難ですが、ビデオ内のポーズの変化を分析することでアクションを推測できます。このタイプのデータ収集は、より高度なハードウェアが利用可能になるまで、汎用ロボットの開発の障壁を取り除くのに役立つ可能性があります。
3. インターネット上には一人称および三人称のビデオが多数あり、これらをロボットに訓練して、ビデオ内で人間が行うさまざまなアクティビティを認識および学習させることで、さらに拡張することができます。データサイズ。
この種のデータ収集を拡大する前に、5000 RPM で回転するモーターと比較して、私たちの身体には高速回転する部品がないことに注意することも重要です。 、筋肉の運動エネルギーは非常に低く、私たちが移動するときに運ぶ有効質量もはるかに小さいため、ロボットの関節角度は人間のそれとほぼ同じであっても、回転モーターによって提供される有効質量は、器用にタスクを実行するには大きすぎます。
効率的な動作制御戦略を開発したとしても、ロボットは、照明を簡単にオン/オフしたり、優雅に走ったりするなどの動作を実行する際に、依然として人間の速度と流暢さに達することはできません。これは、ロボットが物体に触れたときにかかる力が人間とは大きく異なるためです。
人間のビデオをロボットの動作戦略にすばやく変換したい場合は、次のメソッドが必要です:
のような非常に従順で柔軟なロボット 2. 「 」を直接コピーするのではなく、ロボットにビデオのモーション軌跡を 1 倍よりも遅い速度で追跡させます。ヒューマンハードウェア」のダイナミクス。ただし、これは静的な操作タスクにのみ適しており、衣服をたたむ、キッチンで食事を準備するなど、多くの物体との接触が必要なタスクには適していません。
3. 動作計画と動的計画を分離することで、動作計画は目標位置に到達することに重点を置き、動的計画は衝突時の力の制御に重点を置くことができます。 The above is the detailed content of How difficult is it for a robot to master the strength of its hands and do housework safely? 1X Artificial Intelligence Vice President writes a detailed explanation. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




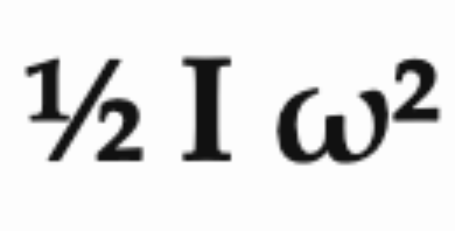 , where I is the moment of inertia and ω is the angular velocity. Because the lever is assumed to have no mass, the inertia of the system is equivalent to that of a fixed cylinder:
, where I is the moment of inertia and ω is the angular velocity. Because the lever is assumed to have no mass, the inertia of the system is equivalent to that of a fixed cylinder:  . Plugging in the values gives us I = 0.24 kg⋅m^2. Therefore, the rotational kinetic energy of this system can be further calculated to be 3 Joules.
. Plugging in the values gives us I = 0.24 kg⋅m^2. Therefore, the rotational kinetic energy of this system can be further calculated to be 3 Joules. 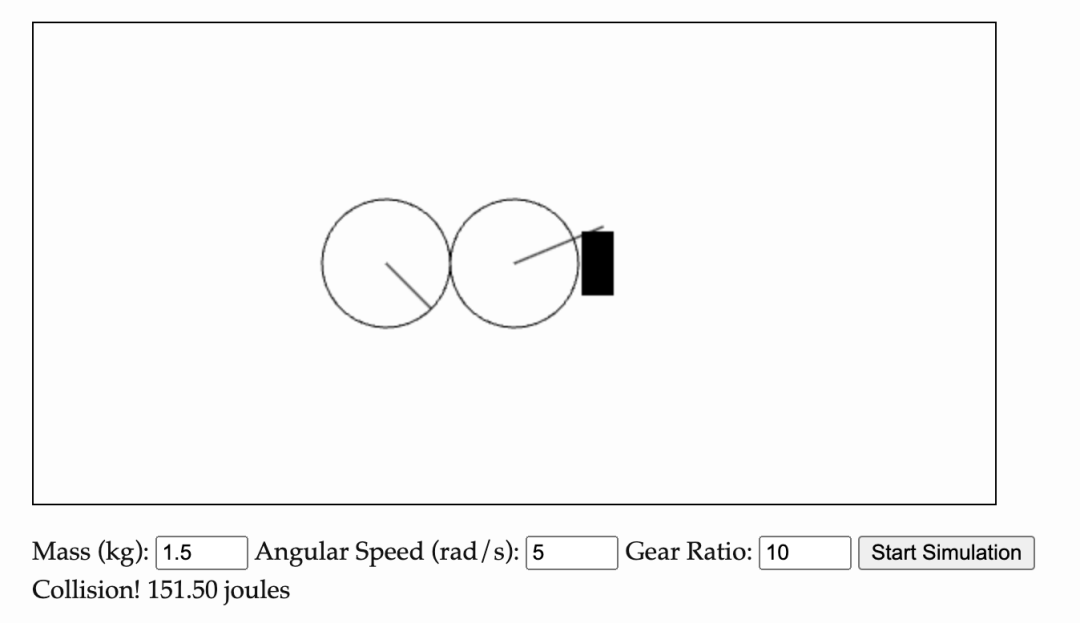

 How to flash Xiaomi phone
How to flash Xiaomi phone
 How to center div in css
How to center div in css
 How to open rar file
How to open rar file
 Methods for reading and writing java dbf files
Methods for reading and writing java dbf files
 How to solve the problem that the msxml6.dll file is missing
How to solve the problem that the msxml6.dll file is missing
 Commonly used permutation and combination formulas
Commonly used permutation and combination formulas
 Virtual mobile phone number to receive verification code
Virtual mobile phone number to receive verification code
 dynamic photo album
dynamic photo album




