
Vite.js is a rapid development tool for modern web projects. It focuses on speed and performance by improving the development experience.
Vite uses native browser ES imports to enable support for modern browsers without a build process.

Vite consists of two major parts:
When ES modules were introduced in ES2015, many browsers had poor support for ES6 modules. To address this, modern browsers now support native ES modules. This allows developers to use the import and export statements natively.
In native ES, the import must get either a relative or absolute URL because it does not support bare module imports such as:
import { someMethod } from 'my-dep'The above code will throw an error in the browser because many browsers do not have support for ES6 modules. So the question now is how does Vite handle this?
Vite will automatically detect bare module imports from your source files and perform the following two actions on them:
/node_modules/.vite/my-dep.js?v=f3sf2ebb
Now that we know what Vite is and how it works, you might be wondering why you should use Vite.
There are many reasons why you should use Vite for your project. Let's take a brief look at some of them.
Pre-bundling with Vite's ESbuild makes it 10 to 100 times faster than using any other JS bundler. This is because it helps improve page speed and convert CommonJS / UMD modules to ESM.
According to the Vite documentation,
"The pre-bundling step is performed with esbuild and makes Vite's cold start time significantly faster than any JavaScript-based bundler."
Vite uses HMR functionalities to keep track of changes in your application without reloading the full page. With the HMR API, the browser will only load the modified section of the page and still retain the application's state.
There's no need to manually configure the HMR API in your app. It's automatically added to your project during application installation.
With HMR performance, you can design lighter and faster applications regardless of the number of modules or the size of your application.
Vite allows you to have more control over your project's configuration by extending the default configuration with vite.config.js or vite.config.ts. These are located in the project's base root directory.
You can also specify different config files with the --config CLI option, as shown below:
vite --config my-config.js
You must have the following software installed on your computer before you can create a Vite project:
Once you have these installed on your computer, you can now create a Vite project.
To create a Vite application, open your terminal and navigate to the folder where you want to save the Vite program. Then run this command:
npm create @vitejs/app my-vite-app
Note: my_vite_app is the name of the Vite application that we want to create. You can change it to whatever name you prefer.
After running the above command, you'll be prompted to select a framework and the template (variant). For the purposes of this tutorial, we'll use React, but you can select any framework and template that you are familiar with.
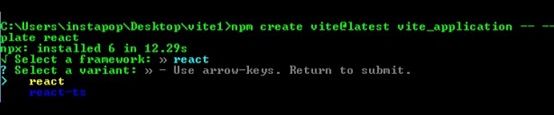
Next, run the following commands to finish the installation:
cd vite_applicationnpm install
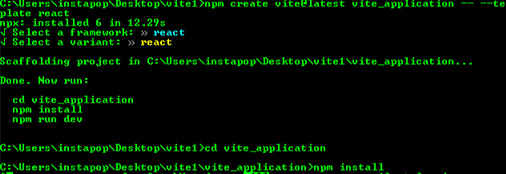
The installation may take a few minutes, so just wait until it's completed.
To run your Vite application on the terminal, navigate to the application folder (vite_application) and then run the dev command below to start the development server:
npm run dev
Running the above command will start the development server. Then open your terminal and enter http://localhost:3000.
You should see something like this in the browser:
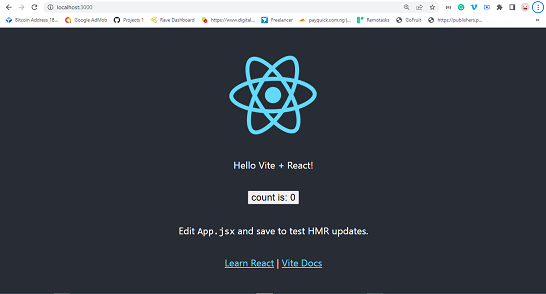 React application
React application
Let's have a look at how Vite application folders are organized. We'll also look at a few of the folders and files in detail.
Note: if you are using a different framework and template, the file name will not be the same.
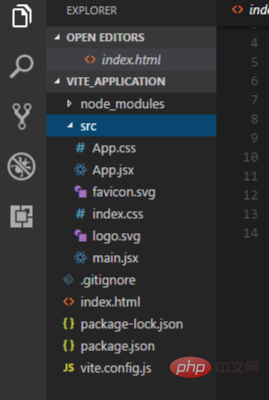
Vite folder structure
The node_modules folder contains all the necessary dependencies for the application, which are specified in the package.json file.
All of the configured dependencies in package.json will be downloaded into the node_modules folder once the npm install command is run.
When pushing your source code to GitHub, you don't need to push the node_modules folder because users can install all the necessary dependencies used in your application through the package.json.
You can find the package.json file in the application parent's root directory.
The src folder is one of the folder that we interact with most when developing Vite applications. This folder contains app.jsx, main.jsx, app.css and index.js.
All of your application's assets, such as images, videos, and other files, must be stored in the src folder because Vite automatically rebases all URLs inside index.html.
The app.jsx file is the base component that serves as a container for all of the other components used in the application.
The main.jsx file is where you target the root id from the index.html and render all the components used in the application.
These files contain all of the CSS styles used in the program. You can add your own CSS file or change the style.
The above is the detailed content of Vite.js Tutorial – How to Install and Use Vite in Your Web Projects. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 How to modify the text on the picture
How to modify the text on the picture
 The difference between computer hibernation and sleep
The difference between computer hibernation and sleep
 What currency is MULTI?
What currency is MULTI?
 What does electronic components mean?
What does electronic components mean?
 Solution to missing xlive.dll
Solution to missing xlive.dll
 What is disk quota
What is disk quota
 How to clean up your computer's C drive when it's full
How to clean up your computer's C drive when it's full
 The difference between * and & in C language
The difference between * and & in C language




