
Have you ever wondered how search engines can find information in a bunch of text almost instantly? Behind the "magic", there are structures and algorithms that index and retrieve this information. One of the most popular tools for this is Apache Lucene.
And who is Apache Lucene?
Lucene is an open-source library written in Java, used for indexing and searching text and its implementation is the basis for other projects and platforms, such as ElasticSearch and Solr.
And to illustrate the concepts of Lucene I decided to implement a simplified version in Python.
How does the search technique work?
The search technique used follows the following steps:


The query is subjected to the same process of tokenization, normalization, removal of stop words and stemming that documents went through during indexing.

For each term processed in the query, we retrieve the documents where the term appears, along with the TF-IDF weight calculated during indexing.

Term scores are summed for each document, reflecting the relevance of the document to all terms in the query.
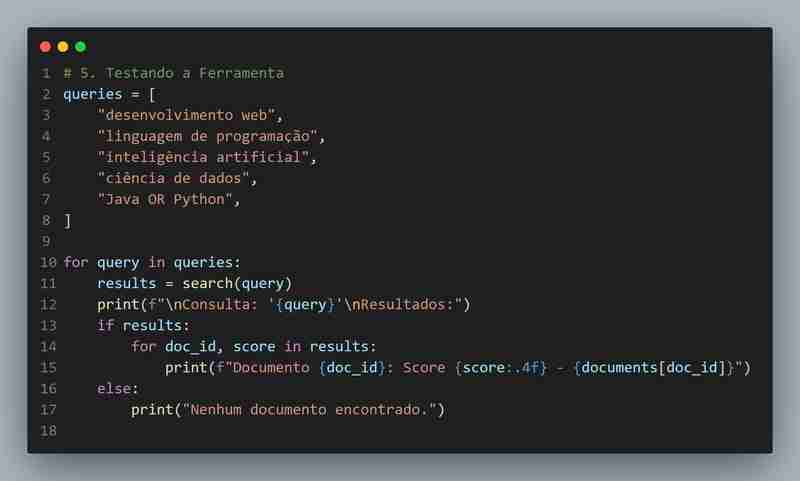
Documents are sorted descending based on total score, ensuring the most relevant results are presented first.
Result

Repository link on GitHub?
https://github.com/joaodest/Artigos/lucene.py
The above is the detailed content of Exploring Apache Lucene with Python: Understanding Search Engines. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Why is my phone not turned off but when someone calls me it prompts me to turn it off?
Why is my phone not turned off but when someone calls me it prompts me to turn it off?
 How to set up hibernation in Win7 system
How to set up hibernation in Win7 system
 What does Jingdong plus mean?
What does Jingdong plus mean?
 The difference between cellpadding and cellspacing
The difference between cellpadding and cellspacing
 Sublime input Chinese method
Sublime input Chinese method
 How to solve garbled characters in PHP
How to solve garbled characters in PHP
 What currency is USDT?
What currency is USDT?
 rtmp server
rtmp server
 What is digital currency
What is digital currency




