Data Structures & Algorithm Linked List
1일차
기본 데이터 구조
우리는 전통적인 방식으로 연결 목록에 대해 배우는 것이 아닙니다. 또한 Node 및 LinkedList 클래스가 무엇인지, 그리고 이들 클래스에서 수행할 수 있는 모든 작업도 살펴보겠습니다.
연결 목록이란 무엇입니까?
연결된 목록은 노드라는 요소의 모음입니다. 각 노드에는 데이터 요소와 시퀀스의 다음 노드에 대한 참조(또는 링크)가 포함되어 있습니다.
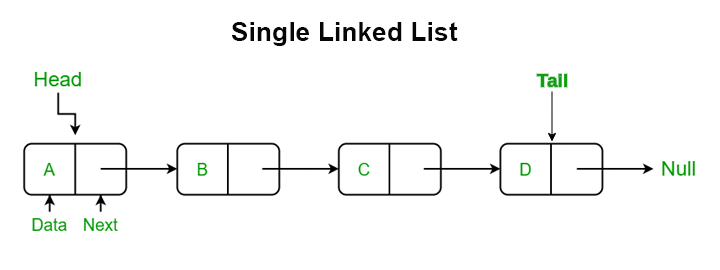
연결된 목록은 요소가 노드에 저장되는 선형 데이터 구조입니다. 각 노드에는 두 부분이 포함됩니다.
배열과 달리 *연결된 목록은 인접한 메모리 위치에 요소를 저장하지 않습니다.
* 대신 각 노드가 다음 노드를 가리키므로 동적 메모리 사용이 가능하고 요소를 쉽게 삽입하거나 삭제할 수 있습니다.
연결리스트의 핵심
1. 노드 구조: 연결된 목록은 노드로 구성되며 각 노드에는 값과 다음 노드에 대한 참조가 포함됩니다. 노드의 구조와 속성을 탐색하면 연결된 목록이 데이터를 구성하고 저장하는 방법을 이해하는 데 도움이 됩니다.
2. 헤드 및 테일: 연결 리스트의 첫 번째 노드를 헤드라고 하고 마지막 노드를 테일이라고 합니다. 연결된 목록을 효율적으로 탐색하고 조작하려면 헤드 및 테일 노드의 특성과 기능을 이해하는 것이 중요합니다.
주요 특징:
동적 크기: 필요에 따라 늘리거나 줄일 수 있습니다.
순차 액세스: 요소에 액세스하려면 첫 번째 노드(헤드)에서 순회해야 합니다.
연결 목록의 유형:
연결 목록에는 세 가지 기본 형태가 있습니다
1. 단일 연결 목록
2. 이중 연결 목록
3. 순환 연결 목록.
이 글에서는 단일 연결 목록을 살펴보겠습니다.
단일 연결 목록.
각 노드에는 다음 노드에 대한 참조가 있습니다.
- 각 노드에는 다음이 포함됩니다.
- 데이터(저장하려는 값).
- 시퀀스의 다음 노드를 가리키는 다음 포인터.
- 마지막 노드의 다음 포인터는 그 뒤에 노드가 없기 때문에 null입니다.
실제 비유: 화살 – 화살은 한번 발사되면 앞으로만 나아갈 수 있습니다.
한번 발사된 화살은 되돌아오지 못한 채 직선으로 날아갑니다.
마찬가지로, 단일 연결 목록에서는 한 노드에서 다음 노드로 이동하면 뒤로 돌아갈 수 없으며 앞으로만 계속 이동할 수 있습니다.
[Data | Next] -> [Data | Next] -> [Data | Next] -> null
단일 연결 목록의 작업
- 순회
- 검색 중
- 길이
- 삽입:
- 처음에 삽입
- 마지막에 삽입
- 특정 위치에 삽입
- 삭제:
- 처음부터 삭제
- 끝부터 삭제
- 특정 노드 삭제
삽입:
처음에 삽입
Node 클래스를 만들어 보겠습니다
class Node {
constructor(data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
Node 클래스를 분해해 보겠습니다.
**Node 클래스는 연결 목록의 각 개별 요소를 나타냅니다. 각 노드에는 두 가지 속성이 포함되어 있습니다.
속성:
- 데이터: 노드에 저장된 값(예: 숫자, 문자열 또는 객체)을 보유합니다.
- 다음: 연결된 목록의 다음 노드에 대한 참조(또는 포인터)를 보유합니다. 처음에는 노드가 생성될 때 아직 다른 노드에 연결되지 않았기 때문에 null로 설정됩니다.
고장:
생성자(생성자(데이터)):
이는 Node 클래스의 새 인스턴스가 생성될 때 호출되는 JavaScript 클래스의 특수 메소드입니다.
data 매개변수는 새 노드 생성 시 전달되며, 해당 노드의 실제 값을 저장합니다.
this.next = null; 노드가 생성될 때 아직 다른 노드에 연결되지 않았기 때문에 다음 속성을 처음에 null로 설정합니다.
예:
let node1 = new Node(10); // Create a node with the value 10 console.log(node1.data); // Output: 10 console.log(node1.next); // Output: null (because it's not linked to any other node yet)
SingleLinkList 클래스를 만들어 보겠습니다
class SinglyLinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null; // Initially, the list is empty, so the head is null.
this.size = 0; // The size is initially 0, as there are no nodes in the list.
}
// Insert at the beginning
insertAtBeginning(data) {
let newNode = new Node(data); // Create a new node with the given data
newNode.next = this.head; // The new node's next points to the current head
this.head = newNode; // Update the head to be the new node
this.size++; // Increment the size of the list
}
}
SinglyLinkedList 클래스는 전체 연결 목록 구조를 나타냅니다. 여러 Node 객체를 관리하고 노드 삽입, 삭제, 순회 등 목록 작업 방법을 제공합니다.
속성:
- 헤드: 연결 리스트의 첫 번째 노드(또는 "헤드")에 대한 참조입니다. 처음에는 목록이 비어 있음을 의미하는 null로 설정되어 있습니다.
- 크기: 현재 연결 목록에 있는 노드 수를 추적합니다. 처음에는 목록이 비어 있으므로 0으로 설정되어 있습니다.
고장:
생성자(constructor()):
this.head = null;: This initializes the linked list with no elements, so the head points to null.
this.size = 0;: The size starts as 0 because there are no nodes in the list.
insertAtBeginning(data): for the sake of simplicity, later on, we will Deep Dive into the insertAtBeginning(data) method
let newNode = new Node(data);: This creates a new node with the value passed in as data.
newNode.next = this.head;: This links the new node to the current head (which could be nullif the list is empty or point to an existing node if the list has elements).
this.head = newNode;: This updates the head of the list to point to the new node, making it the first node in the list.
this.size++;: The size of the linked list is increased by 1 as a new node has been added.
let's Test
let list = new SinglyLinkedList(); list.insertAtBeginning(10); // List becomes: 10 list.insertAtBeginning(20); // List becomes: 20 -> 10 console.log(list.head.data); // Output: 20 (since the head is now the first node with value 20) console.log(list.size); // Output: 2 (since there are two nodes in the list)
Linked List deep dive Line by Line.
let's jump into the insertAtBeginning(data) method .
class Node {
constructor(data) {
this.data = data; // Store the data value (like 10, 20, etc.)
this.next = null; // Initialize the next pointer as null
}
}
class SinglyLinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null; // Initially, the list is empty, so the head is null
this.size = 0; // The size of the list starts at 0
}
// Insert at the beginning of the list
insertAtBeginning(data) {
// Step 1: Create a new node with the given data
let newNode = new Node(data);
// Explanation:
// First time: If we insert 10, the newNode looks like this -> Node { data: 10, next: null }
// Second time: If we insert 20, the newNode looks like this -> Node { data: 20, next: null }
// Step 2: Point the new node's next property to the current head of the list
newNode.next = this.head;
// Explanation:
// First time: Since the list is empty (this.head is null), newNode's next is set to null.
// Second time: this.head is now the node with data 10, so newNode’s next will point to the node with data 10.
// So it looks like this: Node { data: 20, next: Node { data: 10, next: null } }
// Step 3: Make the new node the new head of the list
this.head = newNode;
// Explanation:
// First time: Now, the new node becomes the head. The list looks like this: Node { data: 10, next: null }.
// Second time: The new node (with data 20) becomes the head, and it points to the previous head (which is the node with data 10).
// Step 4: Increment the size of the list
this.size++;
// Explanation:
// First time: The size is now 1 because there is one node (data 10).
// Second time: The size becomes 2 because we added another node (data 20).
}
}
// Example Usage:
let list = new SinglyLinkedList();
list.insertAtBeginning(10); // First insertion: the list becomes [10]
list.insertAtBeginning(20); // Second insertion: the list becomes [20 -> 10]
console.log(list);
// Output:
// SinglyLinkedList {
// head: Node { data: 20, next: Node { data: 10, next: null } },
// size: 2
// }
Coming soon...
The above is the detailed content of Data Structures & Algorithm Linked List. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1664
1664
 14
14
 1421
1421
 52
52
 1315
1315
 25
25
 1266
1266
 29
29
 1239
1239
 24
24
 Demystifying JavaScript: What It Does and Why It Matters
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Demystifying JavaScript: What It Does and Why It Matters
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:07 AM
JavaScript is the cornerstone of modern web development, and its main functions include event-driven programming, dynamic content generation and asynchronous programming. 1) Event-driven programming allows web pages to change dynamically according to user operations. 2) Dynamic content generation allows page content to be adjusted according to conditions. 3) Asynchronous programming ensures that the user interface is not blocked. JavaScript is widely used in web interaction, single-page application and server-side development, greatly improving the flexibility of user experience and cross-platform development.
 The Evolution of JavaScript: Current Trends and Future Prospects
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:33 AM
The Evolution of JavaScript: Current Trends and Future Prospects
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:33 AM
The latest trends in JavaScript include the rise of TypeScript, the popularity of modern frameworks and libraries, and the application of WebAssembly. Future prospects cover more powerful type systems, the development of server-side JavaScript, the expansion of artificial intelligence and machine learning, and the potential of IoT and edge computing.
 JavaScript Engines: Comparing Implementations
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AM
JavaScript Engines: Comparing Implementations
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Different JavaScript engines have different effects when parsing and executing JavaScript code, because the implementation principles and optimization strategies of each engine differ. 1. Lexical analysis: convert source code into lexical unit. 2. Grammar analysis: Generate an abstract syntax tree. 3. Optimization and compilation: Generate machine code through the JIT compiler. 4. Execute: Run the machine code. V8 engine optimizes through instant compilation and hidden class, SpiderMonkey uses a type inference system, resulting in different performance performance on the same code.
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 JavaScript: Exploring the Versatility of a Web Language
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:01 AM
JavaScript: Exploring the Versatility of a Web Language
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:01 AM
JavaScript is the core language of modern web development and is widely used for its diversity and flexibility. 1) Front-end development: build dynamic web pages and single-page applications through DOM operations and modern frameworks (such as React, Vue.js, Angular). 2) Server-side development: Node.js uses a non-blocking I/O model to handle high concurrency and real-time applications. 3) Mobile and desktop application development: cross-platform development is realized through ReactNative and Electron to improve development efficiency.
 How to Build a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Frontend Integration)
Apr 11, 2025 am 08:22 AM
How to Build a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Frontend Integration)
Apr 11, 2025 am 08:22 AM
This article demonstrates frontend integration with a backend secured by Permit, building a functional EdTech SaaS application using Next.js. The frontend fetches user permissions to control UI visibility and ensures API requests adhere to role-base
 From C/C to JavaScript: How It All Works
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AM
From C/C to JavaScript: How It All Works
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AM
The shift from C/C to JavaScript requires adapting to dynamic typing, garbage collection and asynchronous programming. 1) C/C is a statically typed language that requires manual memory management, while JavaScript is dynamically typed and garbage collection is automatically processed. 2) C/C needs to be compiled into machine code, while JavaScript is an interpreted language. 3) JavaScript introduces concepts such as closures, prototype chains and Promise, which enhances flexibility and asynchronous programming capabilities.
 Building a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Backend Integration)
Apr 11, 2025 am 08:23 AM
Building a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Backend Integration)
Apr 11, 2025 am 08:23 AM
I built a functional multi-tenant SaaS application (an EdTech app) with your everyday tech tool and you can do the same. First, what’s a multi-tenant SaaS application? Multi-tenant SaaS applications let you serve multiple customers from a sing




