Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 Building a drone navigation system using matplotlib and A* algorithm
Building a drone navigation system using matplotlib and A* algorithm
Building a drone navigation system using matplotlib and A* algorithm
Nov 29, 2024 am 04:59 AMHave you ever wondered how drones navigate through complex environments? In this blog, we’ll create a simple drone navigation system using Python, Matplotlib, and the A* algorithm. By the end, you’ll have a working system that visualizes a drone solving a maze!
What You'll Learn
- Basic AI terminologies like "agent" and "environment."
- How to create and visualize a maze with Python.
- How the A* algorithm works to solve navigation problems.
- How to implement and visualize the drone's path.
Introduction
To build our drone navigation system, we need the following:
- An agent: The drone ?.
- A path: A 2D maze that the drone will navigate through ?️.
- A search algorithm: The A* algorithm ⭐.
But first, let’s quickly review some basic AI terms for those who are new.
Key AI Terms
- Agent: An entity (like our drone) that perceives its environment (maze) and takes actions to achieve a goal (reaching the end of the maze).
- Environment: The world in which the agent operates, here represented as a 2D maze.
- Heuristic: A rule of thumb or an estimate used to guide the search (like measuring distance to the goal).
The System Design
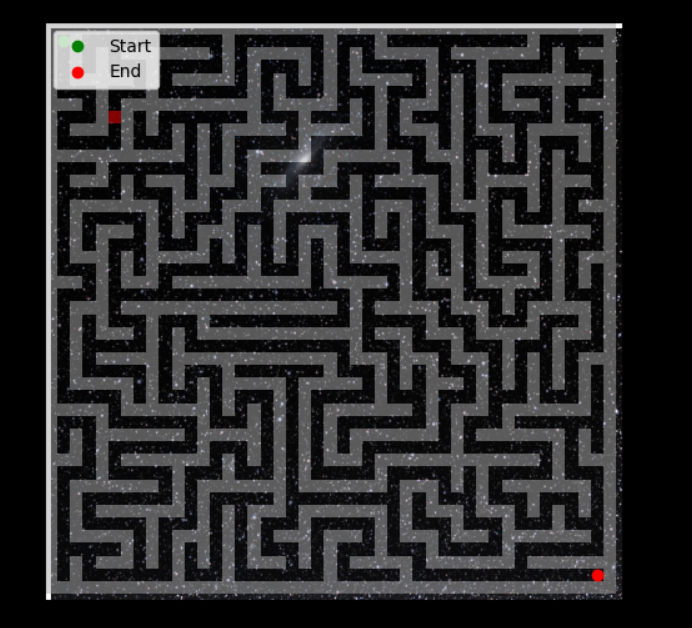
Our drone will navigate a 2D maze. The maze will consist of:
- Walls (impassable regions represented by 1s).
- Paths (open spaces represented by 0s).
The drone’s objectives:
- Avoid walls.?
- Reach the end of the path.?
Here’s what the maze looks like:
Step 1: Setting Up the Maze
Import Required Libraries
First, install and import the required libraries:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np import random import math from heapq import heappop, heappush
Define Maze Dimensions
Let’s define the maze size:
python
WIDTH, HEIGHT = 22, 22
Set Directions and Weights
In real-world navigation, movement in different directions can have varying costs. For example, moving north might be harder than moving east.
DIRECTIONAL_WEIGHTS = {'N': 1.2, 'S': 1.0, 'E': 1.5, 'W': 1.3}
DIRECTIONS = {'N': (-1, 0), 'S': (1, 0), 'E': (0, 1), 'W': (0, -1)}
Initialize the Maze Grid
We start with a grid filled with walls (1s):
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np import random import math from heapq import heappop, heappush
The numpy. ones() function is used to create a new array of given shape and type, filled with ones... useful in initializing an array with default values.
Step 2: Carving the Maze
Now let's define a function that will "carve" out paths in your maze which is right now initialized with just walls
DIRECTIONAL_WEIGHTS = {'N': 1.2, 'S': 1.0, 'E': 1.5, 'W': 1.3}
DIRECTIONS = {'N': (-1, 0), 'S': (1, 0), 'E': (0, 1), 'W': (0, -1)}
Define Start and End Points
maze = np.ones((2 * WIDTH + 1, 2 * HEIGHT + 1), dtype=int)
Step 3: Visualizing the Maze
Use Matplotlib to display the maze:
def carve(x, y):
maze[2 * x + 1, 2 * y + 1] = 0 # Mark current cell as a path
directions = list(DIRECTIONS.items())
random.shuffle(directions) # Randomize directions
for _, (dx, dy) in directions:
nx, ny = x + dx, y + dy
if 0 <= nx < WIDTH and 0 <= ny < HEIGHT and maze[2 * nx + 1, 2 * ny + 1] == 1:
maze[2 * x + 1 + dx, 2 * y + 1 + dy] = 0
carve(nx, ny)
carve(0, 0) # Start carving from the top-left corner
Step 4: Solving the Maze with A*
The A* algorithm finds the shortest path in a weighted maze using a combination of path cost and heuristic.
Define the Heuristic
We use the Euclidean distance as our heuristic:
start = (1, 1) end = (2 * WIDTH - 1, 2 * HEIGHT - 1) maze[start] = 0 maze[end] = 0
A* Algorithm Implementation
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 6))
ax.imshow(maze, cmap='binary', interpolation='nearest')
ax.set_title("2D Maze")
plt.show()
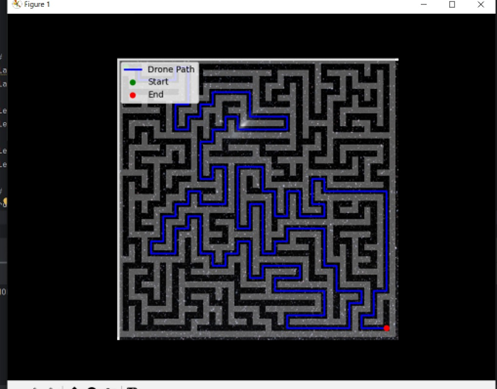
Step 5: Visualizing the Solution
We've got the maze but you can't yet see the drone's path yet.
Lets visualize the drone’s path:
def heuristic(a, b):
return math.sqrt((a[0] - b[0]) ** 2 + (a[1] - b[1]) ** 2)
Conclusion
Congratulations! ? You’ve built a working drone navigation system that:
- Generates a 2D maze.
- Solves it using the A* algorithm.
- Visualizes the shortest path.

Next Steps
- Experiment with different maze sizes and weights.
- Try other heuristics like Manhattan distance.
- Visualize a 3D maze for more complexity!
Feel free to share your results or ask questions in the comments below.
To infinity and beyond ?
The above is the detailed content of Building a drone navigation system using matplotlib and A* algorithm. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot Article

Hot tools Tags

Hot Article

Hot Article Tags

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to Use Python to Find the Zipf Distribution of a Text File
Mar 05, 2025 am 09:58 AM
How to Use Python to Find the Zipf Distribution of a Text File
Mar 05, 2025 am 09:58 AM
How to Use Python to Find the Zipf Distribution of a Text File
 How Do I Use Beautiful Soup to Parse HTML?
Mar 10, 2025 pm 06:54 PM
How Do I Use Beautiful Soup to Parse HTML?
Mar 10, 2025 pm 06:54 PM
How Do I Use Beautiful Soup to Parse HTML?
 How to Perform Deep Learning with TensorFlow or PyTorch?
Mar 10, 2025 pm 06:52 PM
How to Perform Deep Learning with TensorFlow or PyTorch?
Mar 10, 2025 pm 06:52 PM
How to Perform Deep Learning with TensorFlow or PyTorch?
 Introduction to Parallel and Concurrent Programming in Python
Mar 03, 2025 am 10:32 AM
Introduction to Parallel and Concurrent Programming in Python
Mar 03, 2025 am 10:32 AM
Introduction to Parallel and Concurrent Programming in Python
 Serialization and Deserialization of Python Objects: Part 1
Mar 08, 2025 am 09:39 AM
Serialization and Deserialization of Python Objects: Part 1
Mar 08, 2025 am 09:39 AM
Serialization and Deserialization of Python Objects: Part 1
 How to Implement Your Own Data Structure in Python
Mar 03, 2025 am 09:28 AM
How to Implement Your Own Data Structure in Python
Mar 03, 2025 am 09:28 AM
How to Implement Your Own Data Structure in Python
 Mathematical Modules in Python: Statistics
Mar 09, 2025 am 11:40 AM
Mathematical Modules in Python: Statistics
Mar 09, 2025 am 11:40 AM
Mathematical Modules in Python: Statistics