
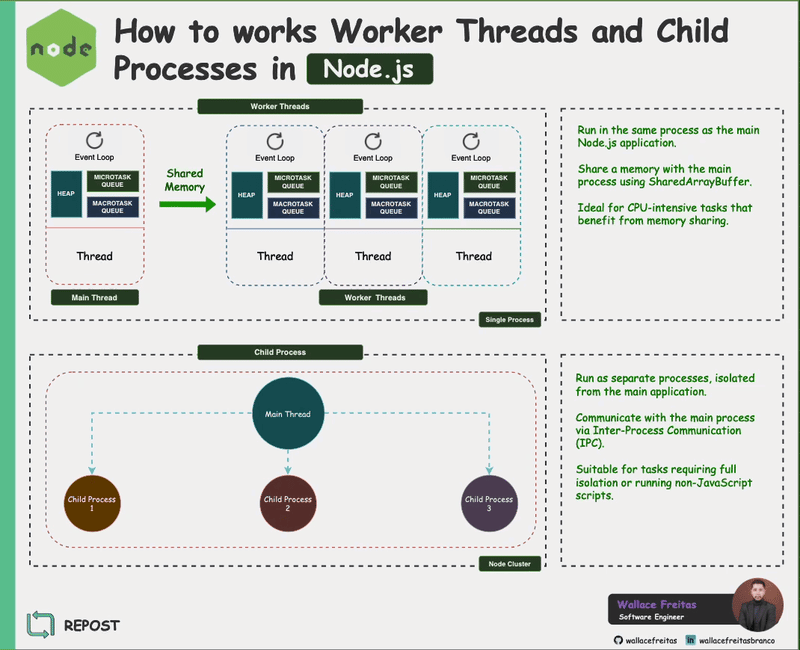
Worker Threads allow you to run JavaScript code in multiple threads. They are ideal for sharing memory between threads via SharedArrayBuffer and for offloading CPU-bound tasks like data processing or computations.
Child Processes
Child Processes enable you to spawn separate processes to run tasks independently from the main Node.js process. They are suitable for tasks requiring isolation or when working with non-JavaScript scripts or binaries.
Real-Life Use Cases for Worker Threads
1️⃣ Image Processing
When handling large-scale image transformations, such as resizing, cropping, or applying filters, Worker Threads can offload these tasks to a separate thread to prevent the main event loop from blocking.
Example:
const { Worker } = require('worker_threads');
function resizeImage(imagePath) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const worker = new Worker('./resizeWorker.js', { workerData: imagePath });
worker.on('message', resolve);
worker.on('error', reject);
});
}
// Usage
resizeImage('image.jpg').then(() => console.log('Image resized!'));
2️⃣ Data Parsing and Transformation
Parsing large JSON files or transforming CSV data can be resource-intensive. Worker Threads can process the data in chunks, ensuring the application remains responsive.
Example:
const { Worker } = require('worker_threads');
const worker = new Worker('./dataParser.js');
worker.postMessage({ filePath: 'largeData.json' });
worker.on('message', (data) => {
console.log('Parsed Data:', data);
});
3️⃣ Mathematical Computations
Worker Threads are excellent for heavy computations, such as generating prime numbers, matrix multiplications, or simulations.
Example:
const { Worker } = require('worker_threads');
function calculatePrimes(limit) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const worker = new Worker('./primeWorker.js', { workerData: limit });
worker.on('message', resolve);
worker.on('error', reject);
});
}
// Usage
calculatePrimes(100000).then(primes => console.log(primes));
Real-Life Use Cases for Child Processes
1️⃣ Executing Shell Commands
When your application needs to interact with the system by running shell commands, Child Processes are the go-to choice.
Example:
const { exec } = require('child_process');
exec('ls -l', (error, stdout, stderr) => {
if (error) {
console.error(`Error: ${error.message}`);
return;
}
console.log(`Output:\n${stdout}`);
});
2️⃣ Running Non-JavaScript Scripts
If your workflow involves Python, Ruby, or other scripting languages, you can use Child Processes to execute these scripts and handle their output.
Example:
const { spawn } = require('child_process');
const pythonProcess = spawn('python', ['script.py']);
pythonProcess.stdout.on('data', (data) => {
console.log(`Output: ${data}`);
});
3️⃣ Microservices Architecture
In a microservices-like approach, you can use Child Processes to handle isolated, independent tasks that communicate with the main process via IPC (Inter-Process Communication).
Example:
const { fork } = require('child_process');
const child = fork('./childService.js');
child.on('message', (message) => {
console.log('Message from child:', message);
});
// Send a task to the child process
child.send({ task: 'processData', payload: [1, 2, 3] });
Choosing Between Worker Threads and Child Processes
| Feature | Worker Threads | Child Processes |
|---|---|---|
| Memory Sharing | Supported via SharedArrayBuffer | Not supported |
| Task Isolation | Shared environment, less isolated | Fully isolated |
| Use Case | CPU-intensive tasks in JavaScript | System-level tasks or external code |
| Overhead | Lower (same process) | Higher (separate processes) |
| Communication | Via message passing, faster | Via IPC, slower |
| Supported Languages | JavaScript/Node.js only | Any scripting or system-level language |
| Startup Time | Faster | Slower |
| Error Containment | Less contained, can crash the process | Fully contained, isolated failures |
Best Practices for Using Worker Threads and Child Processes
✓ Offload Intensive Tasks: Use Worker Threads for CPU-bound tasks and Child Processes for I/O-heavy operations or external script execution.
✓ Monitor Performance: Use tools like Node.js’s built-in profiler to identify bottlenecks.
✓ Handle Errors Gracefully: Always listen for error and exit events to handle failures.
✓ Scale Effectively: Use worker pools or process clusters to distribute tasks across multiple threads or processes.
Conclusion
Worker Threads and Child Processes empower Node.js developers to break free from the limitations of the single-threaded event loop. By leveraging these tools, you can build highly scalable and responsive applications that handle both CPU and I/O-intensive tasks with ease. Whether you’re processing images, executing shell commands, or managing microservices, understanding when to use Worker Threads and Child Processes is key to optimizing performance in your Node.js applications.
The above is the detailed content of Understanding Worker Threads and Child Processes. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




