Building Responsible AI Agents: Balancing Innovation and Ethics
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming industries, with autonomous AI agents like Salesforce’s AgentForce and open-source tools like AutoGPT leading the charge. These agents automate complex tasks, collaborate with other systems, and enhance productivity. However, as they become more autonomous, the need for responsible AI development is critical to address issues like bias, transparency, and accountability.
The rapid adoption of AI agents has sparked debates about their ethical implications. While they offer immense potential to revolutionize industries like healthcare, education, and sales, they also pose risks if not designed responsibly. Developers, organizations, and governments must work together to ensure these systems are both innovative and ethical.
What Does It Mean to Build Responsible AI Agents?
Responsible AI agents are designed to be ethical, transparent, and accountable, ensuring they align with human values and minimize harm. These agents must operate fairly, respect privacy, and provide clear explanations for their decisions.
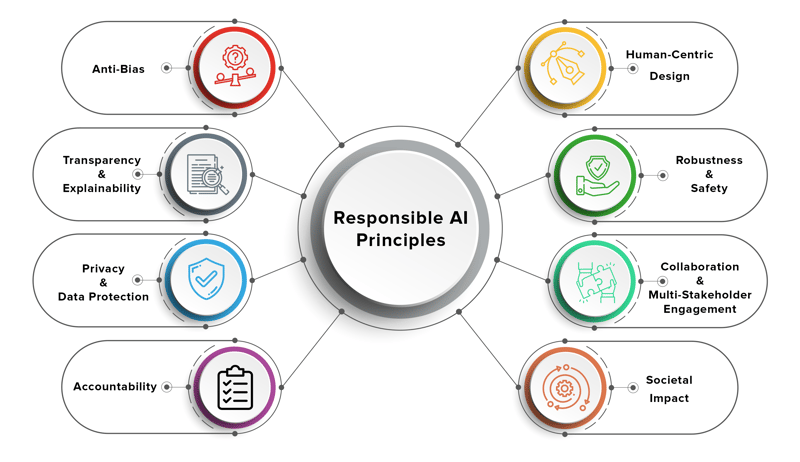
Key principles of responsible AI include:
- Fairness: Avoiding bias in decision-making and ensuring equitable outcomes for all users.
- Transparency: Making AI decisions understandable to users and stakeholders.
- Accountability: Establishing responsibility for AI outcomes and ensuring systems can be audited.
- Privacy: Protecting user data and ensuring secure operations.
- Sustainability: Designing AI systems that are energy-efficient and environmentally friendly.
Building responsible AI is not just a technical challenge—it’s a multidisciplinary effort that requires collaboration between developers, ethicists, policymakers, and end-users.

Examples of Ethical Dilemmas in AI Systems
As AI agents become more autonomous, they face ethical dilemmas that challenge their design and deployment. Here are some real-world examples:

1. Bias in Decision-Making
AI agents trained on biased datasets can make discriminatory decisions. For example:
- A hiring agent might favor certain demographics over others due to historical biases in recruitment data.
- A financial AI agent might deny loans to specific groups based on biased credit scoring models.
2. Lack of Transparency
Many AI agents operate as "black boxes," making decisions that are difficult to interpret or explain. For instance:
- A customer service AI agent might escalate or resolve issues without providing clear reasoning, leading to frustration and mistrust among users.
3. Accountability Gaps
When an AI agent makes a mistake, who is responsible? For example:
- If an autonomous vehicle controlled by an AI agent causes an accident, is the blame on the developer, the manufacturer, or the user?
4. Privacy Violations
AI agents often require access to sensitive user data to function effectively. However:
- A sales AI agent might inadvertently share confidential customer information, violating privacy laws like GDPR.
5. Ethical Use of AI in Sales and Marketing
Tools like Salesforce’s AgentForce are transforming sales and marketing by automating lead generation and customer engagement. However:
- If an AI agent uses manipulative tactics to upsell products, it raises questions about ethical marketing practices.
These dilemmas highlight the importance of embedding ethical considerations into the design and deployment of AI agents.
Frameworks and Best Practices for Responsible AI Development
To address these challenges, developers and organizations can adopt the following frameworks and best practices:
1. Ethical AI Frameworks
Several organizations have developed guidelines for responsible AI, including:
- Google’s AI Principles: Focused on fairness, privacy, and accountability.
- OECD AI Principles: Emphasizing human-centered values and transparency.
- Salesforce’s Ethical AI Guidelines: Aimed at building trust and ensuring fairness in AI systems.
2. Bias Mitigation
- Use diverse and representative datasets to train AI agents.
- Regularly audit AI models for bias and retrain them as needed.
- Implement fairness metrics to evaluate the impact of AI decisions on different groups.
3. Explainability and Transparency
- Use techniques like S*HAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations)* or LIME (Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations) to make AI decisions interpretable.
- Provide users with clear explanations of how AI agents make decisions.
4. Accountability Mechanisms
- Establish clear governance structures for AI projects.
- Assign responsibility for AI outcomes to specific teams or individuals.
- Maintain detailed logs of AI agent actions for auditing purposes.
5. Privacy and Security
- Use encryption and secure protocols to protect user data.
- Implement differential privacy techniques to anonymize sensitive information.
- Comply with data protection regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
6. Continuous Monitoring and Feedback
- Monitor AI agents in real-time to detect and address issues.
- Collect user feedback to improve the performance and ethical alignment of AI agents.
- Regularly update AI models to reflect changing societal norms and values.
The Role of Stakeholders
Building responsible AI agents is a shared responsibility that requires collaboration across multiple stakeholders:
Governments
- Enact regulations to ensure AI systems are fair, transparent, and accountable.
- Promote research and development in ethical AI.
- Establish oversight bodies to monitor the deployment of AI agents.
Organizations
- Develop internal policies and guidelines for responsible AI.
- Invest in training programs to educate employees about ethical AI practices.
- Partner with academic institutions and nonprofits to advance ethical AI research.
Developers
- Prioritize ethical considerations during the design and development of AI agents.
- Advocate for responsible AI practices within their organizations.
- Stay informed about the latest advancements in ethical AI frameworks and tools.
Salesforce and AgentForce: A Case Study
Salesforce, a leader in customer relationship management (CRM), has been at the forefront of responsible AI development. Their AgentForce platform leverages AI agents to automate sales processes, improve customer engagement, and drive business growth.

What sets Salesforce apart is its commitment to ethical AI. The company has implemented robust guidelines to ensure that its AI systems are fair, transparent, and accountable. For example:
- Bias Detection: Salesforce uses tools to identify and mitigate bias in its AI models.
- Explainability: AgentForce provides users with clear insights into how AI-driven recommendations are made.
- Privacy: Salesforce ensures that customer data is handled securely and in compliance with global regulations.
By prioritizing responsible AI, Salesforce has set a benchmark for other organizations to follow.
Conclusion
As AI agents become more autonomous, balancing innovation with ethics is essential. By addressing issues like bias, transparency, and accountability, we can ensure that AI agents are not only innovative but also ethical.
Building responsible AI agents requires a collaborative effort between developers, organizations, and governments. By adopting ethical frameworks, mitigating bias, and ensuring transparency, we can create AI systems that benefit society while minimizing harm. Tools like Salesforce’s AgentForce demonstrate how responsible AI can drive innovation while maintaining trust and fairness.

The future of AI is bright, but it’s up to us to ensure that it’s also responsible.
The above is the detailed content of Building Responsible AI Agents: Balancing Innovation and Ethics. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1664
1664
 14
14
 1423
1423
 52
52
 1317
1317
 25
25
 1268
1268
 29
29
 1242
1242
 24
24
 Demystifying JavaScript: What It Does and Why It Matters
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:07 AM
Demystifying JavaScript: What It Does and Why It Matters
Apr 09, 2025 am 12:07 AM
JavaScript is the cornerstone of modern web development, and its main functions include event-driven programming, dynamic content generation and asynchronous programming. 1) Event-driven programming allows web pages to change dynamically according to user operations. 2) Dynamic content generation allows page content to be adjusted according to conditions. 3) Asynchronous programming ensures that the user interface is not blocked. JavaScript is widely used in web interaction, single-page application and server-side development, greatly improving the flexibility of user experience and cross-platform development.
 The Evolution of JavaScript: Current Trends and Future Prospects
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:33 AM
The Evolution of JavaScript: Current Trends and Future Prospects
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:33 AM
The latest trends in JavaScript include the rise of TypeScript, the popularity of modern frameworks and libraries, and the application of WebAssembly. Future prospects cover more powerful type systems, the development of server-side JavaScript, the expansion of artificial intelligence and machine learning, and the potential of IoT and edge computing.
 JavaScript Engines: Comparing Implementations
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AM
JavaScript Engines: Comparing Implementations
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:05 AM
Different JavaScript engines have different effects when parsing and executing JavaScript code, because the implementation principles and optimization strategies of each engine differ. 1. Lexical analysis: convert source code into lexical unit. 2. Grammar analysis: Generate an abstract syntax tree. 3. Optimization and compilation: Generate machine code through the JIT compiler. 4. Execute: Run the machine code. V8 engine optimizes through instant compilation and hidden class, SpiderMonkey uses a type inference system, resulting in different performance performance on the same code.
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 JavaScript: Exploring the Versatility of a Web Language
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:01 AM
JavaScript: Exploring the Versatility of a Web Language
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:01 AM
JavaScript is the core language of modern web development and is widely used for its diversity and flexibility. 1) Front-end development: build dynamic web pages and single-page applications through DOM operations and modern frameworks (such as React, Vue.js, Angular). 2) Server-side development: Node.js uses a non-blocking I/O model to handle high concurrency and real-time applications. 3) Mobile and desktop application development: cross-platform development is realized through ReactNative and Electron to improve development efficiency.
 How to Build a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Frontend Integration)
Apr 11, 2025 am 08:22 AM
How to Build a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Frontend Integration)
Apr 11, 2025 am 08:22 AM
This article demonstrates frontend integration with a backend secured by Permit, building a functional EdTech SaaS application using Next.js. The frontend fetches user permissions to control UI visibility and ensures API requests adhere to role-base
 Building a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Backend Integration)
Apr 11, 2025 am 08:23 AM
Building a Multi-Tenant SaaS Application with Next.js (Backend Integration)
Apr 11, 2025 am 08:23 AM
I built a functional multi-tenant SaaS application (an EdTech app) with your everyday tech tool and you can do the same. First, what’s a multi-tenant SaaS application? Multi-tenant SaaS applications let you serve multiple customers from a sing
 From C/C to JavaScript: How It All Works
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AM
From C/C to JavaScript: How It All Works
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:05 AM
The shift from C/C to JavaScript requires adapting to dynamic typing, garbage collection and asynchronous programming. 1) C/C is a statically typed language that requires manual memory management, while JavaScript is dynamically typed and garbage collection is automatically processed. 2) C/C needs to be compiled into machine code, while JavaScript is an interpreted language. 3) JavaScript introduces concepts such as closures, prototype chains and Promise, which enhances flexibility and asynchronous programming capabilities.




