 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 Code Your Diagrams: Automate Architecture with Python&#s Diagrams Library
Code Your Diagrams: Automate Architecture with Python&#s Diagrams Library
Code Your Diagrams: Automate Architecture with Python&#s Diagrams Library
Introduction
In the realm of modern infrastructure, where cloud services and microservices reign supreme, managing and visualizing complex architectures is more critical than ever.
Gone are the days of manually creating and updating architecture diagrams. With the Diagrams Python library, you can generate dynamic, code-driven diagrams that evolve alongside your infrastructure. A few lines of Python are all it takes to visualize cloud architectures, network topologies, or microservice interactions. Diagrams ensure your system documentation stays accurate and up-to-date, whether you’re managing multi-cloud deployments, Kubernetes clusters, or on-premise solutions. It’s an effortless way to keep your architecture in sync with your codebase.
In this post, we'll explore the capabilities of the Diagrams library, showcase how to create High-Level Designs (HLDs) for cloud infrastructure, and automate the process of creating architecture diagrams.
Why Use Diagrams Python Library?
- Automation: Generate architecture diagrams directly from your code, ensuring they stay up-to-date with the evolving system.
- Programmatic Control: Diagrams allows you to define your infrastructure visually with Python, offering fine control over how elements are represented.
- Supports Multiple Cloud Providers: The library supports AWS, Azure, GCP, and on-premise systems, making it a versatile tool for visualizing multi-cloud and hybrid architectures.
- Scalable: From small projects to large distributed systems, Diagrams can handle various levels of complexity.
Supported Providers
- OnPrem
- AWS
- Azure
- GCP
- IBM
- Kubernetes (K8s)
- AlibabaCloud
- OCI (Oracle Cloud Infrastructure)
- OpenStack
- Firebase
- DigitalOcean
- Elastic
- Outscale
- Generic
- Programming
- SaaS
- C4 Model
- Custom
Getting Started with Diagrams
To get started with Diagrams, you’ll need to install the library and set up your environment.
Step 0: Prerequisites
To create diagrams using the Diagrams Python library on MacOS/Windows, you'll need to install Graphviz first. Graphviz is the tool that the Diagrams library uses to generate the visual representations of your infrastructure.
- Mac
If you're on macOS, the easiest way to install Graphviz is using Homebrew:
brew install graphviz
- Windows
If you're on Windows, follow the below steps
- Download the Graphviz installer from the official website Graphviz Download Page.
- Run the installer and follow the installation steps.
- During installation, make sure to check the option that adds Graphviz to your system’s PATH.
Step 1: Installation
brew install graphviz
Step 2: Your First Diagram
Let’s create a simple diagram that represents a basic web architecture on AWS.
pip install diagrams
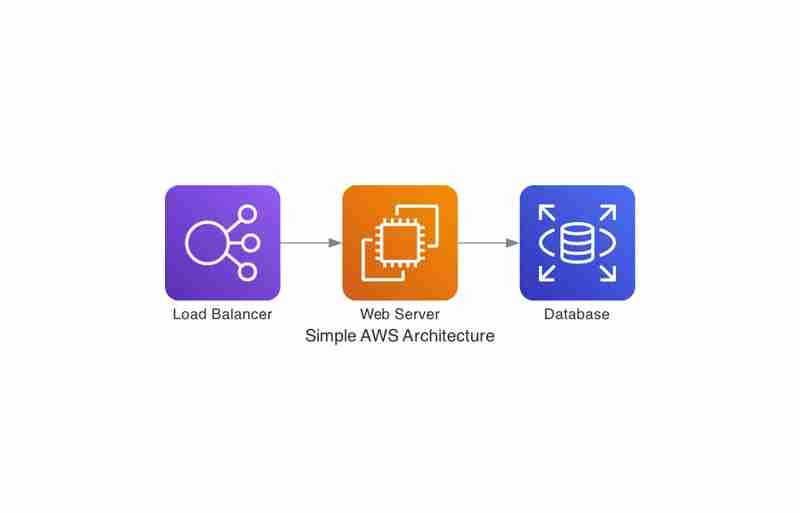
With this minimal code, you can visualize how traffic flows from the Load Balancer to the Web Server, and then to the Database. That’s the power of the Diagrams library: it's quick, intuitive, and highly customizable. And this is just the beginning—there are many more advanced features and components you can leverage, which we'll explore in the following sections.
Advanced Features
Grouping Components (Clustering)
You can group components into clusters to represent different tiers or logical groupings within your architecture.
from diagrams import Diagram
from diagrams.aws.compute import EC2
from diagrams.aws.network import ELB
from diagrams.aws.database import RDS
with Diagram("Simple AWS Architecture", show=False):
lb = ELB("Load Balancer")
web = EC2("Web Server")
db = RDS("Database")
lb >> web >> db
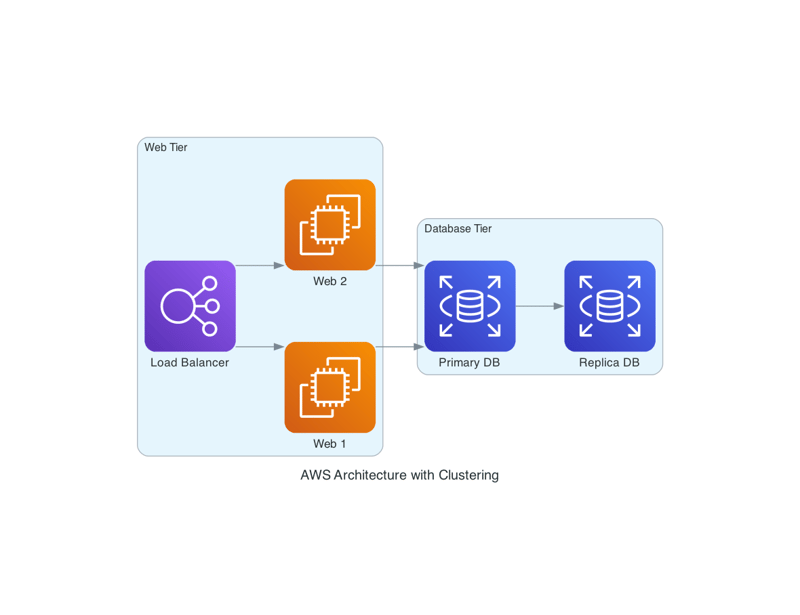
We use Cluster() to group web servers and databases, making the diagram easier to understand by visualizing tiers separately.
Customizing Components
Diagrams allow you to add custom labels, colors, and even custom images to represent specific components. For example, if you want to represent a custom service, you can include external images from local or even from remote.
- Using a Custom Icon from a Local Source
If you have an icon saved locally (for example, a custom_icon.png file), you can use it to represent your custom component in the diagram. The code below shows how to add a custom icon from your local filesystem.
from diagrams import Cluster, Diagram
from diagrams.aws.compute import EC2
from diagrams.aws.network import ELB
from diagrams.aws.database import RDS
with Diagram("AWS Architecture with Clustering", show=False):
with Cluster("Web Tier"):
lb = ELB("Load Balancer")
web_servers = [EC2("Web 1"), EC2("Web 2")]
with Cluster("Database Tier"):
db_primary = RDS("Primary DB")
db_replica = RDS("Replica DB")
lb >> web_servers >> db_primary
db_primary >> db_replica
./custom_icon.png is the path to your local image file.

- Using a Custom Icon from a Remote Source
Similarly, you can use an image from a remote source. Here's how you can download an image from a URL and use it in your diagram.
You can also use custom icons from a remote URL by giving the remote path to the files.
from diagrams.custom import Custom
with Diagram("Custom Service Architecture", show=False):
custom_service = Custom("My Custom Service", "./custom_icon.png")
This allows for even more flexibility in designing architecture that suits your organization's needs.
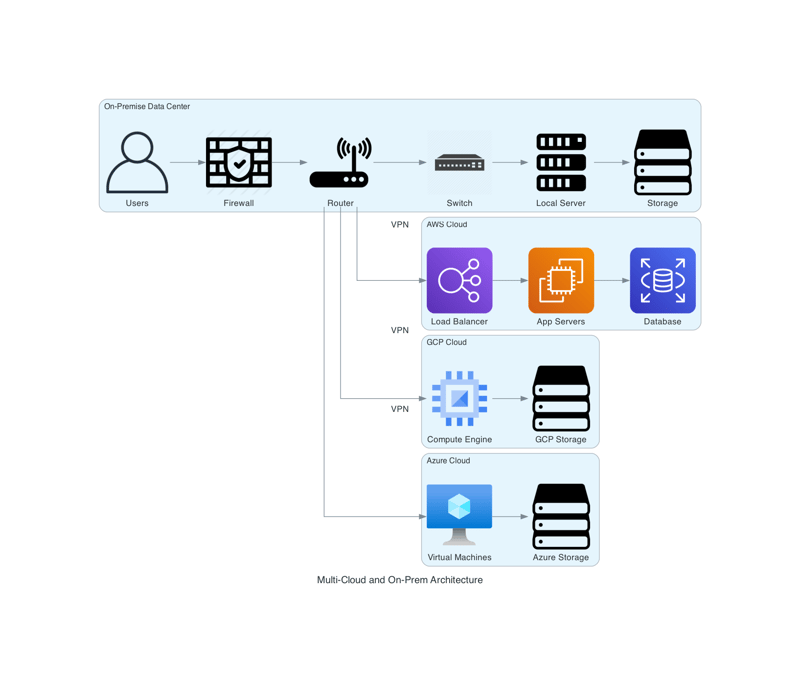
Combining Multi-Cloud and On-Premise Architectures
We can also use a combination of on-premise systems and cloud infrastructure, Diagrams makes it easy to combine these elements into a single view. You can visualize hybrid architectures seamlessly.
brew install graphviz
Challenges and Limitations
Although Diagrams is a powerful tool, there are some challenges:
- Performance: Generating very large diagrams with hundreds of components can be slow.
- Customization Limitations: While Diagrams offers a wide range of predefined components, adding highly customized elements might require extra work.
- Static Output: Diagrams generate static images. If you need interactive or real-time diagrams, you may need to integrate them with other tools.
Conclusion
The Diagrams Python library is a fantastic tool for automating the creation of infrastructure diagrams. By integrating it into your workflows, you can generate architecture diagrams dynamically as your infrastructure changes. Whether you’re documenting your cloud infrastructure or illustrating complex microservice architectures, Diagrams offers a powerful, programmatic way to visualize your systems

GitHub Repository
You can find the complete source code for the examples in this blog on my GitHub:
- My Diagrams Code Repository
Reference
- Diagrams: https://diagrams.mingrammer.com/docs/getting-started/installation
Disclaimer:
This is a personal blog. The views and opinions expressed here are only those of the author and do not represent those of any organization or any individual with whom the author may be associated, professionally or personally.
The above is the detailed content of Code Your Diagrams: Automate Architecture with Python&#s Diagrams Library. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1664
1664
 14
14
 1423
1423
 52
52
 1317
1317
 25
25
 1268
1268
 29
29
 1243
1243
 24
24
 Python vs. C : Applications and Use Cases Compared
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Python vs. C : Applications and Use Cases Compared
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Python is suitable for data science, web development and automation tasks, while C is suitable for system programming, game development and embedded systems. Python is known for its simplicity and powerful ecosystem, while C is known for its high performance and underlying control capabilities.
 Python: Games, GUIs, and More
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python: Games, GUIs, and More
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python excels in gaming and GUI development. 1) Game development uses Pygame, providing drawing, audio and other functions, which are suitable for creating 2D games. 2) GUI development can choose Tkinter or PyQt. Tkinter is simple and easy to use, PyQt has rich functions and is suitable for professional development.
 The 2-Hour Python Plan: A Realistic Approach
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:04 AM
The 2-Hour Python Plan: A Realistic Approach
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:04 AM
You can learn basic programming concepts and skills of Python within 2 hours. 1. Learn variables and data types, 2. Master control flow (conditional statements and loops), 3. Understand the definition and use of functions, 4. Quickly get started with Python programming through simple examples and code snippets.
 Python vs. C : Learning Curves and Ease of Use
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python vs. C : Learning Curves and Ease of Use
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Python is easier to learn and use, while C is more powerful but complex. 1. Python syntax is concise and suitable for beginners. Dynamic typing and automatic memory management make it easy to use, but may cause runtime errors. 2.C provides low-level control and advanced features, suitable for high-performance applications, but has a high learning threshold and requires manual memory and type safety management.
 How Much Python Can You Learn in 2 Hours?
Apr 09, 2025 pm 04:33 PM
How Much Python Can You Learn in 2 Hours?
Apr 09, 2025 pm 04:33 PM
You can learn the basics of Python within two hours. 1. Learn variables and data types, 2. Master control structures such as if statements and loops, 3. Understand the definition and use of functions. These will help you start writing simple Python programs.
 Python and Time: Making the Most of Your Study Time
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Python and Time: Making the Most of Your Study Time
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:02 AM
To maximize the efficiency of learning Python in a limited time, you can use Python's datetime, time, and schedule modules. 1. The datetime module is used to record and plan learning time. 2. The time module helps to set study and rest time. 3. The schedule module automatically arranges weekly learning tasks.
 Python: Exploring Its Primary Applications
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:41 AM
Python: Exploring Its Primary Applications
Apr 10, 2025 am 09:41 AM
Python is widely used in the fields of web development, data science, machine learning, automation and scripting. 1) In web development, Django and Flask frameworks simplify the development process. 2) In the fields of data science and machine learning, NumPy, Pandas, Scikit-learn and TensorFlow libraries provide strong support. 3) In terms of automation and scripting, Python is suitable for tasks such as automated testing and system management.
 Python: Automation, Scripting, and Task Management
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python: Automation, Scripting, and Task Management
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python excels in automation, scripting, and task management. 1) Automation: File backup is realized through standard libraries such as os and shutil. 2) Script writing: Use the psutil library to monitor system resources. 3) Task management: Use the schedule library to schedule tasks. Python's ease of use and rich library support makes it the preferred tool in these areas.



