I Build All My Calendars in Excel—Here's How You Can Too
Calendars are helpful for keeping track of critical dates, tasks, and appointments. While many digital calendar options exist, Excel allows you to create one that suits your style and schedule. With just a few clicks, you can build a custom calendar, either using a template or starting from scratch.
Why Build Calendars in Excel?
An Excel calendar functions like a regular calendar but is created using Microsoft Excel. It can be used to plan your day, week, or specific tasks, and it can even be printed if needed.
Adding a calendar to your Excel sheet helps in planning future activities. For example, if you run a business, you can track employee hours or determine who's available for certain tasks using an Excel calendar.
A weekly or monthly Excel calendar can also enhance team communication by providing everyone with a shared space to view schedules and make updates without constant back-and-forth communication. It's also useful for leaving notes or reminders.
Unlike regular calendars, Excel calendars offer more customization. You can resize rows and columns to fit your text, add colors, label projects or employees, and adjust fonts and styles to suit your needs.
Excel also provides a pre-built calendar template, which you can customize for personal or business use—whether it's for an academic schedule or a social media content calendar.
How to Build a Calendar in Excel
Creating a calendar in Excel is easy, and you can either use a template or design one from scratch. While templates are convenient, building a calendar from scratch enables you to personalize it according to your particular needs.
To begin, open Excel and leave the first row blank. In the second row, type the weekdays across the cells, starting with Monday in A2, Tuesday in B2, and continuing until Sunday in G2.

Alternatively, you can use Excel’s autofill feature by typing Monday in A2, and then dragging the fill handle to G2 to complete the week.
Now, create a month title. In cell A1 (in the first row), type the following formula to display the current month's name:
=TEXT(TODAY(), "mmmm")

Similarly, for the following month, use the EDATE function to add one month:
=TEXT(TODAY(), "mmmm")
Continue this pattern for all other months, increasing the second argument in EDATE by 1 each time.
Now, merge all the first-row columns from A1 to G1 by clicking "Merge & Center" in the Alignment menu.

Next, format all the grid columns of the calendar. Simply, select the cells from A2 to G8, then go to the "Home" tab. Then, under the Cells group, choose "Format" and set the column width and height to your preferred size.

Again, select all the cells from A3 to G8, go to the "Home" tab, and choose a background color.

Also, apply borders by opening the "Borders" menu and selecting "All Borders."

Lastly, input the days of the month. Identify which weekday the 1st of the month falls on, and enter the numbers in the corresponding cells.

Once you've completed one month, copy the worksheet to create the next. To do that, simply right-click the active sheet tab, choose "Move or Copy."

Check the "Create a copy" option and click "OK."

Rename the new sheet and adjust the dates accordingly. Repeat this process for all other months.
Additionally, you can display the current date in any cell outside the calendar grid. Simply click on a cell outside the grid and type =TODAY(). This will automatically update to show today’s date.
To print your calendar, go to File > Print, change the orientation to landscape.

Further, you can enable Gridlines to your printing calendar by going to Page Setup > Sheet > Gridlines.

Moreover, you can adjust the scaling as needed, so the entire calendar fits on one page.
Use Excel Calendar Templates
The simplest way to create a calendar in Excel is by importing a premade template. You can find both yearly and monthly calendars that can be customized for a specific year or reused. One feature I love about these Excel templates is how effortlessly they adjust the dates and days when you change the starting month or year.
While you can access templates from Microsoft’s website, Excel itself provides built-in templates. To access and use them, simply open Excel and navigate to the “File” tab. Then, go to the "New" section and enter "Calendar" into the search bar. This will display a variety of calendar templates.

Look at the templates available and choose one that works perfectly for you. For example, you can choose an "Academic Calendar" for school purposes. However, before inserting it, preview the calendar to ensure it meets your needs. If not, you can step back and select another one.
Once you've chosen a template, hit the “Create” button to generate the calendar, or simply double-click on the template. You can rename the file by double-clicking the sheet tab at the bottom.

You may have customization options, like changing dates, colors, or layout, based on the template you pick.
Furthermore, you can update the year by typing it into the designated area, and all the months will adjust automatically. There's also an option to select whether the week begins on Monday or Sunday. You can even add comments on specific dates, like noting a holiday on a Friday.
Create a Calendar Using VBA Code
For those who prefer working with code, Excel offers an automatic way to create a calendar using Visual Basic. You can do that by pasting and running the VBA code in the VBA editor from the Developer tab. However, if you haven't accessed this option before, you need to activate it from the Excel options settings.
Simply go to File > Options > Customize Ribbon. In the right column, navigate and tick the box next to "Developer" to ensure it’s visible in the Excel ribbon.

After activating the Developer tab, navigate to the section and select "Visual Basic."

Go to the Insert > Module.

Copy and paste the calendar-making code from this Microsoft guide into the module and run the code.

That's it! Excel will generate the calendar on the sheet.

You can also use a free Excel add-in for a quick and easy solution. Head to the "Add-Ins" menu under the "Home" tab and search for a calendar. There are various calendar options available for you to choose from.
The above is the detailed content of I Build All My Calendars in Excel—Here's How You Can Too. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to Create a Timeline Filter in Excel
Apr 03, 2025 am 03:51 AM
How to Create a Timeline Filter in Excel
Apr 03, 2025 am 03:51 AM
In Excel, using the timeline filter can display data by time period more efficiently, which is more convenient than using the filter button. The Timeline is a dynamic filtering option that allows you to quickly display data for a single date, month, quarter, or year. Step 1: Convert data to pivot table First, convert the original Excel data into a pivot table. Select any cell in the data table (formatted or not) and click PivotTable on the Insert tab of the ribbon. Related: How to Create Pivot Tables in Microsoft Excel Don't be intimidated by the pivot table! We will teach you basic skills that you can master in minutes. Related Articles In the dialog box, make sure the entire data range is selected (
 If You Don't Use Excel's Hidden Camera Tool, You're Missing a Trick
Mar 25, 2025 am 02:48 AM
If You Don't Use Excel's Hidden Camera Tool, You're Missing a Trick
Mar 25, 2025 am 02:48 AM
Quick Links Why Use the Camera Tool?
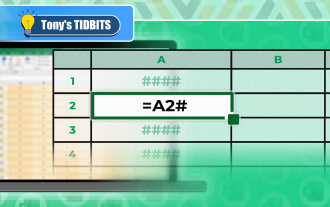 You Need to Know What the Hash Sign Does in Excel Formulas
Apr 08, 2025 am 12:55 AM
You Need to Know What the Hash Sign Does in Excel Formulas
Apr 08, 2025 am 12:55 AM
Excel Overflow Range Operator (#) enables formulas to be automatically adjusted to accommodate changes in overflow range size. This feature is only available for Microsoft 365 Excel for Windows or Mac. Common functions such as UNIQUE, COUNTIF, and SORTBY can be used in conjunction with overflow range operators to generate dynamic sortable lists. The pound sign (#) in the Excel formula is also called the overflow range operator, which instructs the program to consider all results in the overflow range. Therefore, even if the overflow range increases or decreases, the formula containing # will automatically reflect this change. How to list and sort unique values in Microsoft Excel
 Use the PERCENTOF Function to Simplify Percentage Calculations in Excel
Mar 27, 2025 am 03:03 AM
Use the PERCENTOF Function to Simplify Percentage Calculations in Excel
Mar 27, 2025 am 03:03 AM
Excel's PERCENTOF function: Easily calculate the proportion of data subsets Excel's PERCENTOF function can quickly calculate the proportion of data subsets in the entire data set, avoiding the hassle of creating complex formulas. PERCENTOF function syntax The PERCENTOF function has two parameters: =PERCENTOF(a,b) in: a (required) is a subset of data that forms part of the entire data set; b (required) is the entire dataset. In other words, the PERCENTOF function calculates the percentage of the subset a to the total dataset b. Calculate the proportion of individual values using PERCENTOF The easiest way to use the PERCENTOF function is to calculate the single
 If You Don't Rename Tables in Excel, Today's the Day to Start
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:58 AM
If You Don't Rename Tables in Excel, Today's the Day to Start
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:58 AM
Quick link Why should tables be named in Excel How to name a table in Excel Excel table naming rules and techniques By default, tables in Excel are named Table1, Table2, Table3, and so on. However, you don't have to stick to these tags. In fact, it would be better if you don't! In this quick guide, I will explain why you should always rename tables in Excel and show you how to do this. Why should tables be named in Excel While it may take some time to develop the habit of naming tables in Excel (if you don't usually do this), the following reasons illustrate today
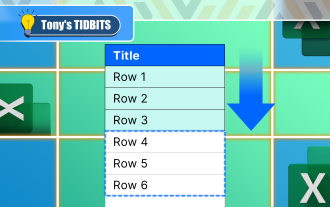 How to Format a Spilled Array in Excel
Apr 10, 2025 pm 12:01 PM
How to Format a Spilled Array in Excel
Apr 10, 2025 pm 12:01 PM
Use formula conditional formatting to handle overflow arrays in Excel Direct formatting of overflow arrays in Excel can cause problems, especially when the data shape or size changes. Formula-based conditional formatting rules allow automatic formatting to be adjusted when data parameters change. Adding a dollar sign ($) before a column reference applies a rule to all rows in the data. In Excel, you can apply direct formatting to the values or background of a cell to make the spreadsheet easier to read. However, when an Excel formula returns a set of values (called overflow arrays), applying direct formatting will cause problems if the size or shape of the data changes. Suppose you have this spreadsheet with overflow results from the PIVOTBY formula,
 How to Use Excel's AGGREGATE Function to Refine Calculations
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:54 AM
How to Use Excel's AGGREGATE Function to Refine Calculations
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:54 AM
Quick Links The AGGREGATE Syntax







