Using the Google Analytics API v3 with PHP: Fetching Data

In the first part of our series, we introduced the Google Analytics API, including the basic usage. In this part, we will continue creating our demo and see how we can extend it with more functionality.
Key Takeaways
- Utilize the Google Analytics API v3 with PHP to effectively fetch and manage user account data, including properties and views.
- Implement the Management API to retrieve lists of accounts, properties, and views, handling data as arrays or objects based on initialization settings in GA_Service.php.
- Leverage the Metadata API to access and cache analytics metadata using Google_CurlIO and Google_HttpRequest, optimizing data retrieval with etag attributes.
- Extend functionality by incorporating sorting, filtering, and segmentation options in API queries, enhancing data customization and relevance.
- Handle authentication, error responses, and JSON data parsing within PHP to ensure secure and efficient interactions with the Google Analytics API.
Google Analytics API
Management API
As we discussed in the first part, the Management API is responsible for getting user accounts, properties, views… for our first example we will retrieve the list of accounts available for our authenticated user.
<span>// app/src/GA_Service.php
</span><span>public function accounts(){
</span> <span>if( !$this->isLoggedIn() ){
</span> <span>//login
</span> <span>}
</span>
<span>$service = new Google_AnalyticsService($this->client);
</span> <span>$man_accounts = $service->management_accounts->listManagementAccounts();
</span> <span>$accounts = [];
</span>
<span>foreach ($man_accounts['items'] as $account) {
</span> <span>$accounts[] = [ 'id' => $account['id'], 'name' => $account['name'] ];
</span> <span>}
</span>
<span>return $accounts;
</span><span>}//accounts
</span>
<span>// app/controllers/HomeController.php
</span><span>public function accounts(){
</span> <span>$accounts = $this->ga->accounts();
</span>
<span>return $accounts;
</span><span>}//accounts
</span>
<span>// app/routes.php
</span><span>Route<span>::</span>get('/accounts', 'HomeController@accounts');</span>Inside GA_Service::accounts we create a new Google_AnalyticsService with our authorized client and then query the API for the list of accounts.
In this case the result is an array, but the API also makes use of objects, we just need to specify that inside our GA_Service::init function. In the following examples, I’m going to use array results.
<span>$this->client->setUseObjects(true);</span>
The listManagementAccounts function returns an array containing:
<span>{
</span> kind<span>: "analytics#accounts",
</span> <span>username: "me@mail.com",
</span> <span>totalResults: 3,
</span> <span>startIndex: 1,
</span> <span>itemsPerPage: 1000,
</span> <span>items: [
</span> <span>{
</span> id<span>: "4449308",
</span> <span>kind: "analytics#account",
</span> <span>selfLink: "https://www.googleapis.com/analytics/v3/management/accounts/4449308",
</span> <span>name: "me@mail.com",
</span> <span>permissions: {
</span> effective<span>: [
</span> <span>"COLLABORATE",
</span> <span>"EDIT",
</span> <span>"MANAGE_USERS",
</span> <span>"READ_AND_ANALYZE"
</span> <span>]
</span> <span>},
</span> <span>created: "2013-10-01T11:04:28.478Z",
</span> <span>updated: "2013-10-01T11:04:28.478Z",
</span> <span>childLink: {
</span> type<span>: "analytics#webproperties",
</span> <span>href: "https://www.googleapis.com/analytics/v3/management/accounts/4449308/webproperties"
</span> <span>}
</span> <span>}
</span> <span>]
</span><span>}</span>Note that when you return an array as a response, Laravel automatically encodes the result as a JSON response and sends it to the browser.
The result contains information about the total results and some pagination info as well. The items column contains the list of accounts with their IDs, permissions, etc., but we looped through items to extract only the id and name from the accounts.
If you would like to have result pagination, you can always pass more options to listManagementAccount:
<span>$service->management_accounts->listManagementAccounts( [ 'max-results' => $max_results, 'start-index' => $start_index ] );</span>
Let’s assume that we’re going to show our users their list of accounts, and when they select one, we load the list of properties associated with it.
<span>// app/src/GA_Service.php
</span><span>public function properties( $account_id ){
</span> <span>if( !$this->isLoggedIn() ){
</span> <span>//login
</span> <span>}
</span>
<span>try {
</span> <span>$service = new Google_AnalyticsService($this->client);
</span> <span>$man_properties = $service->management_webproperties->listManagementWebproperties($account_id);
</span> <span>$properties = [];
</span>
<span>foreach ($man_properties['items'] as $property) {
</span> <span>$properties[] = [ 'id' => $property['id'], 'name' => $property['name'] ];
</span> <span>}//foreach
</span>
<span>return json_encode($properties);
</span> <span>} catch (Google_ServiceException $e) {
</span> <span>return Response<span>::</span>json([
</span> <span>'status' => 0,
</span> <span>'code' => 3,
</span> <span>'message' => $e->getMessage()
</span> <span>]);
</span> <span>}//catch
</span>
<span>}//properties
</span>
<span>// app/controllers/HomeController.php
</span><span>public function properties( $account_id ){
</span> <span>$properties = $this->ga->properties( $account_id );
</span>
<span>return $properties;
</span><span>}//properties
</span>
<span>// app/routes.php
</span><span>Route<span>::</span>get( '/properties/{account_id}', [ 'uses' => 'HomeController@properties' ] )->where('account_id', '\d+');</span>The GA_Service::properties accepts an account ID, and returns the list of properties for that account. We basically have the same process, like retrieving accounts.
[
{
id: "UA-52317977-1",
name: "Prop1"
},
{
id: "UA-52317977-2",
name: "Prop1"
}
]Every property has a subset of views. By default, Google adds a view called All Web Site Data for every new property.
Using an ID from the list of properties and the account ID grabbed from the first part, we will query Google Analytics API for the list of available views for a given account property.
<span>// app/src/GA_Service.php
</span><span>public function accounts(){
</span> <span>if( !$this->isLoggedIn() ){
</span> <span>//login
</span> <span>}
</span>
<span>$service = new Google_AnalyticsService($this->client);
</span> <span>$man_accounts = $service->management_accounts->listManagementAccounts();
</span> <span>$accounts = [];
</span>
<span>foreach ($man_accounts['items'] as $account) {
</span> <span>$accounts[] = [ 'id' => $account['id'], 'name' => $account['name'] ];
</span> <span>}
</span>
<span>return $accounts;
</span><span>}//accounts
</span>
<span>// app/controllers/HomeController.php
</span><span>public function accounts(){
</span> <span>$accounts = $this->ga->accounts();
</span>
<span>return $accounts;
</span><span>}//accounts
</span>
<span>// app/routes.php
</span><span>Route<span>::</span>get('/accounts', 'HomeController@accounts');</span>In the browser, when hitting /views/{account_id}/{property_id} route, we should get something similar to:
<span>$this->client->setUseObjects(true);</span>
Metadata API
To query some statistics from Google Analytics we need to provide a set of dimensions and metrics.
- Metrics: metrics are the individual measurements of user activity on your property, such as sessions and pageviews..
- Dimensions: dimensions break down metrics across some common criteria, such as country or browser.
To grab the list of available metadata you can simply use curl to query data from the following url https://www.googleapis.com/analytics/v3/metadata/ga/columns.
Google Analytics gives us an etag attribute that can be used for caching the response so that we don’t have to query the API on every request.
<span>{
</span> kind<span>: "analytics#accounts",
</span> <span>username: "me@mail.com",
</span> <span>totalResults: 3,
</span> <span>startIndex: 1,
</span> <span>itemsPerPage: 1000,
</span> <span>items: [
</span> <span>{
</span> id<span>: "4449308",
</span> <span>kind: "analytics#account",
</span> <span>selfLink: "https://www.googleapis.com/analytics/v3/management/accounts/4449308",
</span> <span>name: "me@mail.com",
</span> <span>permissions: {
</span> effective<span>: [
</span> <span>"COLLABORATE",
</span> <span>"EDIT",
</span> <span>"MANAGE_USERS",
</span> <span>"READ_AND_ANALYZE"
</span> <span>]
</span> <span>},
</span> <span>created: "2013-10-01T11:04:28.478Z",
</span> <span>updated: "2013-10-01T11:04:28.478Z",
</span> <span>childLink: {
</span> type<span>: "analytics#webproperties",
</span> <span>href: "https://www.googleapis.com/analytics/v3/management/accounts/4449308/webproperties"
</span> <span>}
</span> <span>}
</span> <span>]
</span><span>}</span>- Google_CurlIO: a class wrapped with some curlutilities for dealing with caching, authentication, etc – by using this class we ensure the response is cached using the etagattribute.
- Google_HttpRequest: is a class representing a single HTTP request.
The makeRequest method returns a Google_HttpRequest instance, and we can use the getResponseBody to get our metadata response.
<span>$service->management_accounts->listManagementAccounts( [ 'max-results' => $max_results, 'start-index' => $start_index ] );</span>
Now, when accessing the /metadata route in your browser you should get an array of dimensions and another one for metrics, and each one of them contains a list of grouped elements.
<span>// app/src/GA_Service.php
</span><span>public function properties( $account_id ){
</span> <span>if( !$this->isLoggedIn() ){
</span> <span>//login
</span> <span>}
</span>
<span>try {
</span> <span>$service = new Google_AnalyticsService($this->client);
</span> <span>$man_properties = $service->management_webproperties->listManagementWebproperties($account_id);
</span> <span>$properties = [];
</span>
<span>foreach ($man_properties['items'] as $property) {
</span> <span>$properties[] = [ 'id' => $property['id'], 'name' => $property['name'] ];
</span> <span>}//foreach
</span>
<span>return json_encode($properties);
</span> <span>} catch (Google_ServiceException $e) {
</span> <span>return Response<span>::</span>json([
</span> <span>'status' => 0,
</span> <span>'code' => 3,
</span> <span>'message' => $e->getMessage()
</span> <span>]);
</span> <span>}//catch
</span>
<span>}//properties
</span>
<span>// app/controllers/HomeController.php
</span><span>public function properties( $account_id ){
</span> <span>$properties = $this->ga->properties( $account_id );
</span>
<span>return $properties;
</span><span>}//properties
</span>
<span>// app/routes.php
</span><span>Route<span>::</span>get( '/properties/{account_id}', [ 'uses' => 'HomeController@properties' ] )->where('account_id', '\d+');</span>To speed up the process we will use bootsnipp. If the user is logged in, we will show the home page.

We need to update our HomeController@index to show the home page view.
[
{
id: "UA-52317977-1",
name: "Prop1"
},
{
id: "UA-52317977-2",
name: "Prop1"
}
]As you can see from the screenshot, when the user selects an account we asynchronously change the property and the view accordingly. To achieve that, I wrote some simple JS which you can check in the final repo.
Reporting API
By providing the selected view, metrics and dimensions we can get detailed statistics about users and interactions. The result after the user submission will be something similar to:
<span>// app/src/GA_Service.php
</span><span>public function views( $account_id, $property_id ){
</span> <span>if( !$this->isLoggedIn() ){
</span> <span>//login
</span> <span>}
</span>
<span>try {
</span> <span>$service = new Google_AnalyticsService($this->client);
</span> <span>$man_views = $service->management_profiles->listManagementProfiles( $account_id, $property_id );
</span> <span>$views = [];
</span>
<span>foreach ($man_views['items'] as $view) {
</span> <span>$views[] = [ 'id' => $view['id'], 'name' => $view['name'] ];
</span> <span>}//foreach
</span>
<span>return json_encode($views);
</span> <span>} catch (Google_ServiceException $e) {
</span> <span>return Response<span>::</span>json([
</span> <span>'status' => 0,
</span> <span>'code' => 3,
</span> <span>'message' => $e->getMessage()
</span> <span>]);
</span> <span>}//catch
</span><span>}//views
</span>
<span>// app/controllers/HomeController.php
</span><span>public function views( $account_id, $property_id ){
</span> <span>$views = $this->ga->views( $account_id ,$property_id );
</span>
<span>return $views;
</span><span>}//properties
</span>
<span>// app/routes.php
</span><span>Route<span>::</span>get( '/views/{account_id}/{property_id}', [ 'uses' => 'HomeController@views' ] )->where([ 'account_id', '\d+', 'property_id', '\d+' ]);</span>Our GA_Service::report accepts four arguments: a view ID, a start and end date and an array of metrics.
Google can’t return all your legacy data – instead we provide a start and end date. In my example, I queried the last month’s results.
The third parameter is the list of metrics which we already have from the user selection.
The fourth optional parameter is an array of options.
– max-results: the maximum number of results. (we used 10 to speed up the response).
– dimensions: a comma separated list of values. (ga:country,ga:city)
– filters: a comma separated list of rules to be appilied to the result .(ga:country!=usa,ga:pageviews>100)
In this example we excluded USA from the list of dimensions and only showed pageviews that are greater than 100.
– segment: advanced segment ID to be applied to the data.
– sort: order results by dimensions or metrics. Can combine multiple dimensions and metrics. (ga:country,-ga:pageviews = order by ga:country ascending, and by ga:pageviews descending.
– start-index: can be used for pagination.
<span>// app/src/GA_Service.php
</span><span>public function accounts(){
</span> <span>if( !$this->isLoggedIn() ){
</span> <span>//login
</span> <span>}
</span>
<span>$service = new Google_AnalyticsService($this->client);
</span> <span>$man_accounts = $service->management_accounts->listManagementAccounts();
</span> <span>$accounts = [];
</span>
<span>foreach ($man_accounts['items'] as $account) {
</span> <span>$accounts[] = [ 'id' => $account['id'], 'name' => $account['name'] ];
</span> <span>}
</span>
<span>return $accounts;
</span><span>}//accounts
</span>
<span>// app/controllers/HomeController.php
</span><span>public function accounts(){
</span> <span>$accounts = $this->ga->accounts();
</span>
<span>return $accounts;
</span><span>}//accounts
</span>
<span>// app/routes.php
</span><span>Route<span>::</span>get('/accounts', 'HomeController@accounts');</span>After calling the get Google_AnalyticsService::get method, we use the list of result items, column headers, and total results to output the result as a table.
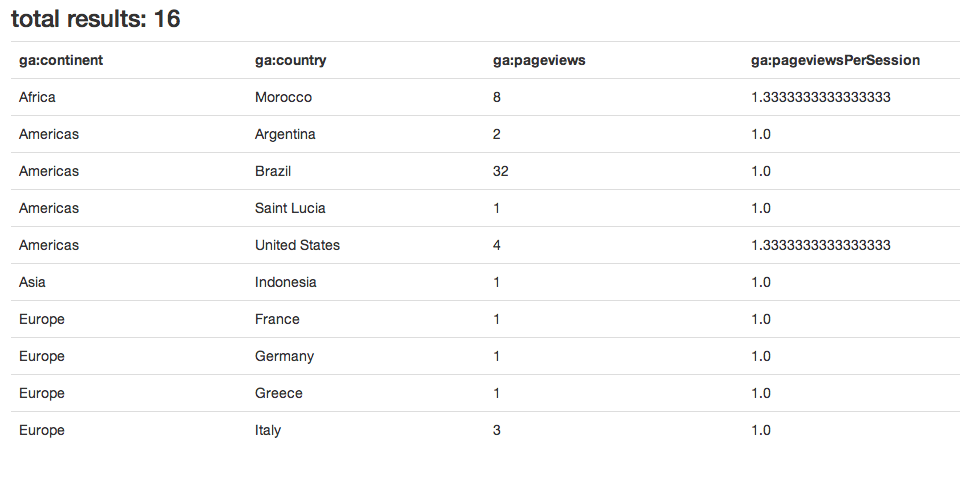
Extending The Demo
Now let’s see how we can extend our demo with filters, sorting and segments.
Filters
Filters are a way to exclude some data from the returned result. They take the following form:
<span>$this->client->setUseObjects(true);</span>
- ga:column: dimension or metric id (Ex: ga:country)
- operator: the operator depends on the choice of metric or dimension column id, check the docs for the list of operators.
- value: the value can be a number, a string, or a regex.
You can combine multiple filters: you can use comma (,) as an OR operator and a semi-colon (;) as an AND operator.
Segments
By default Google Analytics group all your data in one group called All Sessions. However, you can always choose from the built in segments or create a new one depending on your needs. You can group data by referral, device type, age, gender, etc.
You can extend the demo by adding a new select element with the available segment list, and pass the ID to the get method as discussed previously.
<span>{
</span> kind<span>: "analytics#accounts",
</span> <span>username: "me@mail.com",
</span> <span>totalResults: 3,
</span> <span>startIndex: 1,
</span> <span>itemsPerPage: 1000,
</span> <span>items: [
</span> <span>{
</span> id<span>: "4449308",
</span> <span>kind: "analytics#account",
</span> <span>selfLink: "https://www.googleapis.com/analytics/v3/management/accounts/4449308",
</span> <span>name: "me@mail.com",
</span> <span>permissions: {
</span> effective<span>: [
</span> <span>"COLLABORATE",
</span> <span>"EDIT",
</span> <span>"MANAGE_USERS",
</span> <span>"READ_AND_ANALYZE"
</span> <span>]
</span> <span>},
</span> <span>created: "2013-10-01T11:04:28.478Z",
</span> <span>updated: "2013-10-01T11:04:28.478Z",
</span> <span>childLink: {
</span> type<span>: "analytics#webproperties",
</span> <span>href: "https://www.googleapis.com/analytics/v3/management/accounts/4449308/webproperties"
</span> <span>}
</span> <span>}
</span> <span>]
</span><span>}</span>You can visit the /segments page to see the list of available segments with their IDs, and you can of course use this as an option as we saw earlier.
Wrapping up
The Google Analytics API is very flexible and provides a lot of features, but the documentation is not complete yet, and doesn’t provide good examples of use. You get a lot more by digging into the source code and testing possibilities and limits.
In this series, we focused on the basic usage of Google Analytics, but you can extend the demo with options from the Google Analytics dashboard.
You can check the final repo for the source code of this tutorial.
Questions? Comments? Let me know!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Using Google Analytics API v3 with PHP
How can I get started with Google Analytics API v3 with PHP?
To get started with Google Analytics API v3 with PHP, you first need to create a project in the Google Developers Console. After creating the project, enable the Google Analytics API for it. Then, create credentials for the API. You will receive a client ID and client secret, which you will use to authenticate your application with Google. After that, you can start making requests to the API using PHP.
What are the prerequisites for using Google Analytics API v3 with PHP?
Before you can use Google Analytics API v3 with PHP, you need to have a Google account and access to the Google Analytics data you want to retrieve. You also need to have PHP installed on your server and a basic understanding of PHP programming.
How can I authenticate my application with Google using PHP?
To authenticate your application with Google using PHP, you need to use the client ID and client secret you received when you created your API credentials. You can use these credentials to obtain an access token, which you can then use to authenticate your API requests.
How can I retrieve data from Google Analytics using PHP?
To retrieve data from Google Analytics using PHP, you need to make a GET request to the Google Analytics API. You can specify the metrics, dimensions, and filters you want to apply in the request parameters. The API will return the requested data in JSON format, which you can then parse and use in your application.
How can I handle errors when using Google Analytics API v3 with PHP?
When using Google Analytics API v3 with PHP, errors can occur for various reasons, such as invalid request parameters or authentication issues. You can handle these errors by checking the HTTP status code and error message returned by the API. This will give you information about what went wrong and how to fix it.
Can I use Google Analytics API v3 with PHP to track real-time data?
Yes, you can use Google Analytics API v3 with PHP to track real-time data. The API provides a Real Time Reporting API that you can use to retrieve real-time data such as the number of active users on your site.
How can I filter data when using Google Analytics API v3 with PHP?
You can filter data when using Google Analytics API v3 with PHP by specifying filter parameters in your API request. These parameters allow you to restrict the data returned by the API to meet specific criteria.
Can I use Google Analytics API v3 with PHP to retrieve data from multiple Google Analytics accounts?
Yes, you can use Google Analytics API v3 with PHP to retrieve data from multiple Google Analytics accounts. You just need to authenticate with each account separately and make separate API requests for each account.
How can I paginate results when using Google Analytics API v3 with PHP?
You can paginate results when using Google Analytics API v3 with PHP by using the ‘start-index’ and ‘max-results’ parameters in your API request. These parameters allow you to specify the range of results you want to retrieve.
How can I sort data when using Google Analytics API v3 with PHP?
You can sort data when using Google Analytics API v3 with PHP by specifying sort parameters in your API request. These parameters allow you to order the data returned by the API based on specific metrics or dimensions.
The above is the detailed content of Using the Google Analytics API v3 with PHP: Fetching Data. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Alipay PHP SDK transfer error: How to solve the problem of 'Cannot declare class SignData'?
Apr 01, 2025 am 07:21 AM
Alipay PHP SDK transfer error: How to solve the problem of 'Cannot declare class SignData'?
Apr 01, 2025 am 07:21 AM
Alipay PHP...
 Explain JSON Web Tokens (JWT) and their use case in PHP APIs.
Apr 05, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Explain JSON Web Tokens (JWT) and their use case in PHP APIs.
Apr 05, 2025 am 12:04 AM
JWT is an open standard based on JSON, used to securely transmit information between parties, mainly for identity authentication and information exchange. 1. JWT consists of three parts: Header, Payload and Signature. 2. The working principle of JWT includes three steps: generating JWT, verifying JWT and parsing Payload. 3. When using JWT for authentication in PHP, JWT can be generated and verified, and user role and permission information can be included in advanced usage. 4. Common errors include signature verification failure, token expiration, and payload oversized. Debugging skills include using debugging tools and logging. 5. Performance optimization and best practices include using appropriate signature algorithms, setting validity periods reasonably,
 How does session hijacking work and how can you mitigate it in PHP?
Apr 06, 2025 am 12:02 AM
How does session hijacking work and how can you mitigate it in PHP?
Apr 06, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Session hijacking can be achieved through the following steps: 1. Obtain the session ID, 2. Use the session ID, 3. Keep the session active. The methods to prevent session hijacking in PHP include: 1. Use the session_regenerate_id() function to regenerate the session ID, 2. Store session data through the database, 3. Ensure that all session data is transmitted through HTTPS.
 Describe the SOLID principles and how they apply to PHP development.
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Describe the SOLID principles and how they apply to PHP development.
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:04 AM
The application of SOLID principle in PHP development includes: 1. Single responsibility principle (SRP): Each class is responsible for only one function. 2. Open and close principle (OCP): Changes are achieved through extension rather than modification. 3. Lisch's Substitution Principle (LSP): Subclasses can replace base classes without affecting program accuracy. 4. Interface isolation principle (ISP): Use fine-grained interfaces to avoid dependencies and unused methods. 5. Dependency inversion principle (DIP): High and low-level modules rely on abstraction and are implemented through dependency injection.
 How to debug CLI mode in PHPStorm?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 02:57 PM
How to debug CLI mode in PHPStorm?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 02:57 PM
How to debug CLI mode in PHPStorm? When developing with PHPStorm, sometimes we need to debug PHP in command line interface (CLI) mode...
 How to automatically set permissions of unixsocket after system restart?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 11:54 PM
How to automatically set permissions of unixsocket after system restart?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 11:54 PM
How to automatically set the permissions of unixsocket after the system restarts. Every time the system restarts, we need to execute the following command to modify the permissions of unixsocket: sudo...
 Explain late static binding in PHP (static::).
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Explain late static binding in PHP (static::).
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Static binding (static::) implements late static binding (LSB) in PHP, allowing calling classes to be referenced in static contexts rather than defining classes. 1) The parsing process is performed at runtime, 2) Look up the call class in the inheritance relationship, 3) It may bring performance overhead.
 How to send a POST request containing JSON data using PHP's cURL library?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
How to send a POST request containing JSON data using PHP's cURL library?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
Sending JSON data using PHP's cURL library In PHP development, it is often necessary to interact with external APIs. One of the common ways is to use cURL library to send POST�...






