Is ReFT All We Needed?
ReFT: A Revolutionary Approach to Fine-tuning LLMs
ReFT (Representation Finetuning), introduced in Stanford's May 2024 paper, offers a groundbreaking method for efficiently fine-tuning large language models (LLMs). Its potential was immediately apparent, further highlighted by Oxen.ai's July 2024 experiment fine-tuning Llama3 (8B) on a single Nvidia A10 GPU in just 14 minutes.
Unlike existing Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) methods like LoRA, which modify model weights or input, ReFT leverages the Distributed Interchange Intervention (DII) method. DII projects embeddings into a lower-dimensional subspace, enabling fine-tuning through this subspace.
This article first reviews popular PEFT algorithms (LoRA, Prompt Tuning, Prefix Tuning), then explains DII, before delving into ReFT and its experimental results.

Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) Techniques
Hugging Face provides a comprehensive overview of PEFT techniques. Let's briefly summarize key methods:
LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation): Introduced in 2021, LoRA's simplicity and generalizability have made it a leading technique for fine-tuning LLMs and diffusion models. Instead of adjusting all layer weights, LoRA adds low-rank matrices, significantly reducing trainable parameters (often less than 0.3%), accelerating training and minimizing GPU memory usage.

Prompt Tuning: This method uses "soft prompts"—learnable task-specific embeddings—as prefixes, enabling efficient multi-task prediction without duplicating the model for each task.
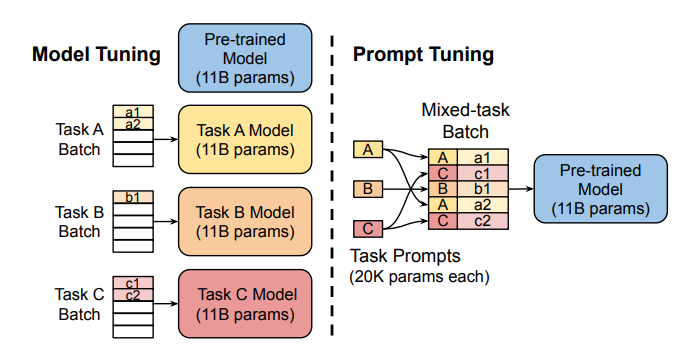
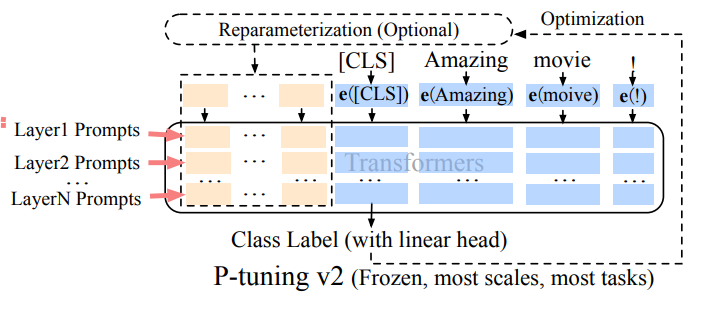
Prefix Tuning (P-Tuning v2): Addressing limitations of prompt tuning at scale, Prefix Tuning adds trainable prompt embeddings to various layers, allowing task-specific learning at different levels.
LoRA's robustness and efficiency make it the most widely used PEFT method for LLMs. A detailed empirical comparison can be found in this paper.
Distributed Interchange Intervention (DII)
DII is rooted in causal abstraction, a framework using intervention between a high-level (causal) model and a low-level (neural network) model to assess alignment. DII projects both models into subspaces via orthogonal projections, creating an intervened model through rotation operations. A detailed visual example is available here.
The DII process can be mathematically represented as:
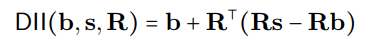
where R represents orthogonal projections, and the distributed alignment search (DAS) optimizes the subspace to maximize the probability of expected counterfactual outputs post-intervention.
ReFT – Representation Finetuning
ReFT intervenes in the model's hidden representation within a lower-dimensional space. The illustration below shows the intervention (phi) applied to layer L and position P:
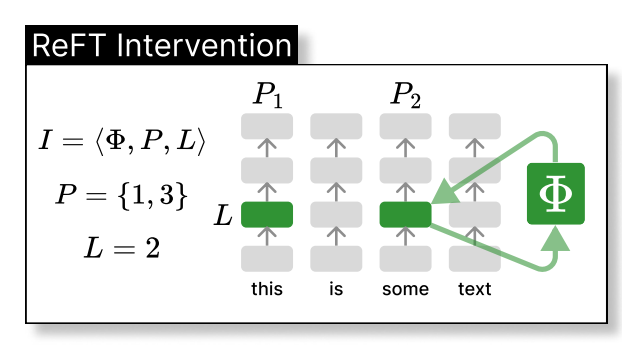
LoReFT (Low-rank Linear Subspace Reft) introduces a learned projected source:
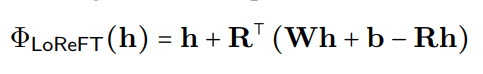
where h is the hidden representation, and Rs edits h in the low-dimensional space spanned by R. The LoReFT integration into a neural network layer is shown below:
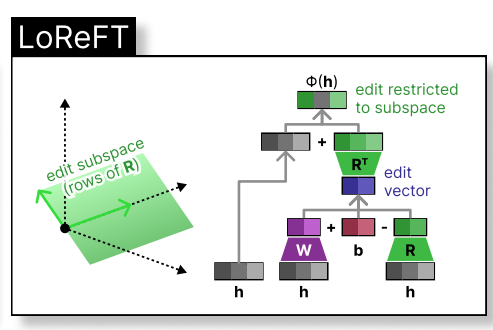
During LLM fine-tuning, the LLM parameters remain frozen, and only the projection parameters (phi={R, W, b}) are trained.
Experimental Results
The original ReFT paper presents comparative experiments against full fine-tuning (FT), LoRA, and Prefix Tuning across various benchmarks. ReFT techniques consistently outperform existing methods, reducing parameters by at least 90% while achieving superior performance.

Discussion
ReFT's appeal stems from its superior performance with Llama-family models across diverse benchmarks and its grounding in causal abstraction, which aids model interpretability. ReFT demonstrates that a linear subspace distributed across neurons can effectively control numerous tasks, offering valuable insights into LLMs.
References
- Wu et al., ReFT: Representation Finetuning for Language Models
- Hu et al., LoRA: Low-Rank Adaptation of Large Language Models
- Zhuang et al., Time-Varying LoRA
- Liu et al., P-tuning v2
- Geiger et al., Finding alignments between interpretable causal variables and distributed neural representations
- Lester et al., The power of scale for parameter-efficient prompt tuning
- Pu et al., Empirical analysis of the strengths and weaknesses of Peft techniques for LLMs
(Note: Please replace the bracketed https://www.php.cn/link/6c11cb78b7bbb5c22d5f5271b5494381 placeholders with the actual links to the research papers.)
The above is the detailed content of Is ReFT All We Needed?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1379
1379
 52
52
 I Tried Vibe Coding with Cursor AI and It's Amazing!
Mar 20, 2025 pm 03:34 PM
I Tried Vibe Coding with Cursor AI and It's Amazing!
Mar 20, 2025 pm 03:34 PM
Vibe coding is reshaping the world of software development by letting us create applications using natural language instead of endless lines of code. Inspired by visionaries like Andrej Karpathy, this innovative approach lets dev
 Top 5 GenAI Launches of February 2025: GPT-4.5, Grok-3 & More!
Mar 22, 2025 am 10:58 AM
Top 5 GenAI Launches of February 2025: GPT-4.5, Grok-3 & More!
Mar 22, 2025 am 10:58 AM
February 2025 has been yet another game-changing month for generative AI, bringing us some of the most anticipated model upgrades and groundbreaking new features. From xAI’s Grok 3 and Anthropic’s Claude 3.7 Sonnet, to OpenAI’s G
 How to Use YOLO v12 for Object Detection?
Mar 22, 2025 am 11:07 AM
How to Use YOLO v12 for Object Detection?
Mar 22, 2025 am 11:07 AM
YOLO (You Only Look Once) has been a leading real-time object detection framework, with each iteration improving upon the previous versions. The latest version YOLO v12 introduces advancements that significantly enhance accuracy
 Best AI Art Generators (Free & Paid) for Creative Projects
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:10 PM
Best AI Art Generators (Free & Paid) for Creative Projects
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:10 PM
The article reviews top AI art generators, discussing their features, suitability for creative projects, and value. It highlights Midjourney as the best value for professionals and recommends DALL-E 2 for high-quality, customizable art.
 Is ChatGPT 4 O available?
Mar 28, 2025 pm 05:29 PM
Is ChatGPT 4 O available?
Mar 28, 2025 pm 05:29 PM
ChatGPT 4 is currently available and widely used, demonstrating significant improvements in understanding context and generating coherent responses compared to its predecessors like ChatGPT 3.5. Future developments may include more personalized interactions and real-time data processing capabilities, further enhancing its potential for various applications.
 Which AI is better than ChatGPT?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 06:05 PM
Which AI is better than ChatGPT?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 06:05 PM
The article discusses AI models surpassing ChatGPT, like LaMDA, LLaMA, and Grok, highlighting their advantages in accuracy, understanding, and industry impact.(159 characters)
 How to Use Mistral OCR for Your Next RAG Model
Mar 21, 2025 am 11:11 AM
How to Use Mistral OCR for Your Next RAG Model
Mar 21, 2025 am 11:11 AM
Mistral OCR: Revolutionizing Retrieval-Augmented Generation with Multimodal Document Understanding Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems have significantly advanced AI capabilities, enabling access to vast data stores for more informed respons
 Top AI Writing Assistants to Boost Your Content Creation
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:11 PM
Top AI Writing Assistants to Boost Your Content Creation
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:11 PM
The article discusses top AI writing assistants like Grammarly, Jasper, Copy.ai, Writesonic, and Rytr, focusing on their unique features for content creation. It argues that Jasper excels in SEO optimization, while AI tools help maintain tone consist




