phpmaster | Error Handling in PHP

Key Takeaways
- PHP error handling is crucial for maintaining the integrity and functionality of a web application. It helps identify and fix issues that may arise during script execution, improving user experience by controlling what they see when an error occurs.
- PHP offers several built-in functions for error handling, including logging and displaying them. It also provides flexibility to customize error handling strategies by registering error handlers and using exceptions.
- Custom error handling in PHP can be achieved using set_error_handler() and set_exception_handler() functions. These allow developers to define custom error handling rules and exceptions, which can be useful for logging errors or sending error notifications.
- Exceptions in PHP are events that occur during script execution, disrupting the normal flow of instructions. They can be handled using try, catch, and finally blocks. If no catch block is found when an exception is thrown, PHP will display a fatal error and stop executing the script.
PHP Error Reporting Levels
All errors and warnings should be logged. Based on the severity of an error, notifications should be sent out to other systems/teams. So that you can better gauge its severity, PHP provides several built-in error levels to describe the nature of an error. Each level is represented by an integer value and named constant which can be used by the programmer. The table below is taken from the official PHP documentation and shows some of the different levels.

Creating Custom Error Handlers
It’s also good practice not to display raw errors to the end user. Errors that are displayed should be abstracted with friendly, custom error messages. PHP not only provides built-in functions for logging and displaying errors, but also for raising them. You can pragmatically trigger an error of a specific level using trigger_error(). For example, this code triggers an E_USER_NOTICE warning if the value of $test is greater than 1:<span><span><?php
</span></span><span><span>$test = 5;
</span></span><span><span>if ($test > 1) {
</span></span><span> <span>trigger_error('Value of $test must be 1 or less', E_USER_NOTICE);
</span></span><span><span>}</span></span>handler(int $errno, string $errstr, string $errfile, int $errline, array $errcontext)

<span><span><?php
</span></span><span><span>$test = 5;
</span></span><span><span>if ($test > 1) {
</span></span><span> <span>trigger_error('Value of $test must be 1 or less', E_USER_NOTICE);
</span></span><span><span>}</span></span>Handling Errors using Exceptions
However good of an error handling framework you have in place, there will always be problems at run-time. Of course you don’t want these errors to show up in the user’s browser. This is where exception handling enters the picture. Exceptions allows you to handle errors and exceptional situations gracefully. Exceptions are represented in PHP by the class Excpetion (or any of its subclasses). They can be raised using throw and can be caught using a try/catch block. You can extend Exception to create custom exception types for trapping specific errors. The code that may trigger an exception is placed within the try block, and the code to handle the exception is placed within the catch block. Consider the following snippet:handler(int $errno, string $errstr, string $errfile, int $errline, array $errcontext)
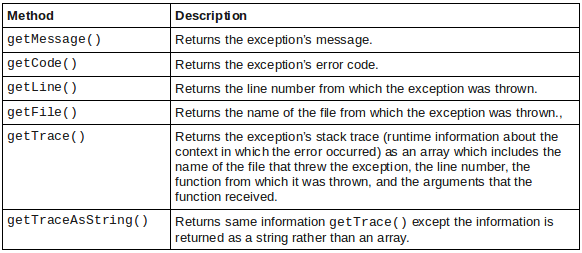
Creating a Custom Exception Handler
PHP will let you throw any object as if it were an exception, but as a rule of thumb the exception should extend PHP’s built-in Exception class. Based on the object’s type, you can handle the exceptions differently. Custom exception handling can perform suitable actions like logging error messages in file, providing exact details about the line on which the error occurred by examining the calling stack, etc. Have a look at this example:<span><span><?php
</span></span><span><span>$test = 5;
</span></span><span><span>if ($test > 1) {
</span></span><span> <span>trigger_error('Value of $test must be 1 or less', E_USER_NOTICE);
</span></span><span><span>}</span></span>Re-throwing Exceptions
try/catch blocks can be nested. Sometimes you’ll want to catch an exception, look at some of its properties, and then throw it again to let a parent catch block handle it. This can often be useful to check an error condition and decide whether it should be fatal or not. This example code demonstrates re-throwing an exception:handler(int $errno, string $errstr, string $errfile, int $errline, array $errcontext)
Uncaught Exception Handler
Similar to how set_error_handler() allows you specify a function to handle run-time errors, the set_exception_handler() function allows you to handle exceptions that make it all the way up the call stack without being caught by any catch blocks. For example, if an exception makes it all the way up your stack, it would be a good idea to log it in a log file. You can create a callback function and register it with set_exception_handler() as shown in the example below.<span><span><?php
</span></span><span><span>function errorHandler($errno, $errstr, $errfile, $errline) {
</span></span><span> <span>static $db;
</span></span><span> <span>if (empty($db)) {
</span></span><span> <span>$db = new PDO(DSN, DBUSER, DBPASS);
</span></span><span> <span>}
</span></span><span>
</span><span> <span>$query = "INSERT INTO errorlog (severity, message, filename, lineno, time) VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, NOW())";
</span></span><span> <span>$stmt = $db->prepare($query);
</span></span><span>
</span><span> <span>switch ($errno) {
</span></span><span> <span>case E_NOTICE:
</span></span><span> <span>case E_USER_NOTICE:
</span></span><span> <span>case E_DEPRECATED:
</span></span><span> <span>case E_USER_DEPRECATED:
</span></span><span> <span>case E_STRICT:
</span></span><span> <span>$stmt->execute(array("NOTICE", $errstr, $errfile, $errline));
</span></span><span> <span>break;
</span></span><span>
</span><span> <span>case E_WARNING:
</span></span><span> <span>case E_USER_WARNING:
</span></span><span> <span>$stmt->execute(array("WARNING", $errstr, $errfile, $errline));
</span></span><span> <span>break;
</span></span><span>
</span><span> <span>case E_ERROR:
</span></span><span> <span>case E_USER_ERROR:
</span></span><span> <span>$stmt->execute(array("FATAL", $errstr, $errfile, $errline));
</span></span><span> <span>exit("FATAL error <span><span>$errstr</span> at <span>$errfile</span>:<span>$errline</span>"</span>);
</span></span><span>
</span><span> <span>default:
</span></span><span> <span>exit("Unknown error at <span><span>$errfile</span>:<span>$errline</span>"</span>);
</span></span><span> <span>}
</span></span><span><span>}
</span></span><span>
</span><span><span>set_error_handler("errorHandler");
</span></span><span>
</span><span><span>$test = 5;
</span></span><span><span>if ($test > 1) {
</span></span><span> <span>trigger_error("Value of <span><span>$test</span> must be 1 or less"</span>, E_USER_NOTICE);
</span></span><span><span>}</span></span>Summary
PHP offers variety of built-in functions for handling error conditions, including logging and displaying them. It also provides you the flexibility to customize your error handling strategies by registering error handlers and using exceptions. Errors are a fact of life, but hopefully the information I presented in this article will help you handle them more gracefully. Image via Ilya Andriyanov / ShutterstockFrequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Error Handling in PHP
What is the importance of error handling in PHP?
Error handling in PHP is crucial for maintaining the integrity and functionality of a web application. It helps developers identify and fix issues that may arise during the execution of a script. Without proper error handling, a minor issue can cause significant problems, such as crashing the application or exposing sensitive information to users. It also improves the user experience as it allows developers to control what the user sees when an error occurs, rather than displaying confusing error messages.
How does PHP handle errors by default?
By default, PHP sends an error report to the server’s error log and displays an error message on the screen. This behavior is not ideal for a live website because it can reveal sensitive information to the user. Therefore, it’s recommended to change the default error handling settings for a live website.
What are the different types of errors in PHP?
PHP classifies errors into several types, including fatal errors, warnings, parse errors, and notices. Fatal errors are critical errors, such as calling a non-existent function or writing to a file that isn’t writable. Warnings are non-fatal errors that allow the script to continue running. Parse errors occur when there’s a syntax mistake in the script. Notices are minor errors or possible errors that PHP encounters while executing a script.
How can I customize error handling in PHP?
PHP provides several functions to customize error handling, such as set_error_handler() and set_exception_handler(). These functions allow you to define custom error handling rules and exceptions. You can specify a custom function to handle errors, which can be useful for logging errors or sending error notifications.
What is an exception in PHP?
An exception is an event that occurs during the execution of a script that disrupts the normal flow of the script’s instructions. When an exception is thrown, PHP will stop executing the script and start looking for a catch block to handle the exception. If no catch block is found, PHP will display a fatal error and stop executing the script.
How can I handle exceptions in PHP?
PHP provides the try, catch, and finally blocks to handle exceptions. The try block contains the code that may throw an exception. The catch block contains the code to handle the exception. The finally block contains the code that will be executed regardless of whether an exception was thrown or not.
What is the difference between errors and exceptions in PHP?
The main difference between errors and exceptions in PHP is how they are handled. Errors are handled by the PHP engine and can be controlled using error reporting settings and custom error handlers. Exceptions, on the other hand, are handled by the script and can be controlled using try, catch, and finally blocks.
How can I turn off error reporting in PHP?
You can turn off error reporting in PHP by using the error_reporting() function with 0 as its argument. However, turning off error reporting is not recommended for a live website because it can make it difficult to identify and fix issues.
What is the role of the @ operator in PHP error handling?
The @ operator in PHP is used to suppress error messages. When prepended to an expression in PHP, any error messages that might be generated by that expression will be ignored.
How can I log errors in PHP?
PHP provides the error_log() function to send an error message to the server’s error log or to a specified file. This function can be useful for keeping track of errors and debugging. You can also configure PHP to log all errors by changing the log_errors directive in the php.ini file.
The above is the detailed content of phpmaster | Error Handling in PHP. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Alipay PHP SDK transfer error: How to solve the problem of 'Cannot declare class SignData'?
Apr 01, 2025 am 07:21 AM
Alipay PHP SDK transfer error: How to solve the problem of 'Cannot declare class SignData'?
Apr 01, 2025 am 07:21 AM
Alipay PHP...
 Explain JSON Web Tokens (JWT) and their use case in PHP APIs.
Apr 05, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Explain JSON Web Tokens (JWT) and their use case in PHP APIs.
Apr 05, 2025 am 12:04 AM
JWT is an open standard based on JSON, used to securely transmit information between parties, mainly for identity authentication and information exchange. 1. JWT consists of three parts: Header, Payload and Signature. 2. The working principle of JWT includes three steps: generating JWT, verifying JWT and parsing Payload. 3. When using JWT for authentication in PHP, JWT can be generated and verified, and user role and permission information can be included in advanced usage. 4. Common errors include signature verification failure, token expiration, and payload oversized. Debugging skills include using debugging tools and logging. 5. Performance optimization and best practices include using appropriate signature algorithms, setting validity periods reasonably,
 How does session hijacking work and how can you mitigate it in PHP?
Apr 06, 2025 am 12:02 AM
How does session hijacking work and how can you mitigate it in PHP?
Apr 06, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Session hijacking can be achieved through the following steps: 1. Obtain the session ID, 2. Use the session ID, 3. Keep the session active. The methods to prevent session hijacking in PHP include: 1. Use the session_regenerate_id() function to regenerate the session ID, 2. Store session data through the database, 3. Ensure that all session data is transmitted through HTTPS.
 How to debug CLI mode in PHPStorm?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 02:57 PM
How to debug CLI mode in PHPStorm?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 02:57 PM
How to debug CLI mode in PHPStorm? When developing with PHPStorm, sometimes we need to debug PHP in command line interface (CLI) mode...
 Describe the SOLID principles and how they apply to PHP development.
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Describe the SOLID principles and how they apply to PHP development.
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:04 AM
The application of SOLID principle in PHP development includes: 1. Single responsibility principle (SRP): Each class is responsible for only one function. 2. Open and close principle (OCP): Changes are achieved through extension rather than modification. 3. Lisch's Substitution Principle (LSP): Subclasses can replace base classes without affecting program accuracy. 4. Interface isolation principle (ISP): Use fine-grained interfaces to avoid dependencies and unused methods. 5. Dependency inversion principle (DIP): High and low-level modules rely on abstraction and are implemented through dependency injection.
 How to automatically set permissions of unixsocket after system restart?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 11:54 PM
How to automatically set permissions of unixsocket after system restart?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 11:54 PM
How to automatically set the permissions of unixsocket after the system restarts. Every time the system restarts, we need to execute the following command to modify the permissions of unixsocket: sudo...
 Explain late static binding in PHP (static::).
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Explain late static binding in PHP (static::).
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Static binding (static::) implements late static binding (LSB) in PHP, allowing calling classes to be referenced in static contexts rather than defining classes. 1) The parsing process is performed at runtime, 2) Look up the call class in the inheritance relationship, 3) It may bring performance overhead.
 How to send a POST request containing JSON data using PHP's cURL library?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
How to send a POST request containing JSON data using PHP's cURL library?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 03:12 PM
Sending JSON data using PHP's cURL library In PHP development, it is often necessary to interact with external APIs. One of the common ways is to use cURL library to send POST�...






