Bash declare Command Usage With Examples
The Bash declare command is a powerful tool for defining, manipulating, and displaying variables and functions. This tutorial provides a comprehensive guide to using declare in Bash scripting on Linux systems.
Table of Contents
-
- Basic
declareUsage
- 1.1. Defining Variables
- 1.2. Uppercase Variables
- 1.3. Lowercase Variables
- Basic
-
- Listing Variables and Values
- 2.1. Listing All Variables
- 2.2. Listing Specific Variables
-
- Special
declareAttributes
- 3.1. Read-Only Variables (
-r) - 3.2. Integer Variables (
-i) - 3.3. Indexed Arrays (
-a) - 3.4. Associative Arrays (
-A) - 3.5. Exporting Variables (
-x)
- Special
-
- Function Management with
declare
- 4.1. Setting Function Attributes
- 4.2. Listing All Functions (
-f) - 4.3. Listing Function Names (
-F) - 4.4. Exporting Functions
- Function Management with
-
- Checking Variable/Function Existence
-
- Removing Attributes
-
- Unsetting Variables/Functions
- Example: Combined Variable and Function Management
- Summary of
declareOptions - Conclusion

1. Basic declare Usage
1.1. Defining Variables
declare can define variables, similar to direct assignment:
declare my_var="Hello, World!" echo "$my_var"
1.2. Uppercase Variables
The -u flag converts variable values to uppercase:
declare -u upper_var="hello world" echo "$upper_var" # Output: HELLO WORLD
1.3. Lowercase Variables
The -l flag converts variable values to lowercase:
declare -l lower_var="HELLO WORLD" echo "$lower_var" # Output: hello world
2. Listing Variables and Values
2.1. Listing All Variables
declare -p
This displays all variables and their values.
2.2. Listing Specific Variables
declare -p my_var
Output (example):
<code>declare -- my_var="Hello, World!"</code>
3. Special declare Attributes
3.1. Read-Only Variables (-r)
The -r flag creates read-only variables:
declare -r readonly_var="Fixed Value" readonly_var="New Value" # This will produce an error
3.2. Integer Variables (-i)
The -i flag enforces integer type:
declare -i num=10 num+=5 echo "$num" # Output: 15
Assigning non-numeric values will result in 0.
3.3. Indexed Arrays (-a)
declare -a my_array=("apple" "banana" "cherry")
echo "${my_array[@]}" # Output: apple banana cherryAccess individual elements using my_array[index].
3.4. Associative Arrays (-A) (Bash 4 )
declare my_var="Hello, World!" echo "$my_var"
Access elements using keys.
3.5. Exporting Variables (-x)
The -x flag exports variables to subshells:
declare -u upper_var="hello world" echo "$upper_var" # Output: HELLO WORLD
This makes the variable available in child processes.
4. Function Management with declare
4.1. Setting Function Attributes
declare can set function attributes (e.g., local variables).
4.2. Listing All Functions (-f)
declare -l lower_var="HELLO WORLD" echo "$lower_var" # Output: hello world
Lists all defined functions with their definitions.
4.3. Listing Function Names (-F)
declare -p
Lists only the names of defined functions.
4.4. Exporting Functions
declare -p my_var
Exports the function to subshells.
5. Checking Variable/Function Existence
Use declare -p with error redirection to check existence.
6. Removing Attributes
Use instead of - to remove attributes (e.g., declare i num).
7. Unsetting Variables/Functions
Use the unset command (e.g., unset my_var, unset -f my_function).
Example: Combined Variable and Function Management
(Illustrative example combining variable and function management with declare.)
Summary of declare Options
(Table summarizing declare options and their purposes.)
Conclusion
The declare command is a crucial tool for advanced Bash scripting, offering fine-grained control over variables and functions. Mastering declare enhances script efficiency and readability.
The above is the detailed content of Bash declare Command Usage With Examples. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1392
1392
 52
52
 36
36
 110
110
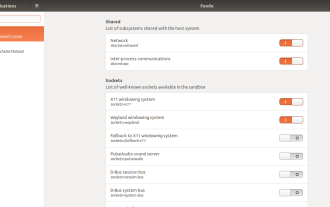 How To Easily Configure Flatpak Apps Permissions With Flatseal
Mar 22, 2025 am 09:21 AM
How To Easily Configure Flatpak Apps Permissions With Flatseal
Mar 22, 2025 am 09:21 AM
Flatpak application permission management tool: Flatseal User Guide Flatpak is a tool designed to simplify Linux software distribution and use. It safely encapsulates applications in a virtual sandbox, allowing users to run applications without root permissions without affecting system security. Because Flatpak applications are located in this sandbox environment, they must request permissions to access other parts of the operating system, hardware devices (such as Bluetooth, network, etc.) and sockets (such as pulseaudio, ssh-auth, cups, etc.). This guide will guide you on how to easily configure Flatpak with Flatseal on Linux
 How To Type Indian Rupee Symbol In Ubuntu Linux
Mar 22, 2025 am 10:39 AM
How To Type Indian Rupee Symbol In Ubuntu Linux
Mar 22, 2025 am 10:39 AM
This brief guide explains how to type Indian Rupee symbol in Linux operating systems. The other day, I wanted to type "Indian Rupee Symbol (₹)" in a word document. My keyboard has a rupee symbol on it, but I don't know how to type it. After
 How To List Or Check All Installed Linux Kernels From Commandline
Mar 23, 2025 am 10:43 AM
How To List Or Check All Installed Linux Kernels From Commandline
Mar 23, 2025 am 10:43 AM
Linux Kernel is the core component of a GNU/Linux operating system. Developed by Linus Torvalds in 1991, it is a free, open-source, monolithic, modular, and multitasking Unix-like kernel. In Linux, it is possible to install multiple kernels on a sing
 How To Enable Bucklespring Keyboard Sound In Linux
Mar 22, 2025 am 09:07 AM
How To Enable Bucklespring Keyboard Sound In Linux
Mar 22, 2025 am 09:07 AM
Experience the satisfying click of a vintage IBM Model M keyboard, even without owning one! This tutorial shows you how to enable the authentic sound of a bucklespring keyboard on your Linux system using the Bucklespring utility. Table of Contents -
 What is the Linux best used for?
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:11 AM
What is the Linux best used for?
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Linux is best used as server management, embedded systems and desktop environments. 1) In server management, Linux is used to host websites, databases, and applications, providing stability and reliability. 2) In embedded systems, Linux is widely used in smart home and automotive electronic systems because of its flexibility and stability. 3) In the desktop environment, Linux provides rich applications and efficient performance.
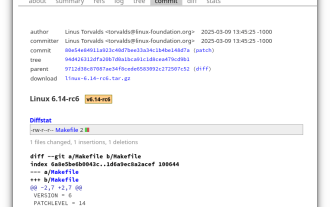 Linux Kernel 6.14 RC6 Released
Mar 24, 2025 am 10:21 AM
Linux Kernel 6.14 RC6 Released
Mar 24, 2025 am 10:21 AM
Linus Torvalds has released Linux Kernel 6.14 Release Candidate 6 (RC6), reporting no significant issues and keeping the release on track. The most notable change in this update addresses an AMD microcode signing issue, while the rest of the updates
 What are the 5 basic components of Linux?
Apr 06, 2025 am 12:05 AM
What are the 5 basic components of Linux?
Apr 06, 2025 am 12:05 AM
The five basic components of Linux are: 1. The kernel, managing hardware resources; 2. The system library, providing functions and services; 3. Shell, the interface for users to interact with the system; 4. The file system, storing and organizing data; 5. Applications, using system resources to implement functions.
 LocalSend - The Open-Source Airdrop Alternative For Secure File Sharing
Mar 24, 2025 am 09:20 AM
LocalSend - The Open-Source Airdrop Alternative For Secure File Sharing
Mar 24, 2025 am 09:20 AM
If you're familiar with AirDrop, you know it's a popular feature developed by Apple Inc. that enables seamless file transfer between supported Macintosh computers and iOS devices using Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. However, if you're using Linux and missing o




