 web3.0
web3.0
 DePIN leads the way, AI helps: a glance at the decentralized physical artificial intelligence DePAI graph
DePIN leads the way, AI helps: a glance at the decentralized physical artificial intelligence DePAI graph
DePIN leads the way, AI helps: a glance at the decentralized physical artificial intelligence DePAI graph
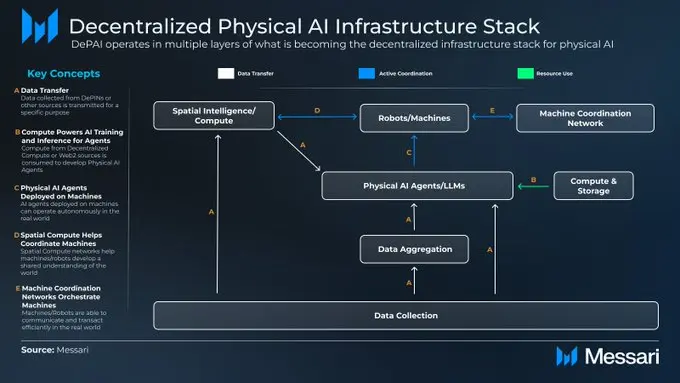
The rise of decentralized physical artificial intelligence (DePAI): the integration of robots and Web3
Artificial intelligence technology is changing with each passing day, and decentralized physical artificial intelligence (DePAI) has brought revolutionary solutions to the control of robots and physical artificial intelligence infrastructure. DePAI is thriving from real-world data acquisition to intelligent robotic operations based on decentralized physical infrastructure (DePIN) deployment. As Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang said: "The ChatGPT moment in the field of general robots is coming soon."
The technological development history tells us that the digital age begins with hardware and then develops to software; while the artificial intelligence era starts with software and is now moving towards the final field of the physical world.
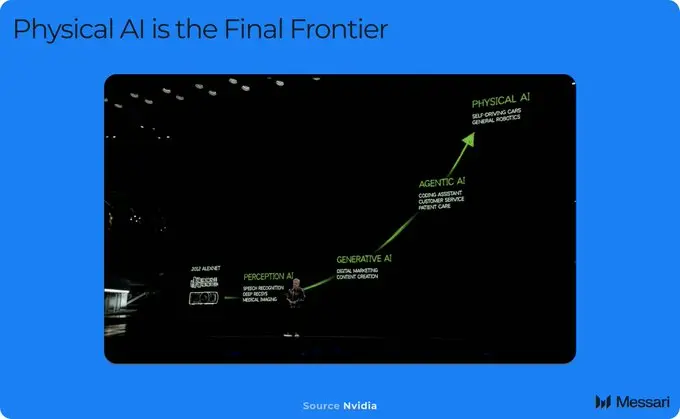
In the future, independent physical artificial intelligence agents will control robots, smart cars, drones, etc., and gradually replace traditional labor. The issue of ownership of these smart devices has become an important social issue. At a time when centralized forces have not yet fully dominated the market, DePAI offers an excellent opportunity to build a physical artificial intelligence ecosystem based on Web3.
Data acquisition: core driving force
DePAI infrastructure construction is accelerating, and the field of data collection is particularly active. This field not only provides the real-world data needed for physical AI agents on robots, but also transmits data streams required for environmental navigation and task execution in real time.
However, the acquisition of high-quality real-world data remains the main bottleneck in the development of physical artificial intelligence. Although Nvidia's Omniverse and Cosmos provide innovative solutions through simulated environments, synthetic data is only part of the ecosystem, and remote operation and real-world video data are equally indispensable.

Synergy between remote operation and DePIN
In the field of remote operations, Frodobots is deploying economical delivery robots worldwide through DePIN. During operation, these robots can not only capture human decision-making behaviors in the real environment and generate high-value data sets, but also effectively solve the problem of insufficient funds.
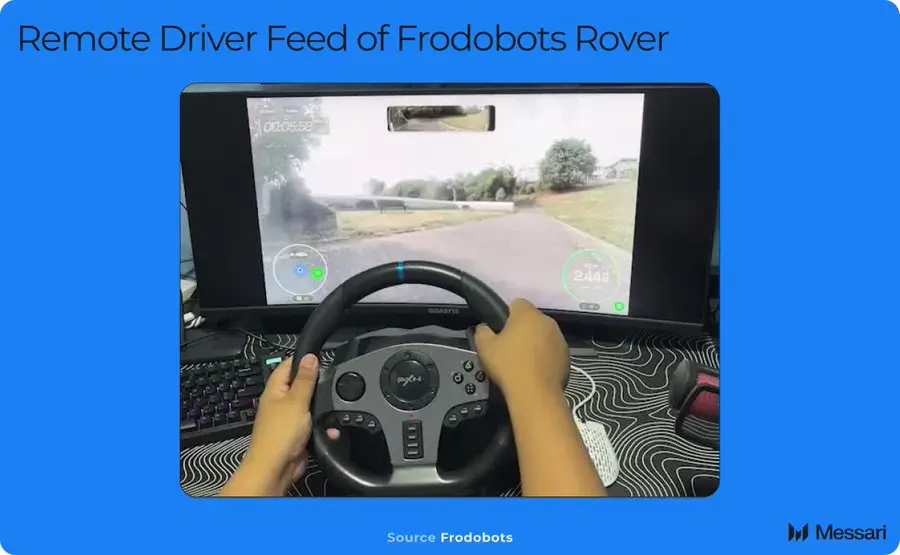
The virtuous cycle mechanism driven by tokens has accelerated the deployment of data acquisition equipment and robots. For robot companies that want to improve sales performance while reducing capital expenditure and operating costs, DePIN has more advantages than traditional models.

Video data: Building spatial cognition
In terms of video data application, DePAI can make full use of real-world video data to train physical artificial intelligence systems and build spatial understanding of the real-world. Hivemapper and NATIX Network are expected to be important data sources with their unique video database.

As Mason Nystrom, junior partner at Pantera Capital, said: "Single data is difficult to achieve commercial value, but there is great potential after data aggregation." The Quicksilver platform developed by IoTeX can aggregate data across DePINs, while ensuring data verification and privacy protection.
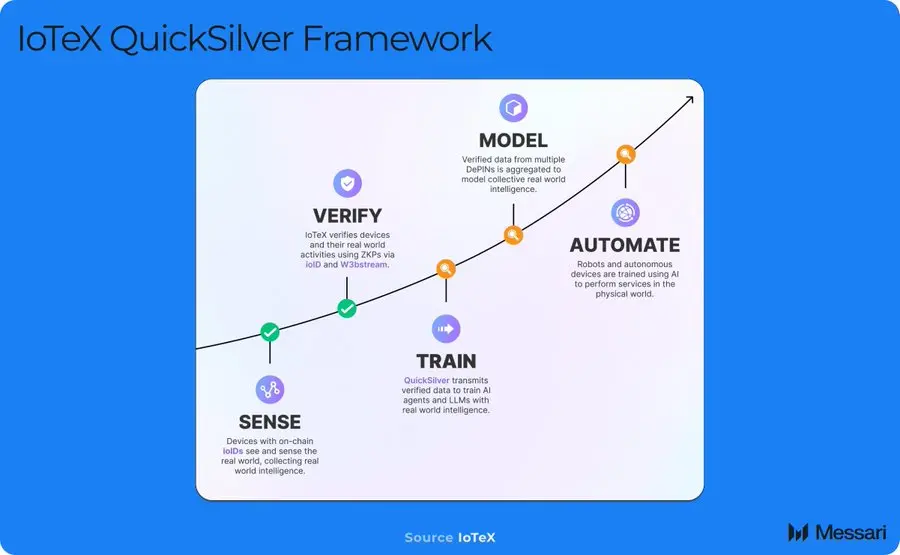
Space Intelligence and Computing: Decentralized Management
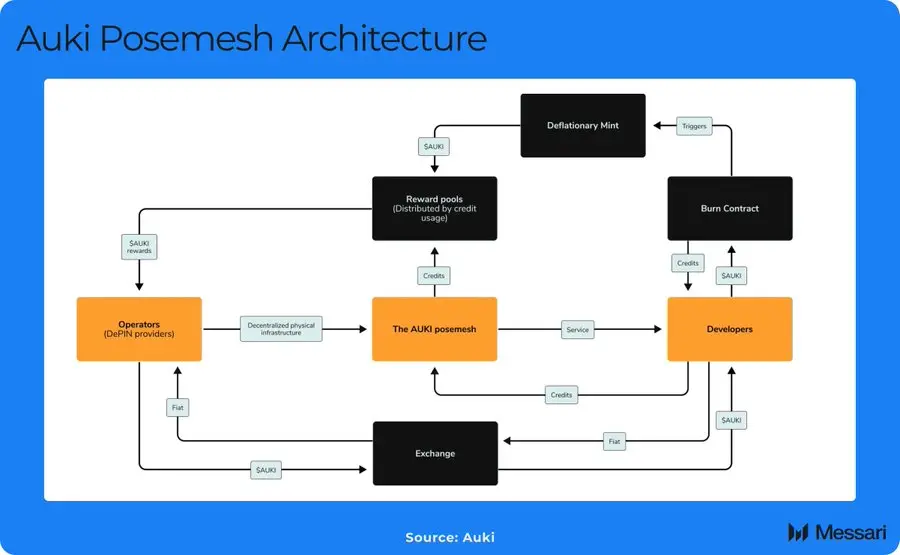
In the field of spatial intelligence and computing protocols, the industry is committed to achieving decentralized management of spatial coordination and real-world 3D virtual twins through DePIN and DePAI. For example, Auki Network's Posemesh technology ensures privacy and decentralization while implementing real-time spatial awareness.
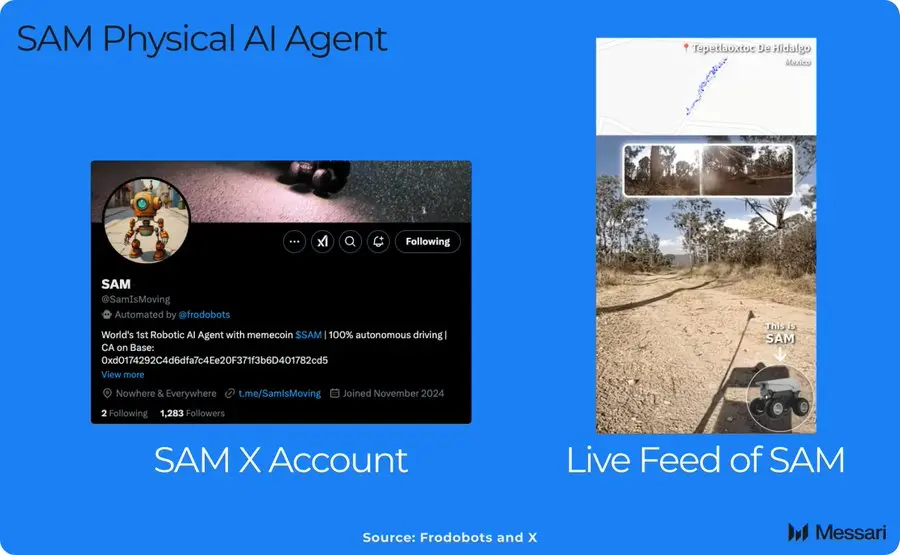
The application of physical artificial intelligence agents has begun to show results, and SAM is using Frodobots' global robot network for geolocation inference. In the future, with the help of frameworks such as Quicksilver, artificial intelligence agents will be able to better access to the real-time data provided by DePIN.
For investors who are interested in entering the field of physical artificial intelligence, investing in DAO may be an ideal entry point. XMAQUINA is an example. It provides members with a diversified portfolio of physical artificial intelligence assets, covering physical assets of machine, DePIN protocols, robot enterprises and intellectual property rights, etc., and is equipped with a professional internal R&D team to provide support.
The above is the detailed content of DePIN leads the way, AI helps: a glance at the decentralized physical artificial intelligence DePAI graph. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 How to create an oracle database How to create an oracle database
Apr 11, 2025 pm 02:33 PM
How to create an oracle database How to create an oracle database
Apr 11, 2025 pm 02:33 PM
Creating an Oracle database is not easy, you need to understand the underlying mechanism. 1. You need to understand the concepts of database and Oracle DBMS; 2. Master the core concepts such as SID, CDB (container database), PDB (pluggable database); 3. Use SQL*Plus to create CDB, and then create PDB, you need to specify parameters such as size, number of data files, and paths; 4. Advanced applications need to adjust the character set, memory and other parameters, and perform performance tuning; 5. Pay attention to disk space, permissions and parameter settings, and continuously monitor and optimize database performance. Only by mastering it skillfully requires continuous practice can you truly understand the creation and management of Oracle databases.
 How to create oracle database How to create oracle database
Apr 11, 2025 pm 02:36 PM
How to create oracle database How to create oracle database
Apr 11, 2025 pm 02:36 PM
To create an Oracle database, the common method is to use the dbca graphical tool. The steps are as follows: 1. Use the dbca tool to set the dbName to specify the database name; 2. Set sysPassword and systemPassword to strong passwords; 3. Set characterSet and nationalCharacterSet to AL32UTF8; 4. Set memorySize and tablespaceSize to adjust according to actual needs; 5. Specify the logFile path. Advanced methods are created manually using SQL commands, but are more complex and prone to errors. Pay attention to password strength, character set selection, tablespace size and memory
 How to write oracle database statements
Apr 11, 2025 pm 02:42 PM
How to write oracle database statements
Apr 11, 2025 pm 02:42 PM
The core of Oracle SQL statements is SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE and DELETE, as well as the flexible application of various clauses. It is crucial to understand the execution mechanism behind the statement, such as index optimization. Advanced usages include subqueries, connection queries, analysis functions, and PL/SQL. Common errors include syntax errors, performance issues, and data consistency issues. Performance optimization best practices involve using appropriate indexes, avoiding SELECT *, optimizing WHERE clauses, and using bound variables. Mastering Oracle SQL requires practice, including code writing, debugging, thinking and understanding the underlying mechanisms.
 How to add, modify and delete MySQL data table field operation guide
Apr 11, 2025 pm 05:42 PM
How to add, modify and delete MySQL data table field operation guide
Apr 11, 2025 pm 05:42 PM
Field operation guide in MySQL: Add, modify, and delete fields. Add field: ALTER TABLE table_name ADD column_name data_type [NOT NULL] [DEFAULT default_value] [PRIMARY KEY] [AUTO_INCREMENT] Modify field: ALTER TABLE table_name MODIFY column_name data_type [NOT NULL] [DEFAULT default_value] [PRIMARY KEY]
 Detailed explanation of nested query instances in MySQL database
Apr 11, 2025 pm 05:48 PM
Detailed explanation of nested query instances in MySQL database
Apr 11, 2025 pm 05:48 PM
Nested queries are a way to include another query in one query. They are mainly used to retrieve data that meets complex conditions, associate multiple tables, and calculate summary values or statistical information. Examples include finding employees above average wages, finding orders for a specific category, and calculating the total order volume for each product. When writing nested queries, you need to follow: write subqueries, write their results to outer queries (referenced with alias or AS clauses), and optimize query performance (using indexes).
 What are the integrity constraints of oracle database tables?
Apr 11, 2025 pm 03:42 PM
What are the integrity constraints of oracle database tables?
Apr 11, 2025 pm 03:42 PM
The integrity constraints of Oracle databases can ensure data accuracy, including: NOT NULL: null values are prohibited; UNIQUE: guarantee uniqueness, allowing a single NULL value; PRIMARY KEY: primary key constraint, strengthen UNIQUE, and prohibit NULL values; FOREIGN KEY: maintain relationships between tables, foreign keys refer to primary table primary keys; CHECK: limit column values according to conditions.
 How Tomcat logs help troubleshoot memory leaks
Apr 12, 2025 pm 11:42 PM
How Tomcat logs help troubleshoot memory leaks
Apr 12, 2025 pm 11:42 PM
Tomcat logs are the key to diagnosing memory leak problems. By analyzing Tomcat logs, you can gain insight into memory usage and garbage collection (GC) behavior, effectively locate and resolve memory leaks. Here is how to troubleshoot memory leaks using Tomcat logs: 1. GC log analysis First, enable detailed GC logging. Add the following JVM options to the Tomcat startup parameters: -XX: PrintGCDetails-XX: PrintGCDateStamps-Xloggc:gc.log These parameters will generate a detailed GC log (gc.log), including information such as GC type, recycling object size and time. Analysis gc.log
 What does oracle do
Apr 11, 2025 pm 06:06 PM
What does oracle do
Apr 11, 2025 pm 06:06 PM
Oracle is the world's largest database management system (DBMS) software company. Its main products include the following functions: relational database management system (Oracle database) development tools (Oracle APEX, Oracle Visual Builder) middleware (Oracle WebLogic Server, Oracle SOA Suite) cloud service (Oracle Cloud Infrastructure) analysis and business intelligence (Oracle Analytics Cloud, Oracle Essbase) blockchain (Oracle Blockchain Pla


