How To Keep Your Linux System Awake With Keep-Alive
Keep your computer awake effortlessly with Keep-Alive! This lightweight tool prevents your system from sleeping, ideal for long downloads, continuous processes, or simply maintaining system activity. Compatible with Linux, macOS, and Windows, Keep-Alive offers a hassle-free solution.
Table of Contents
- Key Features
- How Keep-Alive Works
- Linux Installation
- Building from Source
- Preventing Sleep on Linux (Command-line & Interactive Modes)
- Why Choose Keep-Alive?
- Conclusion
What is Keep-Alive?
Keep-Alive is a compact program designed to prevent your computer from entering sleep mode. Perfect for:
- Extended downloads
- Maintaining persistent connections
- Ensuring uninterrupted operation during crucial tasks
Its simplicity and cross-platform compatibility make it a versatile choice.
Key Features
- Customizable Duration: Set the desired wake time (e.g., 2 hours, 30 minutes).
- Cross-Platform Support: Works seamlessly on macOS, Windows, and Linux.
- Lightweight Design: Minimal resource consumption.
- User-Friendly Interface: Simple download and execution.
- Zero Configuration: Ready to use immediately.
How Keep-Alive Works
Keep-Alive employs OS-specific methods to maintain system wakefulness:
Linux: Utilizes systemd-inhibit (preferred) or xset commands/GNOME settings if systemd is unavailable.
macOS: Leverages the caffeinate command to prevent sleep across various system components (display, disk). It also simulates user activity.
Windows: Employs the SetThreadExecutionState API, with a PowerShell fallback for enhanced reliability.
Linux Installation
- Download:
curl -LO https://github.com/stigoleg/keep-alive/releases/latest/download/keep-alive_Linux_x86_64.tar.gz
- Extract:
tar xzf keep-alive_*_x86_64.tar.gz
- Install:
sudo mv keepalive /usr/local/bin/
Building from Source
Prerequisites (Linux): systemd (recommended) or X11, a TUI-compatible terminal, and Go 1.21 or later.
- Clone:
git clone https://github.com/stigoleg/keep-alive.git cd keep-alive
- Build:
go build -o keepalive ./cmd/keepalive
Preventing Sleep on Linux
Command-Line Usage
Use the -d flag to specify wake duration:
keepalive -d 2h30m // Keeps the system awake for 2 hours and 30 minutes.
Version check: keepalive -v
Help: keepalive -h
Interactive Mode
Run keepalive without flags for a menu-driven experience. Use arrow keys (or j/k) to navigate and Enter to select. Press q or Esc to exit.

Why Choose Keep-Alive?
- Robustness: Continuous system monitoring and process restarts.
- Clean Shutdown: Restores original system settings upon exit.
- Efficiency: Minimal resource usage.
Conclusion
Keep-Alive is a valuable tool for maintaining system wakefulness during essential tasks. Its ease of use and cross-platform compatibility make it a practical solution for preventing unexpected system sleep.
Resources:
- Keep-Alive GitHub Repository
Further Reading:
- How To Auto Logout Inactive Users After A Period Of Time In Linux
- 4 Ways To Keep A Command Running After You Log Out Of The SSH Session In Linux
The above is the detailed content of How To Keep Your Linux System Awake With Keep-Alive. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1371
1371
 52
52
 Mastering Text Manipulation With the Sed Command
Mar 16, 2025 am 09:48 AM
Mastering Text Manipulation With the Sed Command
Mar 16, 2025 am 09:48 AM
The Linux command line interface provides a wealth of text processing tools, one of the most powerful tools is the sed command. sed is the abbreviation of Stream EDitor, a multi-functional tool that allows complex processing of text files and streams. What is Sed? sed is a non-interactive text editor that operates on pipeline inputs or text files. By providing directives, you can let it modify and process text in a file or stream. The most common use cases of sed include selecting text, replacing text, modifying original files, adding lines to text, or removing lines from text. It can be used from the command line in Bash and other command line shells. Sed command syntax sed
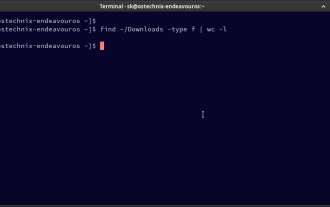 How To Count Files And Directories In Linux: A Beginner's Guide
Mar 19, 2025 am 10:48 AM
How To Count Files And Directories In Linux: A Beginner's Guide
Mar 19, 2025 am 10:48 AM
Efficiently Counting Files and Folders in Linux: A Comprehensive Guide Knowing how to quickly count files and directories in Linux is crucial for system administrators and anyone managing large datasets. This guide demonstrates using simple command-l
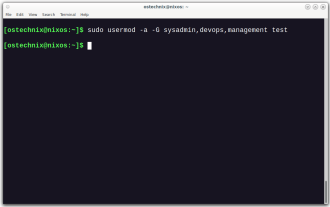 How To Add A User To Multiple Groups In Linux
Mar 18, 2025 am 11:44 AM
How To Add A User To Multiple Groups In Linux
Mar 18, 2025 am 11:44 AM
Efficiently managing user accounts and group memberships is crucial for Linux/Unix system administration. This ensures proper resource and data access control. This tutorial details how to add a user to multiple groups in Linux and Unix systems. We
 How To List Or Check All Installed Linux Kernels From Commandline
Mar 23, 2025 am 10:43 AM
How To List Or Check All Installed Linux Kernels From Commandline
Mar 23, 2025 am 10:43 AM
Linux Kernel is the core component of a GNU/Linux operating system. Developed by Linus Torvalds in 1991, it is a free, open-source, monolithic, modular, and multitasking Unix-like kernel. In Linux, it is possible to install multiple kernels on a sing
 How To Type Indian Rupee Symbol In Ubuntu Linux
Mar 22, 2025 am 10:39 AM
How To Type Indian Rupee Symbol In Ubuntu Linux
Mar 22, 2025 am 10:39 AM
This brief guide explains how to type Indian Rupee symbol in Linux operating systems. The other day, I wanted to type "Indian Rupee Symbol (₹)" in a word document. My keyboard has a rupee symbol on it, but I don't know how to type it. After
 Locating Leviathan Files in Linux
Mar 13, 2025 pm 12:11 PM
Locating Leviathan Files in Linux
Mar 13, 2025 pm 12:11 PM
Introduction In the realm of Linux, where the command line is often the compass by which we navigate, the efficient management of disk space is crucial. Whether you’re sailing through personal projects or steering the ship o
![Install Fedora Linux 41 Workstation [Step-by-Step Guide]](https://img.php.cn/upload/article/001/242/473/174149047084567.png?x-oss-process=image/resize,m_fill,h_207,w_330) Install Fedora Linux 41 Workstation [Step-by-Step Guide]
Mar 09, 2025 am 11:21 AM
Install Fedora Linux 41 Workstation [Step-by-Step Guide]
Mar 09, 2025 am 11:21 AM
This guide provides a comprehensive walkthrough for installing Fedora Linux 41 Workstation Edition. Let's get started! Table of Contents - Step 1: Prepare Your Fedora 41 Installation Media Step 2: Boot from the Fedora 41 Installation Media Step 3:
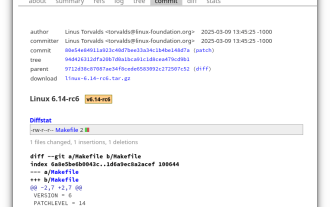 Linux Kernel 6.14 RC6 Released
Mar 24, 2025 am 10:21 AM
Linux Kernel 6.14 RC6 Released
Mar 24, 2025 am 10:21 AM
Linus Torvalds has released Linux Kernel 6.14 Release Candidate 6 (RC6), reporting no significant issues and keeping the release on track. The most notable change in this update addresses an AMD microcode signing issue, while the rest of the updates




