PostgresML Tutorial: Doing Machine Learning With SQL
The prevailing trend in machine learning involves transferring data to the model's environment for training. However, what if we reversed this process? Given that modern databases are significantly larger than machine learning models, wouldn't it be more efficient to move the models to the datasets?
This is the fundamental concept behind PostgresML – the data remains in its location, and you bring your code to the database. This inverted approach to machine learning offers numerous practical advantages that challenge conventional notions of a "database."
PostgresML: An Overview and its Advantages
PostgresML is a comprehensive machine learning platform built upon the widely-used PostgreSQL database. It introduces a novel approach called "in-database" machine learning, enabling you to execute various ML tasks within SQL without needing separate tools for each step.
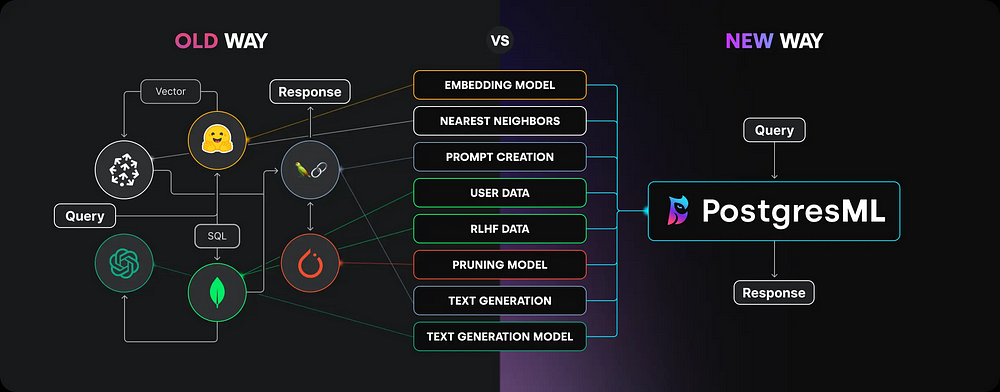
Despite its relative novelty, PostgresML offers several key benefits:
- In-database ML: Trains, deploys, and runs ML models directly within your PostgreSQL database. This eliminates the need for constant data transfer between the database and external ML frameworks, enhancing efficiency and reducing latency.
- SQL API: Leverages SQL for training, fine-tuning, and deploying machine learning models. This simplifies workflows for data analysts and scientists less familiar with multiple ML frameworks.
- Pre-trained Models: Integrates seamlessly with HuggingFace, providing access to numerous pre-trained models like Llama, Falcon, Bert, and Mistral.
- Customization and Flexibility: Supports a wide range of algorithms from Scikit-learn, XGBoost, LGBM, PyTorch, and TensorFlow, allowing for diverse supervised learning tasks directly within the database.
- Ecosystem Integration: Works with any environment supporting Postgres and offers SDKs for multiple programming languages (JavaScript, Python, and Rust are particularly well-supported).

This tutorial will demonstrate these features using a typical machine learning workflow:
- Data Loading
- Data Preprocessing
- Model Training
- Hyperparameter Fine-tuning
- Production Deployment
All these steps will be performed within a Postgres database. Let's begin!
A Complete Supervised Learning Workflow with PostgresML
Getting Started: PostgresML Free Tier
- Create a free account at https://www.php.cn/link/3349958a3e56580d4e415da345703886:
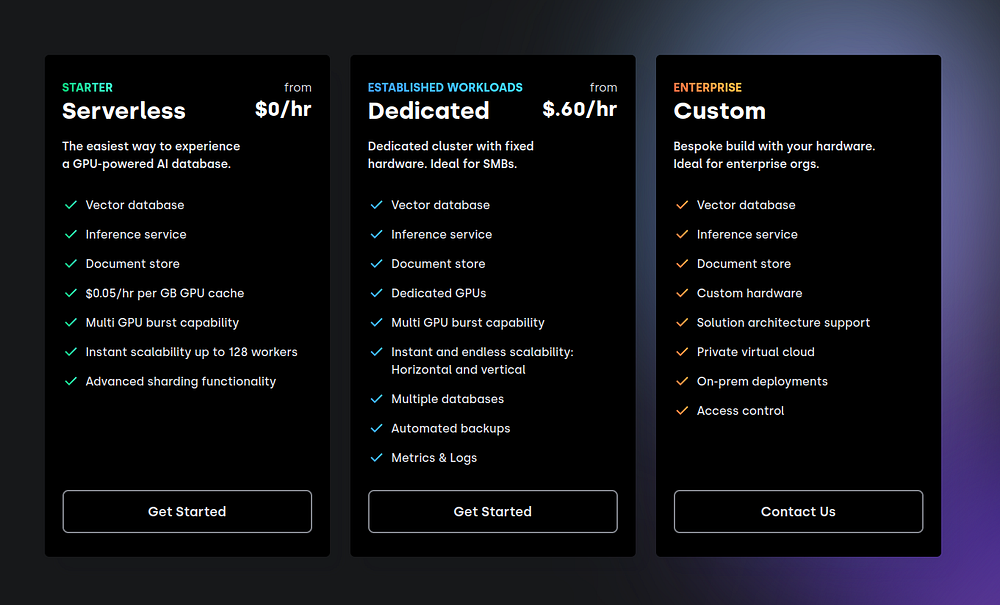
- Select the free tier, which offers generous resources:
After signup, you'll access your PostgresML console for managing projects and resources.

The "Manage" section allows you to scale your environment based on computational needs.

1. Installing and Setting Up Postgres
PostgresML requires PostgreSQL. Installation guides for various platforms are available:
- Windows
- Mac OS
- Linux
For WSL2, the following commands suffice:
sudo apt update sudo apt install postgresql postgresql-contrib sudo passwd postgres # Set a new Postgres password # Close and reopen your terminal
Verify the installation:
psql --version
For a more user-friendly experience than the terminal, consider the VSCode extension.

2. Database Connection
Use the connection details from your PostgresML console:
Connect using psql:
psql -h "host" -U "username" -p 6432 -d "database_name"
Alternatively, use the VSCode extension as described in its documentation.
Enable the pgml extension:
CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS pgml;
Verify the installation:
SELECT pgml.version();
3. Data Loading
We'll use the Diamonds dataset from Kaggle. Download it as a CSV or use this Python snippet:
import seaborn as sns
diamonds = sns.load_dataset("diamonds")
diamonds.to_csv("diamonds.csv", index=False)Create the table:
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS diamonds ( index SERIAL PRIMARY KEY, carat FLOAT, cut VARCHAR(255), color VARCHAR(255), clarity VARCHAR(255), depth FLOAT, table_ FLOAT, price INT, x FLOAT, y FLOAT, z FLOAT );
Populate the table:
INSERT INTO diamonds (carat, cut, color, clarity, depth, table_, price, x, y, z) FROM '~/full/path/to/diamonds.csv' DELIMITER ',' CSV HEADER;
Verify the data:
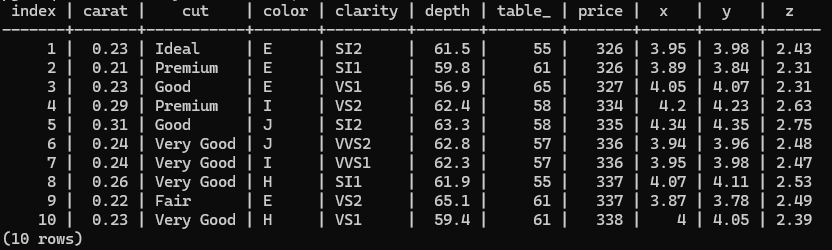
SELECT * FROM diamonds LIMIT 10;
4. Model Training
Basic Training
Train an XGBoost regressor:
SELECT pgml.train( project_name => 'Diamond prices prediction', task => 'regression', relation_name => 'diamonds', y_column_name => 'price', algorithm => 'xgboost' );
Train a multi-class classifier:
SELECT pgml.train( project_name => 'Diamond cut quality prediction', task => 'classification', relation_name => 'diamonds', y_column_name => 'cut', algorithm => 'xgboost', test_size => 0.1 );
Preprocessing
Train a random forest model with preprocessing:
SELECT pgml.train(
project_name => 'Diamond prices prediction',
task => 'regression',
relation_name => 'diamonds',
y_column_name => 'price',
algorithm => 'random_forest',
preprocess => '{
"carat": {"scale": "standard"},
"depth": {"scale": "standard"},
"table_": {"scale": "standard"},
"cut": {"encode": "target", "scale": "standard"},
"color": {"encode": "target", "scale": "standard"},
"clarity": {"encode": "target", "scale": "standard"}
}'::JSONB
);PostgresML provides various preprocessing options (encoding, imputing, scaling).
Specifying Hyperparameters
Train an XGBoost regressor with custom hyperparameters:
sudo apt update sudo apt install postgresql postgresql-contrib sudo passwd postgres # Set a new Postgres password # Close and reopen your terminal
Hyperparameter Tuning
Perform a grid search:
psql --version
5. Model Evaluation
Use pgml.predict for predictions:
psql -h "host" -U "username" -p 6432 -d "database_name"
To use a specific model, specify its ID:
CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS pgml;
Retrieve model IDs:
SELECT pgml.version();
6. Model Deployment
PostgresML automatically deploys the best-performing model. For finer control, use pgml.deploy:
import seaborn as sns
diamonds = sns.load_dataset("diamonds")
diamonds.to_csv("diamonds.csv", index=False)Deployment strategies include best_score, most_recent, and rollback.
Further Exploration of PostgresML
PostgresML extends beyond supervised learning. The homepage features a SQL editor for experimentation. Building a consumer-facing ML service might involve:
- Creating a user interface (e.g., using Streamlit or Taipy).
- Developing a backend (Python, Node.js).
- Using libraries like
psycopg2orpg-promisefor database interaction. - Preprocessing data in the backend.
- Triggering
pgml.predictupon user interaction.
Conclusion
PostgresML offers a novel approach to machine learning. To further your understanding, explore the PostgresML documentation and consider resources like DataCamp's SQL courses and AI fundamentals tutorials.
The above is the detailed content of PostgresML Tutorial: Doing Machine Learning With SQL. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Best AI Art Generators (Free & Paid) for Creative Projects
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:10 PM
Best AI Art Generators (Free & Paid) for Creative Projects
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:10 PM
The article reviews top AI art generators, discussing their features, suitability for creative projects, and value. It highlights Midjourney as the best value for professionals and recommends DALL-E 2 for high-quality, customizable art.
 Getting Started With Meta Llama 3.2 - Analytics Vidhya
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:04 PM
Getting Started With Meta Llama 3.2 - Analytics Vidhya
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:04 PM
Meta's Llama 3.2: A Leap Forward in Multimodal and Mobile AI Meta recently unveiled Llama 3.2, a significant advancement in AI featuring powerful vision capabilities and lightweight text models optimized for mobile devices. Building on the success o
 Best AI Chatbots Compared (ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude & More)
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:09 PM
Best AI Chatbots Compared (ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude & More)
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:09 PM
The article compares top AI chatbots like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Claude, focusing on their unique features, customization options, and performance in natural language processing and reliability.
 Is ChatGPT 4 O available?
Mar 28, 2025 pm 05:29 PM
Is ChatGPT 4 O available?
Mar 28, 2025 pm 05:29 PM
ChatGPT 4 is currently available and widely used, demonstrating significant improvements in understanding context and generating coherent responses compared to its predecessors like ChatGPT 3.5. Future developments may include more personalized interactions and real-time data processing capabilities, further enhancing its potential for various applications.
 Top AI Writing Assistants to Boost Your Content Creation
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:11 PM
Top AI Writing Assistants to Boost Your Content Creation
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:11 PM
The article discusses top AI writing assistants like Grammarly, Jasper, Copy.ai, Writesonic, and Rytr, focusing on their unique features for content creation. It argues that Jasper excels in SEO optimization, while AI tools help maintain tone consist
 Choosing the Best AI Voice Generator: Top Options Reviewed
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:12 PM
Choosing the Best AI Voice Generator: Top Options Reviewed
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:12 PM
The article reviews top AI voice generators like Google Cloud, Amazon Polly, Microsoft Azure, IBM Watson, and Descript, focusing on their features, voice quality, and suitability for different needs.
 Top 7 Agentic RAG System to Build AI Agents
Mar 31, 2025 pm 04:25 PM
Top 7 Agentic RAG System to Build AI Agents
Mar 31, 2025 pm 04:25 PM
2024 witnessed a shift from simply using LLMs for content generation to understanding their inner workings. This exploration led to the discovery of AI Agents – autonomous systems handling tasks and decisions with minimal human intervention. Buildin
 AV Bytes: Meta's Llama 3.2, Google's Gemini 1.5, and More
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:01 PM
AV Bytes: Meta's Llama 3.2, Google's Gemini 1.5, and More
Apr 11, 2025 pm 12:01 PM
This week's AI landscape: A whirlwind of advancements, ethical considerations, and regulatory debates. Major players like OpenAI, Google, Meta, and Microsoft have unleashed a torrent of updates, from groundbreaking new models to crucial shifts in le






