Fortifying Web Applications on Debian Servers

In the ever-changing digital age, web application security has become the cornerstone of IT strategies in various industries. As cyber threats become increasingly complex, sound security measures are becoming especially important, especially web applications running on Linux-based servers such as Debian. This guide aims to dive into web application security, focusing on how to enhance the security of applications hosted on Debian servers.
Risk Assessment
Web applications are common targets for cybercriminals because of their accessibility and valuable data that they often process. Identifying common vulnerabilities is the first step in defense:
Common Web Application Vulnerabilities
- SQL Injection: Malicious SQL statements are inserted into the input field, allowing the attacker to manipulate the database.
- Cross-site scripting (XSS): Malicious scripts are injected into websites viewed by other users, hijacking user sessions or tampering with the website.
- Cross-site Request Forgery (CSRF): Users are tricked into performing actions they have done unintentionally, usually in their authenticated web applications.
- Misse security configuration: Improper permission configuration, outdated software, and default settings can make the application vulnerable.
- Sensitive Data Breach: Inadequate protection of sensitive data (such as passwords, credit card numbers and personal information) may lead to data breaches.
Specific Challenges on Debian Server
The popularity and widespread use of Debian in server environments makes it a major target for attacks. Specific challenges include managing complex dependencies for package management and maintaining security through frequent updates.
Debian Server Security Configuration
Protect Debian servers involve multiple layers of defense, from initial setup to continuous management.
Initial Server Settings
- Protect SSH access: Change the default SSH port, disable root login, and use key-based authentication.
-
System updates and patches: Regularly use
apt-get updateandapt-get upgradeto update all installed packages to prevent vulnerabilities. - User and permission management: User and permission management using the principle of least permissions.
Installing and configuring a firewall
- Uncomplicated Firewall (UFW): A user-friendly interface for managing firewall rules in Debian. It simplifies the iptables configuration process.
- Use Iptables for advanced configuration: For users who need more granular control, iptables provides a detailed rule set that protects deeper server operations.
Protect the web server
It is crucial to select a web server like Apache or Nginx and protect it correctly.
Protect Apache/Nginx
- SSL/TLS Configuration: Implement SSL/TLS to protect data transmission. Get a free SSL certificate using tools like Let's Encrypt.
- Security Module: Use modules such as Apache's ModSecurity, which provides a powerful web application firewall to block common exploits.
- Permissions: Correct file and directory permissions can prevent unauthorized access or modification.
Server-side scripting and execution
-
PHP Configuration: Disable functions that allow command execution, such as
exec(), and use Suhosin patches for enhanced security.
Database security
Protecting a database is as important as protecting a web server.
Safe installation MySQL/MariaDB
-
Installation Practice: Run
mysql_secure_installationto delete the default values and protect database access. - Permissions: Assign the minimum required permissions to the database user.
- Connection encryption: Use SSL to encrypt the connection between the database and the web application.
Application-level safety measures
At the application level, coding practice plays a key role.
Safe coding practices
- Input Verification and Cleaning: Enterprise Verification and Cleaning: Ensure that all user input is verified and cleaned to prevent SQL injection and XSS attacks.
- Error handling and logging: Configure error handling to avoid excessive information leakage and retain detailed logs for security audits.
Session Management
- Cookie handling: Use security and HttpOnly flags to protect cookies.
- HTTPS: Force use of HTTPS on all pages to protect the transmitted user data.
Web Application Firewall (WAF)
- WAF Introduction: Discuss using tools such as OWASP ModSecurity Core Rule Set, which provides a common set of attack detection rules that can be used with ModSecurity or a compatible web application firewall.
Routine maintenance and monitoring
The security of a web application is not a one-time setting, but a continuous process.
- Update and patch: Regularly update the software and patch any known vulnerabilities.
- Security Audit: Conduct regular security audits and penetration tests to find and fix security issues.
- Monitoring Tools: Implement tools such as log analyzers and intrusion detection systems to monitor and respond to potential security threats in real time.
Best Practices and More Resources
Anyway, protecting web applications on Debian servers requires a layered approach, including server setup, application development, and regular maintenance. Resources such as OWASP Guides, Security Forums, and Advanced Training Courses are invaluable for those looking to deepen their knowledge.
Conclusion
By following these practices, organizations can protect themselves from most web threats. Security is an ongoing process – a commitment to continual adaptation and improvement of defense measures to address changing threat environments.
The above is the detailed content of Fortifying Web Applications on Debian Servers. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 Mastering Text Manipulation With the Sed Command
Mar 16, 2025 am 09:48 AM
Mastering Text Manipulation With the Sed Command
Mar 16, 2025 am 09:48 AM
The Linux command line interface provides a wealth of text processing tools, one of the most powerful tools is the sed command. sed is the abbreviation of Stream EDitor, a multi-functional tool that allows complex processing of text files and streams. What is Sed? sed is a non-interactive text editor that operates on pipeline inputs or text files. By providing directives, you can let it modify and process text in a file or stream. The most common use cases of sed include selecting text, replacing text, modifying original files, adding lines to text, or removing lines from text. It can be used from the command line in Bash and other command line shells. Sed command syntax sed
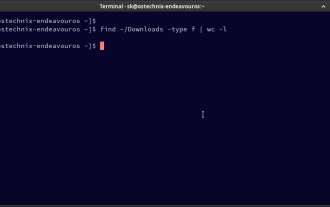 How To Count Files And Directories In Linux: A Beginner's Guide
Mar 19, 2025 am 10:48 AM
How To Count Files And Directories In Linux: A Beginner's Guide
Mar 19, 2025 am 10:48 AM
Efficiently Counting Files and Folders in Linux: A Comprehensive Guide Knowing how to quickly count files and directories in Linux is crucial for system administrators and anyone managing large datasets. This guide demonstrates using simple command-l
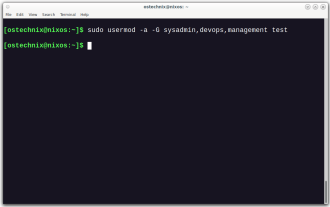 How To Add A User To Multiple Groups In Linux
Mar 18, 2025 am 11:44 AM
How To Add A User To Multiple Groups In Linux
Mar 18, 2025 am 11:44 AM
Efficiently managing user accounts and group memberships is crucial for Linux/Unix system administration. This ensures proper resource and data access control. This tutorial details how to add a user to multiple groups in Linux and Unix systems. We
 Locating Leviathan Files in Linux
Mar 13, 2025 pm 12:11 PM
Locating Leviathan Files in Linux
Mar 13, 2025 pm 12:11 PM
Introduction In the realm of Linux, where the command line is often the compass by which we navigate, the efficient management of disk space is crucial. Whether you’re sailing through personal projects or steering the ship o
 How To List Or Check All Installed Linux Kernels From Commandline
Mar 23, 2025 am 10:43 AM
How To List Or Check All Installed Linux Kernels From Commandline
Mar 23, 2025 am 10:43 AM
Linux Kernel is the core component of a GNU/Linux operating system. Developed by Linus Torvalds in 1991, it is a free, open-source, monolithic, modular, and multitasking Unix-like kernel. In Linux, it is possible to install multiple kernels on a sing
 How To Type Indian Rupee Symbol In Ubuntu Linux
Mar 22, 2025 am 10:39 AM
How To Type Indian Rupee Symbol In Ubuntu Linux
Mar 22, 2025 am 10:39 AM
This brief guide explains how to type Indian Rupee symbol in Linux operating systems. The other day, I wanted to type "Indian Rupee Symbol (₹)" in a word document. My keyboard has a rupee symbol on it, but I don't know how to type it. After
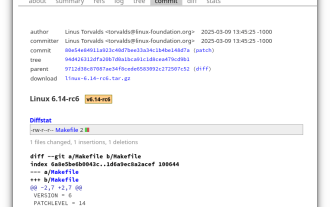 Linux Kernel 6.14 RC6 Released
Mar 24, 2025 am 10:21 AM
Linux Kernel 6.14 RC6 Released
Mar 24, 2025 am 10:21 AM
Linus Torvalds has released Linux Kernel 6.14 Release Candidate 6 (RC6), reporting no significant issues and keeping the release on track. The most notable change in this update addresses an AMD microcode signing issue, while the rest of the updates
 LocalSend - The Open-Source Airdrop Alternative For Secure File Sharing
Mar 24, 2025 am 09:20 AM
LocalSend - The Open-Source Airdrop Alternative For Secure File Sharing
Mar 24, 2025 am 09:20 AM
If you're familiar with AirDrop, you know it's a popular feature developed by Apple Inc. that enables seamless file transfer between supported Macintosh computers and iOS devices using Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. However, if you're using Linux and missing o




