iPhone vs. Android - What is The Difference Between Them?
Choosing between iOS and Android: A Detailed Comparison
The mobile phone market is dominated by two major players: iOS and Android. Both boast millions of users globally, each benefiting from over 15 years of development. While both are excellent, key differences exist, particularly concerning security. This comparison delves into the strengths and weaknesses of each platform.

Essential Security Tips for Both iOS and Android:
- Install reputable antivirus software on all devices.
- Never open email attachments from unknown senders.
- Use strong, unique passwords for each account.
- Keep your device and apps updated.
- Avoid jailbreaking or rooting your device.
iOS vs. Android: A Head-to-Head Analysis

The core differences stem from Android's open-source nature versus iOS's closed ecosystem. Google licenses Android widely, while Apple restricts iOS to its own devices.

App Ecosystem:
Android boasts a significantly larger app library (Google Play Store). However, the Apple App Store generally offers higher-quality apps due to stricter app review processes and reduced piracy. This difference arises from Apple's rigorous vetting, the prevalence of piracy on Android, and the broader device compatibility challenges faced by Android developers. Android users can install apps from third-party sources, unlike iPhone users (though this may change in the EU). Despite the quantity difference, most popular apps are available on both platforms.
Security:

Both platforms prioritize security with features like encryption and regular updates. However:
- iOS is more restrictive, limiting app installation sources, reducing malware risk.
- Android's larger market share makes it a more attractive target for hackers.
- iOS offers more consistent updates across all supported devices, unlike Android, where updates depend on individual manufacturers.
Privacy:

Both platforms offer robust permission management, allowing users to control app access to resources like cameras, contacts, and location. iOS offers a simpler, more user-friendly permission manager, while Android provides more granular control but can be less intuitive. Both offer privacy dashboards to monitor app activity. Neither OS can fully protect against third-party service privacy issues.
Updates:

Both platforms release annual major updates and regular security patches. Key differences include:
- iOS generally offers longer device support (6-8 years vs. approximately 5 years for Android).
- Android update timelines vary significantly due to manufacturer-specific customization and compatibility issues.
- iOS offers greater consistency across devices, while Android experiences fragmentation due to manufacturer modifications.
Hardware:

Apple designs and manufactures its hardware, while Android devices are produced by numerous companies. This leads to:
- Apple's control over processors and a lack of expandable storage.
- Android's greater variety in device sizes, specifications, features (including foldable phones), and price points.
- Easier access to accessories for iPhones compared to the wider range of Android devices.
Messaging and Calls:

iMessage and FaceTime provide seamless communication between iPhones. Android utilizes RCS (Rich Communication Services) or manufacturer-specific apps, leading to potential compatibility issues with iPhones (SMS/MMS). Many third-party apps work across both platforms.
Payment Capabilities:

Apple Pay and Google Pay offer similar functionalities but differ in data handling. Apple Pay uses a unique device number, while Google Pay stores encrypted card details on its servers. Both support contactless payments and additional features like storing tickets and loyalty cards.
Ecosystem and Security Implications:
Apple's closed ecosystem offers tighter integration between devices, resulting in more consistent security. Android's open nature offers greater flexibility but requires managing security across a potentially wider range of devices and operating systems. Mac users might find the iOS ecosystem more seamless. Regardless of choice, using antivirus software on all devices is crucial. MacKeeper, for example, provides comprehensive protection for macOS.
The above is the detailed content of iPhone vs. Android - What is The Difference Between Them?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Spotify on Apple Watch: How to use it in 2025
Apr 04, 2025 am 09:55 AM
Spotify on Apple Watch: How to use it in 2025
Apr 04, 2025 am 09:55 AM
With the support of Apple devices' interconnected ecosystem, managing and synchronizing your Apple devices has become a breeze. Unlock Mac with Apple Watch? Simple! (If you haven't set this unlocking method yet, you should really try it, it's very time-saving). Can you pay with Apple Watch without using iPhone? Apple can handle it easily! Today we will focus on how to download the Spotify playlist to an Apple Watch and play without an iPhone. Spoiler: This is possible. How to use Spotify on Apple Watch: A quick overview Let's dive into the key issues and their solutions directly. If this form helps you, that would be great! If you
 Floating screen recording: how to capture a specific app window on a Mac
Mar 28, 2025 am 09:16 AM
Floating screen recording: how to capture a specific app window on a Mac
Mar 28, 2025 am 09:16 AM
Mac Screen Recording: Easily capture windows, areas and drop-down menus The screenshot tool (Command Shift 5) that comes with Mac systems can record full screen or selected areas, but cannot record specific application windows separately. At this time, more powerful tools are needed to complete the task. This article will introduce several ways to help you record your Mac windows as easily as a professional. Record the application window separately Record a single window to avoid cluttered desktop backgrounds and create more professional and prominent images and videos. Here are some excellent screen recording applications: Function comparison Gifox CleanShot X Dropshare Record a specific window ✓ ✓ ✓
 Email is not syncing? How to refresh the Mail app on Mac
Apr 04, 2025 am 09:45 AM
Email is not syncing? How to refresh the Mail app on Mac
Apr 04, 2025 am 09:45 AM
Mac mail synchronization failed? Quick solution! Many Mac users rely on the included Mail app because it is simple and convenient. But even reliable software can have problems. One of the most common problems is that Mail cannot be synced, resulting in recent emails not being displayed. This article will guide you through email synchronization issues and provide some practical tips to prevent such issues. How to refresh the Mail app on your Mac Operation steps Click the envelope icon Open the Mail app > View > Show Tab Bar > Click the Envelope icon to refresh. Use shortcut keys or menu options Press Shift Command N. Or open the Mail app
 How to show only active apps in Dock on Mac
Apr 09, 2025 am 11:44 AM
How to show only active apps in Dock on Mac
Apr 09, 2025 am 11:44 AM
Mac Dockbar Optimization Guide: Show only running applications The dock bar of your Mac is the core of the system, from which you can launch Finder, Trash, recently used apps, active apps, and bookmark apps, and even add folders such as Document and Downloads. By default, the Mac dock bar will display more than a dozen Apple-owned applications. Most users will add more applications, but rarely delete any applications, resulting in the dock bar being cluttered and difficult to use effectively. This article will introduce several ways to help you organize and clean up your Mac dock bar in just a few minutes. Method 1: Manually organize the dock bar You can manually remove unused applications and keep only commonly used applications. Remove the application: Right-click on the application
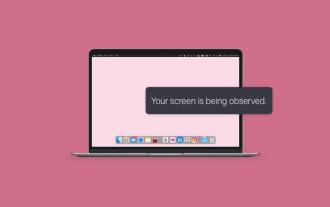 How to get rid of 'Your screen is being observed' error
Apr 05, 2025 am 10:19 AM
How to get rid of 'Your screen is being observed' error
Apr 05, 2025 am 10:19 AM
When you see the message "Your screen is being monitored", the first thing you think of is someone hacking into your computer. But that's not always the case. Let's try to find out if there are any issues that need you to worry about. Protect your Mac With Setapp, you don't need to worry about choosing a tool to protect your computer. You can quickly form your own suite of privacy and security software on Setapp. Free Trial Security Test What does "Your screen is being monitored" mean? There are many reasons why there is a Mac lock screen message that appears with “Your screen is being monitored”. You are sharing the screen with others You are recording the screen You are using AirPlay You are using some apps that try to access your screen Your computer is infected with evil









