An Introduction to Prompt Engineering with LangChain
LangChain: Streamlining LLM Application Development with Enhanced Prompt Engineering
LangChain, an open-source framework, simplifies building applications leveraging language models like GPT, LLaMA, and Mistral. Its strength lies in its advanced prompt engineering capabilities, optimizing prompts for accurate and relevant responses. This guide explores LangChain's core features: prompts, prompt templates, memory, agents, and chains, illustrated with Python code examples.

Understanding Prompt Engineering

Prompt engineering crafts effective text inputs for generative AI. It's about how you ask, encompassing wording, tone, context, and even assigning roles to the AI (e.g., simulating a native speaker). Few-shot learning, using examples within the prompt, is also valuable for complex tasks. For image or audio generation, prompts detail desired outputs, from subject and style to mood.
Essential Prompt Components

Effective prompts typically include:
- Instructions: Specify the task, information usage, query handling, and output format.
- Example Input: Sample inputs demonstrating expectations.
- Example Output: Corresponding outputs for the sample inputs.
- Query: The actual input for processing.
While the query is essential, instructions significantly impact response quality. Examples guide the desired output format.
Leveraging LangChain Prompts
LangChain's PromptTemplate simplifies prompt creation and management. Templates structure prompts, including directives, example inputs (few-shot examples), questions, and context. LangChain aims for model-agnostic templates, facilitating easy transfer between models.
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
prompt_template = PromptTemplate.from_template(
"Tell me a {adjective} joke about {content}."
)
print(prompt_template.format(adjective="sad", content="data scientists"))Output: Tell me a sad joke about data scientists.
Even without variables:
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
prompt_template = PromptTemplate.from_template("Tell me a joke")
print(prompt_template.format())Output: Tell me a joke
For chat applications, ChatPromptTemplate manages message history:
from langchain.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
chat_template = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
("system", "You are a helpful AI bot. Your name is {name}."),
("human", "Hello, how are you doing?"),
("ai", "I'm doing well, thanks!"),
("human", "{user_input}"),
]
)
messages = chat_template.format_messages(name="Bob", user_input="What is your name?")
print(messages)Why use PromptTemplate? Reusability, modularity, readability, and easier maintenance are key advantages.
LangChain Memory: Preserving Conversational Context
In chat applications, remembering past interactions is crucial. LangChain's memory features enhance prompts with past conversation details. ConversationBufferMemory is a simple example:
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
prompt_template = PromptTemplate.from_template(
"Tell me a {adjective} joke about {content}."
)
print(prompt_template.format(adjective="sad", content="data scientists"))This returns a dictionary containing the conversation history.
LangChain Chains: Orchestrating Multi-Step Processes
For complex tasks, chaining multiple steps or models is necessary. LangChain's Chains (using the recommended LCEL or the legacy Chain interface) facilitate this:
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
prompt_template = PromptTemplate.from_template("Tell me a joke")
print(prompt_template.format())The pipe operator (|) chains operations.
LangChain Agents: Intelligent Action Selection
Agents use language models to choose actions, unlike pre-defined chains. They utilize tools and toolkits, making decisions based on user input and intermediate steps. More details can be found in the official LangChain guide.
Conclusion
LangChain streamlines LLM application development through its sophisticated prompt engineering tools. Features like PromptTemplate and memory enhance efficiency and relevance. Chains and agents extend capabilities to complex, multi-step applications. LangChain offers a user-friendly approach to building powerful LLM applications.
The above is the detailed content of An Introduction to Prompt Engineering with LangChain. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1382
1382
 52
52
 I Tried Vibe Coding with Cursor AI and It's Amazing!
Mar 20, 2025 pm 03:34 PM
I Tried Vibe Coding with Cursor AI and It's Amazing!
Mar 20, 2025 pm 03:34 PM
Vibe coding is reshaping the world of software development by letting us create applications using natural language instead of endless lines of code. Inspired by visionaries like Andrej Karpathy, this innovative approach lets dev
 Top 5 GenAI Launches of February 2025: GPT-4.5, Grok-3 & More!
Mar 22, 2025 am 10:58 AM
Top 5 GenAI Launches of February 2025: GPT-4.5, Grok-3 & More!
Mar 22, 2025 am 10:58 AM
February 2025 has been yet another game-changing month for generative AI, bringing us some of the most anticipated model upgrades and groundbreaking new features. From xAI’s Grok 3 and Anthropic’s Claude 3.7 Sonnet, to OpenAI’s G
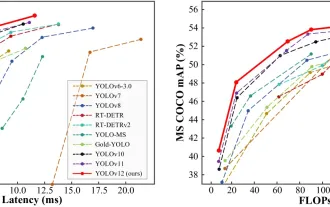 How to Use YOLO v12 for Object Detection?
Mar 22, 2025 am 11:07 AM
How to Use YOLO v12 for Object Detection?
Mar 22, 2025 am 11:07 AM
YOLO (You Only Look Once) has been a leading real-time object detection framework, with each iteration improving upon the previous versions. The latest version YOLO v12 introduces advancements that significantly enhance accuracy
 Best AI Art Generators (Free & Paid) for Creative Projects
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:10 PM
Best AI Art Generators (Free & Paid) for Creative Projects
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:10 PM
The article reviews top AI art generators, discussing their features, suitability for creative projects, and value. It highlights Midjourney as the best value for professionals and recommends DALL-E 2 for high-quality, customizable art.
 Is ChatGPT 4 O available?
Mar 28, 2025 pm 05:29 PM
Is ChatGPT 4 O available?
Mar 28, 2025 pm 05:29 PM
ChatGPT 4 is currently available and widely used, demonstrating significant improvements in understanding context and generating coherent responses compared to its predecessors like ChatGPT 3.5. Future developments may include more personalized interactions and real-time data processing capabilities, further enhancing its potential for various applications.
 Which AI is better than ChatGPT?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 06:05 PM
Which AI is better than ChatGPT?
Mar 18, 2025 pm 06:05 PM
The article discusses AI models surpassing ChatGPT, like LaMDA, LLaMA, and Grok, highlighting their advantages in accuracy, understanding, and industry impact.(159 characters)
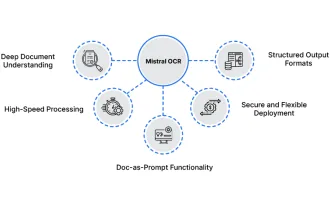 How to Use Mistral OCR for Your Next RAG Model
Mar 21, 2025 am 11:11 AM
How to Use Mistral OCR for Your Next RAG Model
Mar 21, 2025 am 11:11 AM
Mistral OCR: Revolutionizing Retrieval-Augmented Generation with Multimodal Document Understanding Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems have significantly advanced AI capabilities, enabling access to vast data stores for more informed respons
 Top AI Writing Assistants to Boost Your Content Creation
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:11 PM
Top AI Writing Assistants to Boost Your Content Creation
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:11 PM
The article discusses top AI writing assistants like Grammarly, Jasper, Copy.ai, Writesonic, and Rytr, focusing on their unique features for content creation. It argues that Jasper excels in SEO optimization, while AI tools help maintain tone consist




