 System Tutorial
System Tutorial
 LINUX
LINUX
 Best Practices and Strategic Insights to Dockerizing Your Linux Applications
Best Practices and Strategic Insights to Dockerizing Your Linux Applications
Best Practices and Strategic Insights to Dockerizing Your Linux Applications

Docker: Guide to Containerization of Linux Applications
In the field of software development and deployment, Docker has revolutionized the way applications are created, deployed and run with its containerization technology. Developers can use containers to package the application and all its required components, such as libraries and dependencies, into one unit for delivery. This guide explores best practices, deployment strategies and more for Docker applications on Linux systems, and aims to help developers and DevOps professionals improve efficiency.
Understanding Docker and Containerization
Docker is a platform that uses operating system-level virtualization technology to package software into units called "containers". Containers are isolated from each other and contain their own software, libraries, and configuration files; they can communicate with each other through well-defined channels. Unlike traditional virtual machines, containers do not contain a complete operating system, only applications and their dependencies. This makes them very lightweight and efficient.
Advantages of Docker:
- Cross-environment consistency: Docker containers ensure applications run seamlessly in any environment, from the developer's personal laptop to the production server.
- Isolation: Applications in Docker containers run in isolated environments, reducing conflicts between applications and between applications and host systems.
- Resource efficiency: Container shares the host system kernel and starts up much faster than virtual machines. They also require less compute and memory resources.
- Scalability and Modularity: Docker simplifies the process of breaking down applications into microservices, making them easier to scale and update.
Set up Docker on Linux
Docker installation process varies by Linux distribution. For example, for Ubuntu, you can install Docker with just a few commands:
sudo apt update sudo apt install docker.io sudo systemctl start docker sudo systemctl enable docker
After the installation is complete, execute sudo docker run hello-world to verify that Docker is running. This command will pull a test image from Docker Hub and run it in the container, printing a message.
Dockerized applications: Best practices
Create efficient Dockerfile
Dockerfile is a script that contains a series of commands and directives for building Docker images. The key to efficient Dockerfiles is to minimize build time and image size.
-
Build with multi-stage: This feature allows you to use multiple
FROMstatements in your Dockerfile, allowing you to separate the build environment from the runtime environment. This can significantly reduce the size of the final mirror. -
Minimize the number of layers: Combine relevant commands into a single
RUNstatement to reduce the number of layers in the image, which helps reduce the image size. -
Cache Dependencies: Copy the project's dependency files (e.g.,
package.json,requirements.txt) and install the dependencies before copying the entire project. This takes advantage of Docker's caching mechanism to avoid unnecessary reinstallation of dependencies.
Manage dependencies
Efficiently handling dependencies is essential for Docker-based applications. It is best to include only the necessary dependencies in the container to keep it lightweight. Take advantage of Docker's caching mechanism by adding dependencies before application code, ensuring that rebuilding the image after the code changes does not unnecessarily reinstall the dependencies.
Environment Configuration
Configuration with environment variables and .env files to avoid hard-coded values. Docker supports setting environment variables when Dockerfile and container startup. This is essential for maintaining different configurations in development, testing, and production environments without changing code.
Security Considerations
Security measures in Docker-based environments include using official images as a basis, using tools such as Clair to scan for vulnerabilities in images regularly, and avoiding running containers as root unless absolutely necessary. Implementing these practices helps maintain secure deployments.
Deployment Policy
Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD)
Integrating Docker with CI/CD pipelines automates the process of testing and deploying applications. Tools such as Jenkins, GitLab CI, and GitHub Actions can build Docker images from source, run tests in containers, and push images that pass tests to the registry. This automation simplifies the deployment process and ensures that only tested stable code can enter production.
Orchestration Tools
Orchestration Tools such as Kubernetes and Docker Swarm are invaluable for managing multiple containers across different hosts. They help automate deployment, scaling, and managing containerized applications.
- Docker Swarm is a native clustering tool for Docker, easy to set up and well integrated with the Docker ecosystem.
- KubernetesProviding a wider range of features, it is the preferred solution for complex, scalable systems. It can effectively handle deployment modes, extensions, and container self-healing.
Monitoring and Maintenance
Monitoring tools such as Prometheus and Grafana can be used to monitor container metrics and performance. Centralized logging with ELK Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana) or similar solutions helps aggregate logs from multiple containers, making it easier to troubleshoot problems.
Practical Case and Case Studies
Spotify, Netflix, and PayPal have adopted Docker to simplify development and deployment processes, achieving unprecedented scalability and efficiency. These case studies highlight the power of change in Docker when leveraging best practices in real scenarios.
Conclusion
Dockerized applications on Linux provide a powerful way to achieve efficiency, consistency, and scalability in software development and deployment. By following the best practices outlined and leveraging the power of the Docker ecosystem, developers and organizations can significantly improve their operations capabilities and deliver better software faster.
As Docker and containerization technologies continue to evolve, keeping abreast of the latest practices and tools is essential to maintaining a competitive edge in software development and deployment. Embracing the Docker philosophy not only simplifies deployment challenges, but also paves the way for innovation in cloud computing and microservice architectures.
The above is the detailed content of Best Practices and Strategic Insights to Dockerizing Your Linux Applications. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1382
1382
 52
52
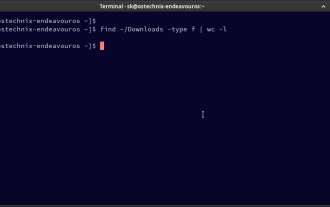 How To Count Files And Directories In Linux: A Beginner's Guide
Mar 19, 2025 am 10:48 AM
How To Count Files And Directories In Linux: A Beginner's Guide
Mar 19, 2025 am 10:48 AM
Efficiently Counting Files and Folders in Linux: A Comprehensive Guide Knowing how to quickly count files and directories in Linux is crucial for system administrators and anyone managing large datasets. This guide demonstrates using simple command-l
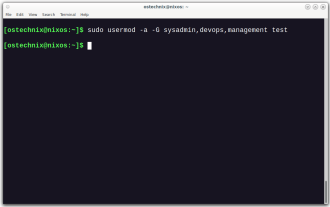 How To Add A User To Multiple Groups In Linux
Mar 18, 2025 am 11:44 AM
How To Add A User To Multiple Groups In Linux
Mar 18, 2025 am 11:44 AM
Efficiently managing user accounts and group memberships is crucial for Linux/Unix system administration. This ensures proper resource and data access control. This tutorial details how to add a user to multiple groups in Linux and Unix systems. We
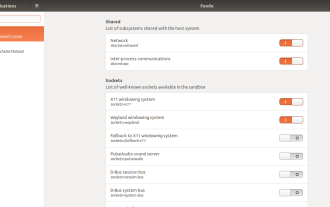 How To Easily Configure Flatpak Apps Permissions With Flatseal
Mar 22, 2025 am 09:21 AM
How To Easily Configure Flatpak Apps Permissions With Flatseal
Mar 22, 2025 am 09:21 AM
Flatpak application permission management tool: Flatseal User Guide Flatpak is a tool designed to simplify Linux software distribution and use. It safely encapsulates applications in a virtual sandbox, allowing users to run applications without root permissions without affecting system security. Because Flatpak applications are located in this sandbox environment, they must request permissions to access other parts of the operating system, hardware devices (such as Bluetooth, network, etc.) and sockets (such as pulseaudio, ssh-auth, cups, etc.). This guide will guide you on how to easily configure Flatpak with Flatseal on Linux
 How To List Or Check All Installed Linux Kernels From Commandline
Mar 23, 2025 am 10:43 AM
How To List Or Check All Installed Linux Kernels From Commandline
Mar 23, 2025 am 10:43 AM
Linux Kernel is the core component of a GNU/Linux operating system. Developed by Linus Torvalds in 1991, it is a free, open-source, monolithic, modular, and multitasking Unix-like kernel. In Linux, it is possible to install multiple kernels on a sing
 How To Type Indian Rupee Symbol In Ubuntu Linux
Mar 22, 2025 am 10:39 AM
How To Type Indian Rupee Symbol In Ubuntu Linux
Mar 22, 2025 am 10:39 AM
This brief guide explains how to type Indian Rupee symbol in Linux operating systems. The other day, I wanted to type "Indian Rupee Symbol (₹)" in a word document. My keyboard has a rupee symbol on it, but I don't know how to type it. After
 Yt-dlp Commands: The Complete Tutorial For Beginners (2025)
Mar 21, 2025 am 11:00 AM
Yt-dlp Commands: The Complete Tutorial For Beginners (2025)
Mar 21, 2025 am 11:00 AM
Have you ever wanted to save your favorite videos from the internet? Whether it's a funny cat video or a tutorial you want to watch later, Yt-dlp is here to help! In this comprehensive yt-dlp tutorial, we will explain what yt-dlp is, how to install i
 What is the Linux best used for?
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:11 AM
What is the Linux best used for?
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Linux is best used as server management, embedded systems and desktop environments. 1) In server management, Linux is used to host websites, databases, and applications, providing stability and reliability. 2) In embedded systems, Linux is widely used in smart home and automotive electronic systems because of its flexibility and stability. 3) In the desktop environment, Linux provides rich applications and efficient performance.
 LocalSend - The Open-Source Airdrop Alternative For Secure File Sharing
Mar 24, 2025 am 09:20 AM
LocalSend - The Open-Source Airdrop Alternative For Secure File Sharing
Mar 24, 2025 am 09:20 AM
If you're familiar with AirDrop, you know it's a popular feature developed by Apple Inc. that enables seamless file transfer between supported Macintosh computers and iOS devices using Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. However, if you're using Linux and missing o



