 Mobile Game Tutorial
Mobile Game Tutorial
 Mobile Game Guide
Mobile Game Guide
 How to access DeepSeekapi - DeepSeekapi access call tutorial
How to access DeepSeekapi - DeepSeekapi access call tutorial
How to access DeepSeekapi - DeepSeekapi access call tutorial
Detailed explanation of DeepSeek API access and call: Quick guide
This article will provide you with detailed instructions on how to access and call the DeepSeek API, helping you easily use powerful AI models.

Step 1: Obtain the API key
- Visit the DeepSeek official website and click on the "Open Platform" in the upper right corner.

You will get a certain number of free tokens (for metering API usage). In the menu on the left, click "API Keys" and then click "Create API key".
Name your API key (for example, "test") and copy the generated key immediately. Be sure to save this key properly as it will only be displayed once.


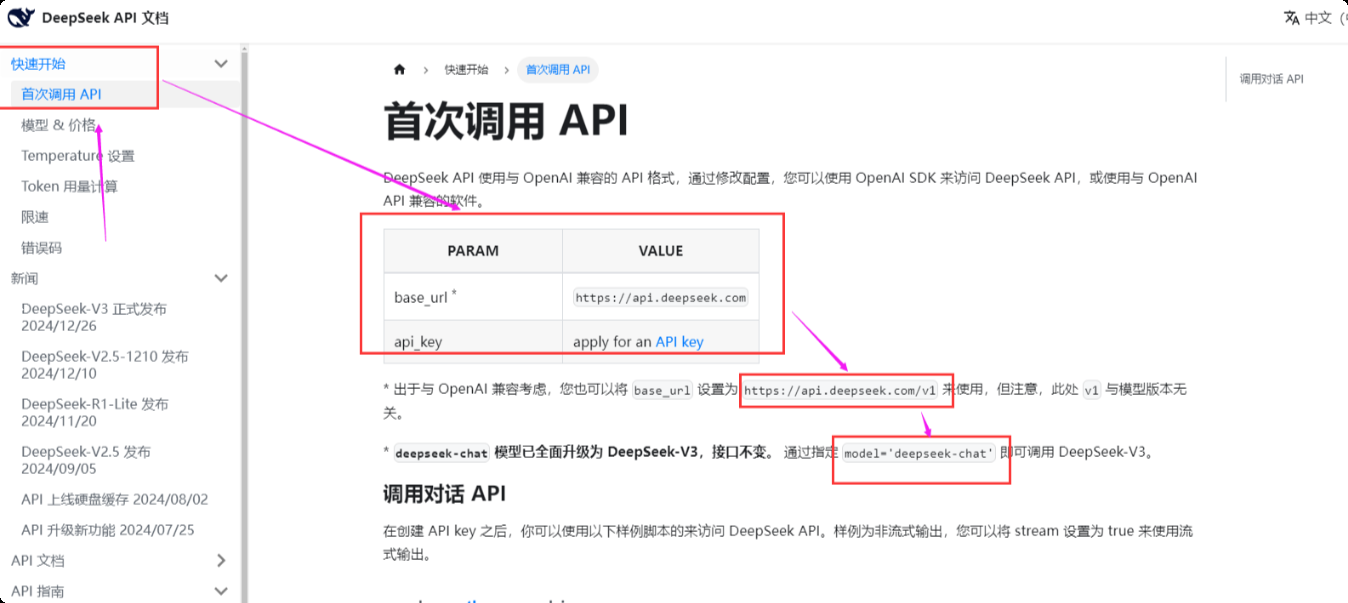
Step 2: Get base_url and chat_model
- In the Quick Start section of the DeepSeek API documentation, find
base_urlandchat_modelparameters. The acquisition methods of other platforms are similar.
Step 3: Configure model parameters
For security reasons, it is recommended to store the API key in environment variables rather than writing directly into the code. The following two methods are provided:
Method 1: The terminal temporarily sets environment variables (only valid in the current terminal session)
Enter the following command in the terminal to add your API key to the environment variable (replace YOUR_API_KEY with your actual key):
export API_KEY="YOUR_API_KEY"
Method 2: Create .env file (recommended)
- Create a file named
.env. - Add the following in the
.envfile, replacingYOUR_API_KEYwith your actual key:
<code>API_KEY="YOUR_API_KEY"</code>
In Python code, use the python-dotenv library to read environment variables:
from dotenv import load_dotenv
import os
load_dotenv() # Load the .env file api_key = os.getenv("API_KEY")Step 4: Create a client
Create a DeepSeek client using base_url and api_key . (The specific client creation method depends on the library you are using)
Step 5: Test API calls
Here is a simple Python code example for testing API connections:
# ... (Previous code, including client creation) ...
response = client.chat(model=chat_model, messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "Hello"}])
print(response)If everything is configured correctly, you will receive a reply from the model. If an error occurs, check that your API key and configuration are correct.
For more details, please refer to the official DeepSeek document. Original link (please replace it with the actual link)
The above is the detailed content of How to access DeepSeekapi - DeepSeekapi access call tutorial. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1376
1376
 52
52
 Navicat's method to view MongoDB database password
Apr 08, 2025 pm 09:39 PM
Navicat's method to view MongoDB database password
Apr 08, 2025 pm 09:39 PM
It is impossible to view MongoDB password directly through Navicat because it is stored as hash values. How to retrieve lost passwords: 1. Reset passwords; 2. Check configuration files (may contain hash values); 3. Check codes (may hardcode passwords).
 What is the way Navicat password storage?
Apr 08, 2025 pm 09:15 PM
What is the way Navicat password storage?
Apr 08, 2025 pm 09:15 PM
Navicat uses AES encryption algorithm to encrypt passwords and uses a dynamic key mechanism to protect passwords, but it is not foolproof. To enhance security, it is recommended to set up complex passwords, modify them regularly, keep the system and software updated, and protect against malware.
 How secure is Navicat's password?
Apr 08, 2025 pm 09:24 PM
How secure is Navicat's password?
Apr 08, 2025 pm 09:24 PM
Navicat's password security relies on the combination of symmetric encryption, password strength and security measures. Specific measures include: using SSL connections (provided that the database server supports and correctly configures the certificate), regularly updating Navicat, using more secure methods (such as SSH tunnels), restricting access rights, and most importantly, never record passwords.
 Navicat connects to database error code and solution
Apr 08, 2025 pm 11:06 PM
Navicat connects to database error code and solution
Apr 08, 2025 pm 11:06 PM
Common errors and solutions when connecting to databases: Username or password (Error 1045) Firewall blocks connection (Error 2003) Connection timeout (Error 10060) Unable to use socket connection (Error 1042) SSL connection error (Error 10055) Too many connection attempts result in the host being blocked (Error 1129) Database does not exist (Error 1049) No permission to connect to database (Error 1000)
 How to add a new column in SQL
Apr 09, 2025 pm 02:09 PM
How to add a new column in SQL
Apr 09, 2025 pm 02:09 PM
Add new columns to an existing table in SQL by using the ALTER TABLE statement. The specific steps include: determining the table name and column information, writing ALTER TABLE statements, and executing statements. For example, add an email column to the Customers table (VARCHAR(50)): ALTER TABLE Customers ADD email VARCHAR(50);
 How to view database passwords in Navicat Premium?
Apr 08, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
How to view database passwords in Navicat Premium?
Apr 08, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
Navicat Premium does not store database passwords. The connection information is just a connection parameter, and the password is stored encrypted or not stored. If you forget your password, you need to use the database tool to reset it. If you need to check the connected database password, it is not feasible; if you suspect that the leak is found, you need to check the installation directory and system security. The first principle is safety first, and do not believe in cracking tools easily.
 How to view database password in Navicat for MongoDB?
Apr 08, 2025 pm 09:21 PM
How to view database password in Navicat for MongoDB?
Apr 08, 2025 pm 09:21 PM
Navicat for MongoDB cannot view the database password because the password is encrypted and only holds connection information. Retrieving passwords requires MongoDB itself, and the specific operation depends on the deployment method. Security first, develop good password habits, and never try to obtain passwords from third-party tools to avoid security risks.
 Navicat Connection Timeout: How to Resolve
Apr 08, 2025 pm 11:03 PM
Navicat Connection Timeout: How to Resolve
Apr 08, 2025 pm 11:03 PM
Reasons for Navicat connection timeout: network instability, busy database, firewall blocking, server configuration problems, and improper Navicat settings. Solution steps: Check network connection, database status, firewall settings, adjust server configuration, check Navicat settings, restart the software and server, and contact the administrator for help.



