
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) empowers large language models (LLMs) by incorporating information retrieval. This allows LLMs to access external knowledge bases, resulting in more accurate, current, and contextually appropriate responses. Corrective RAG (CRAG), an advanced RAG technique, further enhances accuracy by introducing self-reflection and self-assessment mechanisms for retrieved documents.
This article covers:
Published as part of the Data Science Blogathon.
Table of Contents
CRAG's Underlying Mechanism
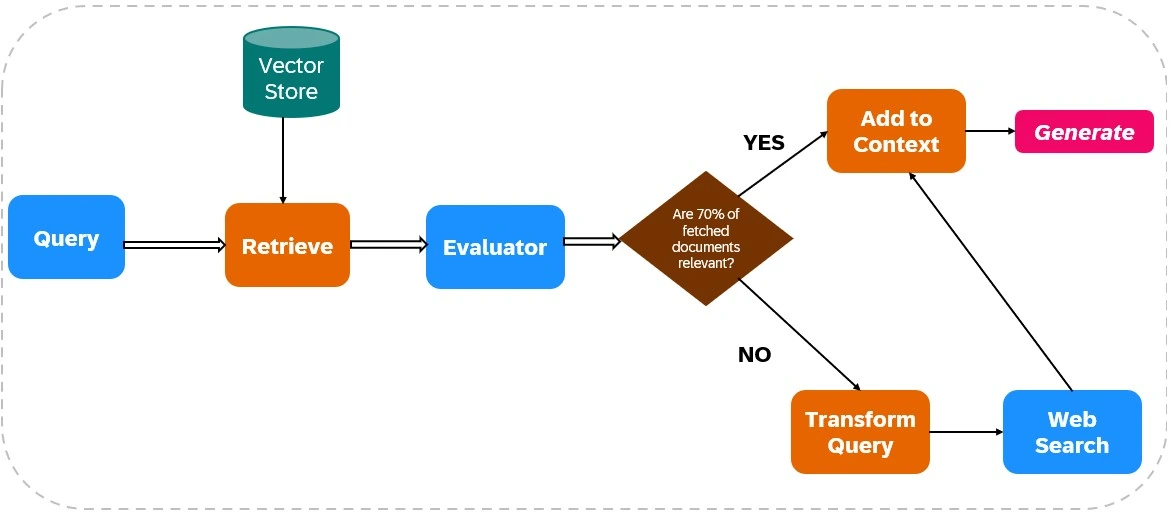
CRAG enhances the dependability of LLM outputs by integrating web search into its retrieval and generation processes (see Figure 1).
Document Retrieval:
Relevance Assessment:
An evaluator assesses retrieved document relevance. If over 70% of documents are deemed irrelevant, corrective actions are initiated; otherwise, response generation proceeds.
Web Search Integration:
If document relevance is insufficient, CRAG uses web search:
Response Generation:
CRAG synthesizes data from both initial retrieval and web searches to create a coherent, accurate response.
CRAG vs. Traditional RAG
CRAG actively verifies and refines retrieved information, unlike traditional RAG, which relies on retrieved documents without verification. CRAG often incorporates real-time web search, providing access to the most up-to-date information, unlike traditional RAG's reliance on static knowledge bases. This makes CRAG ideal for applications requiring high accuracy and real-time data integration.
Practical CRAG Implementation
This section details a CRAG implementation using Python, LangChain, and Tavily.
Step 1: Library Installation
Install necessary libraries:
!pip install tiktoken langchain-openai langchainhub chromadb langchain langgraph tavily-python !pip install -qU pypdf langchain_community
Step 2: API Key Configuration
Set your API keys:
import os os.environ["TAVILY_API_KEY"] = "" os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = ""
Step 3: Library Imports
Import required libraries (code omitted for brevity, but similar to the original example).
Step 4: Document Chunking and Retriever Creation
(Code omitted for brevity, but similar to the original example, using PyPDFLoader, RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter, OpenAIEmbeddings, and Chroma).
Step 5: RAG Chain Setup
(Code omitted for brevity, but similar to the original example, using hub.pull("rlm/rag-prompt") and ChatOpenAI).
Step 6: Evaluator Setup
(Code omitted for brevity, but similar to the original example, defining the Evaluator class and using ChatOpenAI for evaluation).
Step 7: Query Rewriter Setup
(Code omitted for brevity, but similar to the original example, using ChatOpenAI for query rewriting).
Step 8: Web Search Setup
from langchain_community.tools.tavily_search import TavilySearchResults web_search_tool = TavilySearchResults(k=3)
Step 9-12: LangGraph Workflow Setup and Execution
(Code omitted for brevity, but conceptually similar to the original example, defining the GraphState, function nodes (retrieve, generate, evaluate_documents, transform_query, web_search), and connecting them using StateGraph.) The final output and comparison with traditional RAG are also conceptually similar.
CRAG's Challenges
CRAG's effectiveness depends heavily on the evaluator's accuracy. A weak evaluator can introduce errors. Scalability and adaptability are also concerns, requiring continuous updates and training. Web search integration introduces the risk of biased or unreliable information, necessitating robust filtering mechanisms.
Conclusion
CRAG significantly improves LLM output accuracy and reliability. Its ability to evaluate and supplement retrieved information with real-time web data makes it valuable for applications demanding high precision and up-to-date information. However, continuous refinement is crucial to address the challenges related to evaluator accuracy and web data reliability.
Key Takeaways (similar to the original, but rephrased for conciseness)
Frequently Asked Questions (similar to the original, but rephrased for conciseness)
(Note: The image remains unchanged and is included as in the original input.)
The above is the detailed content of Corrective RAG (CRAG) in Action. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




