The Symbiotic Orchestra of Linux and Blockchain

In the heart of the digital age, the way we interact, transact, and process information has been continuously morphing, paving the way for innovative solutions to antiquated problems. Two such innovative veins—Linux and Blockchain Technology—are not just advancing in parallel, but are synergistically fostering a decentralized digital frontier. Linux, a robust open-source operating system, epitomizes the spirit of community-driven innovation, while blockchain technology with its immutable, transparent, and decentralized nature is set to redefine trust in the digital domain. Together, their convergence is perceived as a catalyst propelling a new era of decentralized applications and solutions. This article endeavors to unpack the intricacies of how Linux and blockchain technology intertwine, creating a fertile ground for decentralized innovation.
Historical ContextThe Linux Lineage
Tracing back to 1991, Linux emerged from the sparks of a hobbyist project by Linus Torvalds, metamorphosing over the decades into an enterprise-grade operating system. It's not just an OS; it's a movement that underscores the essence of open-source collaboration.
The Blockchain Breakthrough
The blockchain saga commenced with the inception of Bitcoin in 2009, by an anonymous entity known as Satoshi Nakamoto. Over time, the underlying technology burgeoned beyond cryptocurrency, heralding a new paradigm of decentralized applications (dApps).
The Open Source Movement
Both Linux and blockchain are prodigies of the open-source movement, an ethos that fosters innovation through collective intelligence, transparency, and shared ownership.
Technical SynergyLinux: The Bedrock of Blockchain
Linux, known for its stability, security, and scalability, presents an ideal abode for blockchain development. Several blockchain projects like Hyperledger, Ethereum, and others find their roots embedded in Linux infrastructure, exemplifying the symbiotic rapport between the two.
Blockchain: The Decentralization Dynamo
Blockchain, with its decentralized ledger system, complements Linux's open-source philosophy, offering a new framework for building trustless, autonomous systems.
Ecosystem DevelopmentCommunity-driven Innovation
The collaboration between communities of Linux and blockchain aficionados has catalyzed a myriad of projects. The open forums, consortiums, and joint initiatives exemplify the cross-pollination of ideas and resources.
Industry Adoption
Various industries are pivoting towards Linux-based blockchain solutions to address challenges like supply chain transparency, identity management, and data integrity. Companies like IBM, ConsenSys, and others are at the forefront of this adoption, demonstrating the boundless potential of this convergence.
Regulatory LandscapeRegulatory Ruminations
As blockchain ventures into mainstream applications, regulatory bodies worldwide are crafting frameworks to ensure its safe and ethical deployment, a venture that also impacts Linux-based blockchain projects.
Future Frameworks
The discourse on future regulatory landscapes is ongoing, with potential to mold the trajectory of Linux and blockchain synergy.
Challenges and OpportunitiesNavigating the Nexus
The alliance of Linux and blockchain, though promising, is laden with technical, ethical, and logistical challenges. The exploration for solutions continues, driven by a global community of developers, entrepreneurs, and visionaries.
Unveiling the Horizon
The potential for overcoming current technological limitations and unveiling new horizons is colossal. As Linux and blockchain continue to evolve, the prospects of their amalgamation hold promise for a decentralized, transparent, and equitable digital realm.
ConclusionThe digital symphony orchestrated by Linux and blockchain technology is not just a narrative of technological innovation but a testimony to the power of open-source, decentralized ethos in redefining the contours of digital interaction, trust, and innovation. The journey ahead, though laden with challenges, is bright with the promise of uncovering new dimensions of what we can achieve in a decentralized, digitally interconnected world.
The above is the detailed content of The Symbiotic Orchestra of Linux and Blockchain. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1381
1381
 52
52
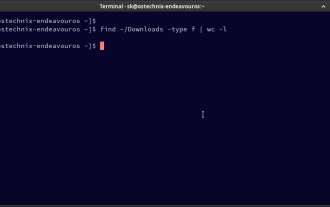 How To Count Files And Directories In Linux: A Beginner's Guide
Mar 19, 2025 am 10:48 AM
How To Count Files And Directories In Linux: A Beginner's Guide
Mar 19, 2025 am 10:48 AM
Efficiently Counting Files and Folders in Linux: A Comprehensive Guide Knowing how to quickly count files and directories in Linux is crucial for system administrators and anyone managing large datasets. This guide demonstrates using simple command-l
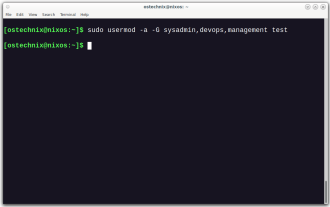 How To Add A User To Multiple Groups In Linux
Mar 18, 2025 am 11:44 AM
How To Add A User To Multiple Groups In Linux
Mar 18, 2025 am 11:44 AM
Efficiently managing user accounts and group memberships is crucial for Linux/Unix system administration. This ensures proper resource and data access control. This tutorial details how to add a user to multiple groups in Linux and Unix systems. We
 How To List Or Check All Installed Linux Kernels From Commandline
Mar 23, 2025 am 10:43 AM
How To List Or Check All Installed Linux Kernels From Commandline
Mar 23, 2025 am 10:43 AM
Linux Kernel is the core component of a GNU/Linux operating system. Developed by Linus Torvalds in 1991, it is a free, open-source, monolithic, modular, and multitasking Unix-like kernel. In Linux, it is possible to install multiple kernels on a sing
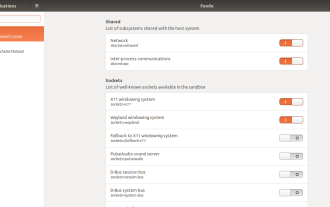 How To Easily Configure Flatpak Apps Permissions With Flatseal
Mar 22, 2025 am 09:21 AM
How To Easily Configure Flatpak Apps Permissions With Flatseal
Mar 22, 2025 am 09:21 AM
Flatpak application permission management tool: Flatseal User Guide Flatpak is a tool designed to simplify Linux software distribution and use. It safely encapsulates applications in a virtual sandbox, allowing users to run applications without root permissions without affecting system security. Because Flatpak applications are located in this sandbox environment, they must request permissions to access other parts of the operating system, hardware devices (such as Bluetooth, network, etc.) and sockets (such as pulseaudio, ssh-auth, cups, etc.). This guide will guide you on how to easily configure Flatpak with Flatseal on Linux
 How To Type Indian Rupee Symbol In Ubuntu Linux
Mar 22, 2025 am 10:39 AM
How To Type Indian Rupee Symbol In Ubuntu Linux
Mar 22, 2025 am 10:39 AM
This brief guide explains how to type Indian Rupee symbol in Linux operating systems. The other day, I wanted to type "Indian Rupee Symbol (₹)" in a word document. My keyboard has a rupee symbol on it, but I don't know how to type it. After
 What is the Linux best used for?
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:11 AM
What is the Linux best used for?
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Linux is best used as server management, embedded systems and desktop environments. 1) In server management, Linux is used to host websites, databases, and applications, providing stability and reliability. 2) In embedded systems, Linux is widely used in smart home and automotive electronic systems because of its flexibility and stability. 3) In the desktop environment, Linux provides rich applications and efficient performance.
 Linux Kernel 6.14 RC6 Released
Mar 24, 2025 am 10:21 AM
Linux Kernel 6.14 RC6 Released
Mar 24, 2025 am 10:21 AM
Linus Torvalds has released Linux Kernel 6.14 Release Candidate 6 (RC6), reporting no significant issues and keeping the release on track. The most notable change in this update addresses an AMD microcode signing issue, while the rest of the updates
 LocalSend - The Open-Source Airdrop Alternative For Secure File Sharing
Mar 24, 2025 am 09:20 AM
LocalSend - The Open-Source Airdrop Alternative For Secure File Sharing
Mar 24, 2025 am 09:20 AM
If you're familiar with AirDrop, you know it's a popular feature developed by Apple Inc. that enables seamless file transfer between supported Macintosh computers and iOS devices using Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. However, if you're using Linux and missing o




