Linux Kernel 6.11 RC4 Released: Normal Development Cycle Continues
Linux Kernel 6.11 fourth release candidate (rc4) release: Improved file system, drivers, and network cores
Linus Torvalds, the creator and main developer of the Linux kernel, announced the fourth release candidate (rc4) of Linux kernel 6.11. This release contains significant updates to the file system, drivers, and core networks.
Although the difference statistics for this release candidate are larger than that of rc2 and rc3, Torvalds guarantees this is a normal pattern with no exceptions.
As Geert Uytterhoeven mentioned in a separate report, there are 11 new build errors and 2 new build warnings in the 6.11-rc4 kernel compared to previous versions. However, the total errors were reduced by 21 and warnings were reduced by 19.
Uytterhoeven provides a detailed breakdown of these changes and encourages the resolution of these issues. He also noted that two specific bugs related to the Sparc architecture and Intel Xe graphics card are already well known and that there are patches available.

Major changes in Linux kernel 6.11 RC4:
- A large number of updates to the file system, most notably the update to bcachefs.
- Updates to drivers, especially to GPUs, networks, and various drivers.
- Updates to memory management (MM), architecture, core network and documentation.
- Compared with version 6.10, there are significant improvements in build errors (-21) and warning improvements (-19).
- Compared with version 6.10, there are fewer build error regressions (11) and fewer warning regressions (2).
- Compared with 6.11-rc3 version, there are fewer build error regressions (6) and fewer improvements (-4). Warnings have no regression or improvement.
Error fixes and improvements in Linux kernel 6.11 RC4:
Linux Kernel 6.11-rc4 contains many bug fixes and improvements. Here are some main contents:
- File system
- Bcachefs has made major updates, including fixes for flawed fast paths, disk billing, race conditions and memory leaks.
- Btrfs fixes range map reduction, data cloning during sending and incorrect inode state use.
- XFS fixed issues related to property branching and real-time flags.
- Netfs improves Ceph integration, write-back flag processing, and DIO reading.
- Drivers
- Many graphics driver updates, especially for AMD GPUs, include fixes for MES ring buffer overflow, JPEG command submission, and cursor display.
- Network drivers received updates, including updates for Intel, Mellanox and Realtek devices.
- Fixed memory leak in Thunderbolt driver.
- Supports shutdown function in the MLXBF3 GPIO driver.
- Fixed potential null pointer access issues in MT7921 Wi-Fi drivers.
- Fixed a deadlock issue that could occur when configuring traffic classes during HNS3 network driver reset.
- A common notification chain was introduced for the ideapad-laptop platform driver.
- Other driver fixes resolve issues in areas such as USB, I2C, and SPI.
- Kernel Subsystem
- KVM (Kernel Virtual Machine) fixes SEV, SVM, and ARM64 virtualization.
- Improved memory management, including fixes for hugelb locking, migration deadlocks and memory billing.
- Core network updates, including updates for TCP, UDP, and network namespaces.
- tool
- Most of the changes involve synchronizing header files in the tool directory, especially for x86 architectures.
Build regressions and improvements:
This update also addresses many build regressions and improvements in various architectures including Sparc, PowerPC, MIPS, and x86.
During the transition to Linux kernel 6.11-rc4, a total of 11 build error regressions and 21 build error improvements were observed. There are also 2 build warning regressions and 19 build warning improvements .
It is worth noting that these numbers are based on a comparison between v6.11-rc4 and v6.10 . When v6.11-rc4 is compared with previous release candidate v6.11-rc3, there are 6 build error regressions and 4 build error improvements , with no changes in the build warning.
Testing Linux kernel 6.11 RC4:
Now that RC4 is available, the kernel community will continue to test and improve the code.
Developers and users are encouraged to test the fourth release candidate for 6.11 by downloading it from the Kernel.org website or Linus Torvalds' git tree and report any issues they have.
Oh, I forgot to mention it. Linus Torvalds said he has some upcoming travel plans. He expressed his hope that the development process would be calmed down, presumably to allow him to focus on his travels.
For more details, please refer to the Linux Kernel 6.11 RC4 Release Notes .
The above is the detailed content of Linux Kernel 6.11 RC4 Released: Normal Development Cycle Continues. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1384
1384
 52
52
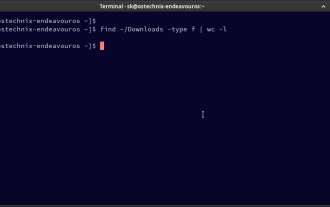 How To Count Files And Directories In Linux: A Beginner's Guide
Mar 19, 2025 am 10:48 AM
How To Count Files And Directories In Linux: A Beginner's Guide
Mar 19, 2025 am 10:48 AM
Efficiently Counting Files and Folders in Linux: A Comprehensive Guide Knowing how to quickly count files and directories in Linux is crucial for system administrators and anyone managing large datasets. This guide demonstrates using simple command-l
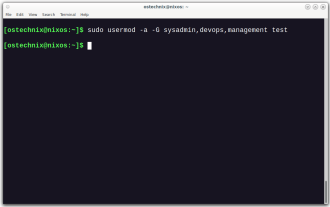 How To Add A User To Multiple Groups In Linux
Mar 18, 2025 am 11:44 AM
How To Add A User To Multiple Groups In Linux
Mar 18, 2025 am 11:44 AM
Efficiently managing user accounts and group memberships is crucial for Linux/Unix system administration. This ensures proper resource and data access control. This tutorial details how to add a user to multiple groups in Linux and Unix systems. We
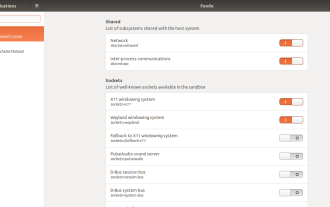 How To Easily Configure Flatpak Apps Permissions With Flatseal
Mar 22, 2025 am 09:21 AM
How To Easily Configure Flatpak Apps Permissions With Flatseal
Mar 22, 2025 am 09:21 AM
Flatpak application permission management tool: Flatseal User Guide Flatpak is a tool designed to simplify Linux software distribution and use. It safely encapsulates applications in a virtual sandbox, allowing users to run applications without root permissions without affecting system security. Because Flatpak applications are located in this sandbox environment, they must request permissions to access other parts of the operating system, hardware devices (such as Bluetooth, network, etc.) and sockets (such as pulseaudio, ssh-auth, cups, etc.). This guide will guide you on how to easily configure Flatpak with Flatseal on Linux
 How To List Or Check All Installed Linux Kernels From Commandline
Mar 23, 2025 am 10:43 AM
How To List Or Check All Installed Linux Kernels From Commandline
Mar 23, 2025 am 10:43 AM
Linux Kernel is the core component of a GNU/Linux operating system. Developed by Linus Torvalds in 1991, it is a free, open-source, monolithic, modular, and multitasking Unix-like kernel. In Linux, it is possible to install multiple kernels on a sing
 How To Type Indian Rupee Symbol In Ubuntu Linux
Mar 22, 2025 am 10:39 AM
How To Type Indian Rupee Symbol In Ubuntu Linux
Mar 22, 2025 am 10:39 AM
This brief guide explains how to type Indian Rupee symbol in Linux operating systems. The other day, I wanted to type "Indian Rupee Symbol (₹)" in a word document. My keyboard has a rupee symbol on it, but I don't know how to type it. After
 Yt-dlp Commands: The Complete Tutorial For Beginners (2025)
Mar 21, 2025 am 11:00 AM
Yt-dlp Commands: The Complete Tutorial For Beginners (2025)
Mar 21, 2025 am 11:00 AM
Have you ever wanted to save your favorite videos from the internet? Whether it's a funny cat video or a tutorial you want to watch later, Yt-dlp is here to help! In this comprehensive yt-dlp tutorial, we will explain what yt-dlp is, how to install i
 What is the Linux best used for?
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:11 AM
What is the Linux best used for?
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Linux is best used as server management, embedded systems and desktop environments. 1) In server management, Linux is used to host websites, databases, and applications, providing stability and reliability. 2) In embedded systems, Linux is widely used in smart home and automotive electronic systems because of its flexibility and stability. 3) In the desktop environment, Linux provides rich applications and efficient performance.
 LocalSend - The Open-Source Airdrop Alternative For Secure File Sharing
Mar 24, 2025 am 09:20 AM
LocalSend - The Open-Source Airdrop Alternative For Secure File Sharing
Mar 24, 2025 am 09:20 AM
If you're familiar with AirDrop, you know it's a popular feature developed by Apple Inc. that enables seamless file transfer between supported Macintosh computers and iOS devices using Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. However, if you're using Linux and missing o




