
Scene Text Recognition (STR) remains a significant challenge for researchers due to the wide variety of text appearances in real-world settings. Recognizing text on a document is different from identifying text on a t-shirt, for instance. The Multi-Granularity Prediction for Scene Text Recognition (MGP-STR) model, introduced at ECCV 2022, offers a groundbreaking approach. MGP-STR combines the robustness of Vision Transformers (ViT) with innovative multi-granularity linguistic predictions, significantly improving its ability to handle complex STR tasks. This results in higher accuracy and better usability across diverse, challenging real-world scenarios, providing a simple yet powerful solution.
*This article is part of the***Data Science Blogathon.
MGP-STR is a vision-based STR model excelling without needing a separate language model. It integrates linguistic information directly into its architecture using the Multi-Granularity Prediction (MGP) strategy. This implicit approach allows MGP-STR to outperform both purely visual models and language-enhanced methods, achieving state-of-the-art STR results.
The architecture consists of two key components:
The fusion of predictions at character, subword, and word levels through a simple yet effective strategy ensures MGP-STR captures both visual and linguistic details.
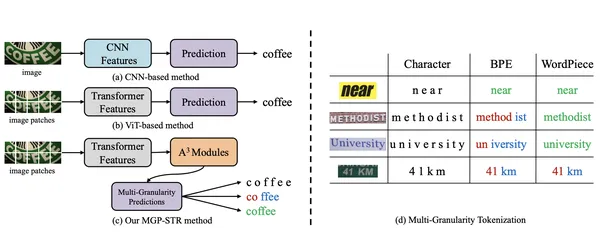
MGP-STR is primarily for OCR tasks on text images. Its unique ability to implicitly incorporate linguistic knowledge makes it particularly useful in real-world scenarios with varied and distorted text. Examples include:
This section shows how to use MGP-STR for scene text recognition on a sample image. You'll need PyTorch, the Transformers library, and dependencies (PIL, requests).
Import the required libraries: transformers for model handling, PIL for image manipulation, and requests for fetching online images.
<code>from transformers import MgpstrProcessor, MgpstrForSceneTextRecognition import requests import base64 from io import BytesIO from PIL import Image from IPython.display import display, Image as IPImage</code>
Load the MGP-STR base model and its processor from Hugging Face Transformers.
<code>processor = MgpstrProcessor.from_pretrained('alibaba-damo/mgp-str-base')
model = MgpstrForSceneTextRecognition.from_pretrained('alibaba-damo/mgp-str-base')</code>Create a function to input image URLs, process them using MGP-STR, and return text predictions. This handles image conversion, base64 encoding, and text decoding.
<code>def predict(url):
image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw).convert("RGB")
pixel_values = processor(images=image, return_tensors="pt").pixel_values
outputs = model(pixel_values)
generated_text = processor.batch_decode(outputs.logits)['generated_text']
buffered = BytesIO()
image.save(buffered, format="PNG")
image_base64 = base64.b64encode(buffered.getvalue()).decode("utf-8")
display(IPImage(data=base64.b64decode(image_base64)))
print("\n\n")
return generated_text</code>The examples with image URLs and predictions are omitted here to save space, but they would follow the same structure as in the original text, calling the predict function with different image URLs.
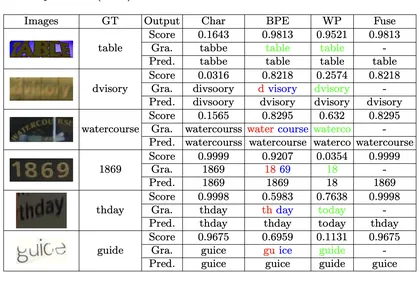
The model's accuracy is evident from the image examples. Its efficiency is noteworthy, running on a CPU with low RAM usage. This makes it easily adaptable for fine-tuning on domain-specific tasks.
MGP-STR effectively combines vision and language understanding. Its innovative multi-granularity predictions provide a comprehensive approach to STR, improving accuracy and adaptability without external language models. Its simple yet accurate architecture makes it a valuable tool for researchers and developers in OCR and STR. Its open-source nature promotes further advancements in the field.
Q1: What is MGP-STR and how does it differ from traditional STR models? A1: MGP-STR integrates linguistic predictions directly into its vision-based framework using MGP, eliminating the need for separate language models found in traditional methods.
Q2: What datasets were used to train MGP-STR? A2: The base model was trained on MJSynth and SynthText.
Q3: Can MGP-STR handle distorted or low-quality text images? A3: Yes, its multi-granularity prediction mechanism allows it to handle such challenges.
Q4: Is MGP-STR suitable for languages other than English? A4: While optimized for English, it can be adapted to other languages with appropriate training data.
Q5: How does the A³ module contribute to MGP-STR’s performance? A5: The A³ module refines ViT outputs, enabling subword-level predictions and embedding linguistic information.
Note: The image placeholders remain the same as in the original input. Remember to replace the bracketed links with actual links.
The above is the detailed content of Scene Text Recognition Using Vision-Based Text Recognition. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




