Core Knowledge That Modern Linux Kernel Developer Should Have
Linux Kernel Development Guide: Skills, Tools, and Environments

programming language:
The Linux kernel is mainly written in C language, so proficient in C language (especially C11 and GNU extensions) is the core skill. Some architecture-related code and high-performance drivers may use assembly language (x86, ARM, or RISC-V, depending on the hardware platform). The Rust language is also gaining increasing attention because it provides a safer and more reliable alternative.
Build system and scripts:
Understanding KBuild and Make build systems is crucial for modifying and extending kernel code. Shell scripting skills are also essential for automated repetitive tasks.
Software environment:
Git version control system is an indispensable part of the Linux kernel development process. The Qemu/KVM virtualization platform provides an efficient environment for development and debugging, allowing code testing in virtual machines to avoid frequent restarts of real hardware.
Debugging and performance analysis:
Traditional kernel debugging methods include printing debugging information using the printk function and viewing it through the dmesg command. Modern kernel development widely uses the Ftrace framework for efficient kernel tracking and debugging, as well as perf tools for performance analysis. The eBPF framework provides a revolutionary improvement in kernel observability, allowing user programs to be run inside the kernel and pass information to user space.
Embedded development:
The Linux kernel is widely used in embedded systems. Embedded developers need to be familiar with the Buildroot or Yocto build system, as well as the DTS files (describing hardware components) and the U-boot bootloader. Busybox is a commonly used lightweight user space framework.
Development environment:
Most kernel developers use vim (or other terminal editor), tmux terminal multiplexer, and cscope code cross-reference tools.
Core concept:
Linux kernel development skills are divided into general skills and domain-specific skills.
General skills:
- Kernel encoding style: Follow the encoding style specifications of the Linux kernel and check the code using
scripts/checkpatch.plscript. - Kernel encoding mode: Be familiar with the recommended encoding modes of the kernel, such as using goto statements to handle multi-step resource initialization.
- Kernel internal data structure: Master commonly used kernel data structures, such as linked lists, queues, hash tables, binary trees, red and black trees, etc.
- Synchronous primitives: Understand and proficient in various synchronization primitives, such as atomic operations, spin locks, semaphores, mutexes, RCUs, etc., to deal with multithreaded concurrency problems.
- Interrupt processing: Understand the upper and lower half mechanisms of interrupt processing, as well as various delay working mechanisms (task queues, softirqs, taskslets, workqueues, etc.).
- Memory management: Be familiar with the kernel's memory management mechanism, including kmalloc/kfree and slab allocator.
- Virtual File System (VFS): Understand the common interface of VFS and its interaction with various file systems.
- Scheduler: Understand the basic principles of kernel schedulers.
- System call interface: Understand the system call interface between the kernel and user space.
- /sys /proc directory: Familiar with the system information and settings under the /sys and /proc directory.
- Loadable kernel modules: Understand the structure and loading/unloading mechanism of the kernel module, as well as the communication methods with user space (sysfs attributes, MMIO, kernel module parameters, etc.).
- Udev: Understand the Udev subsystem and device hot-swap event handling.
- Fault injection framework: used to test exception code paths.
- Kernel disinfector: (KASAN, KMSAN, etc.) is used to detect memory corruption and other problems.
- Lock Correctivity Verifier: Used to detect deadlocks and live locks.
- Kdump/Kexec: used to analyze kernel crashes.
Domain-specific skills: depends on the specific development field (network, storage, virtualization, encryption, embedded, etc.).
User Space Tools:
Kernel developers need to be proficient in using the following user space tools:
- bash (or other shell)
- ssh
- tmux
- minicom (for serial communication for embedded devices)
- vim
- gdb (for debugging kernel errors)
Soft Skills:
- enthusiasm
- patience
- will
Hope this guide can help you better understand Linux kernel development. Remember that continuous learning and practice are the key to becoming a good kernel developer.
The above is the detailed content of Core Knowledge That Modern Linux Kernel Developer Should Have. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
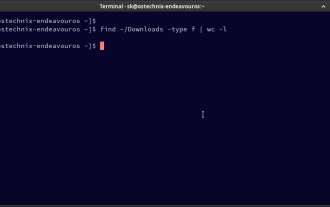 How To Count Files And Directories In Linux: A Beginner's Guide
Mar 19, 2025 am 10:48 AM
How To Count Files And Directories In Linux: A Beginner's Guide
Mar 19, 2025 am 10:48 AM
Efficiently Counting Files and Folders in Linux: A Comprehensive Guide Knowing how to quickly count files and directories in Linux is crucial for system administrators and anyone managing large datasets. This guide demonstrates using simple command-l
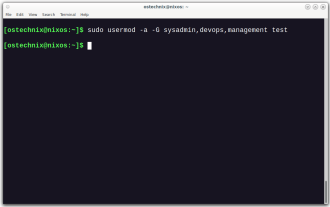 How To Add A User To Multiple Groups In Linux
Mar 18, 2025 am 11:44 AM
How To Add A User To Multiple Groups In Linux
Mar 18, 2025 am 11:44 AM
Efficiently managing user accounts and group memberships is crucial for Linux/Unix system administration. This ensures proper resource and data access control. This tutorial details how to add a user to multiple groups in Linux and Unix systems. We
 How To List Or Check All Installed Linux Kernels From Commandline
Mar 23, 2025 am 10:43 AM
How To List Or Check All Installed Linux Kernels From Commandline
Mar 23, 2025 am 10:43 AM
Linux Kernel is the core component of a GNU/Linux operating system. Developed by Linus Torvalds in 1991, it is a free, open-source, monolithic, modular, and multitasking Unix-like kernel. In Linux, it is possible to install multiple kernels on a sing
 How To Type Indian Rupee Symbol In Ubuntu Linux
Mar 22, 2025 am 10:39 AM
How To Type Indian Rupee Symbol In Ubuntu Linux
Mar 22, 2025 am 10:39 AM
This brief guide explains how to type Indian Rupee symbol in Linux operating systems. The other day, I wanted to type "Indian Rupee Symbol (₹)" in a word document. My keyboard has a rupee symbol on it, but I don't know how to type it. After
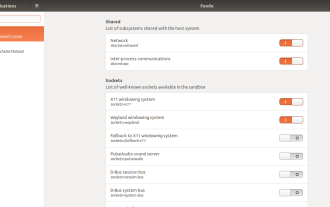 How To Easily Configure Flatpak Apps Permissions With Flatseal
Mar 22, 2025 am 09:21 AM
How To Easily Configure Flatpak Apps Permissions With Flatseal
Mar 22, 2025 am 09:21 AM
Flatpak application permission management tool: Flatseal User Guide Flatpak is a tool designed to simplify Linux software distribution and use. It safely encapsulates applications in a virtual sandbox, allowing users to run applications without root permissions without affecting system security. Because Flatpak applications are located in this sandbox environment, they must request permissions to access other parts of the operating system, hardware devices (such as Bluetooth, network, etc.) and sockets (such as pulseaudio, ssh-auth, cups, etc.). This guide will guide you on how to easily configure Flatpak with Flatseal on Linux
 What is the Linux best used for?
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:11 AM
What is the Linux best used for?
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Linux is best used as server management, embedded systems and desktop environments. 1) In server management, Linux is used to host websites, databases, and applications, providing stability and reliability. 2) In embedded systems, Linux is widely used in smart home and automotive electronic systems because of its flexibility and stability. 3) In the desktop environment, Linux provides rich applications and efficient performance.
 Linux Kernel 6.14 RC6 Released
Mar 24, 2025 am 10:21 AM
Linux Kernel 6.14 RC6 Released
Mar 24, 2025 am 10:21 AM
Linus Torvalds has released Linux Kernel 6.14 Release Candidate 6 (RC6), reporting no significant issues and keeping the release on track. The most notable change in this update addresses an AMD microcode signing issue, while the rest of the updates
 LocalSend - The Open-Source Airdrop Alternative For Secure File Sharing
Mar 24, 2025 am 09:20 AM
LocalSend - The Open-Source Airdrop Alternative For Secure File Sharing
Mar 24, 2025 am 09:20 AM
If you're familiar with AirDrop, you know it's a popular feature developed by Apple Inc. that enables seamless file transfer between supported Macintosh computers and iOS devices using Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. However, if you're using Linux and missing o




