Ubuntu Server Security Best Practices

Bolstering Ubuntu Server Security: A Comprehensive Guide
Ubuntu Server, a globally popular open-source operating system, powers countless infrastructures. Its efficiency and ease of use make it a favorite, but like any system, it's vulnerable to security threats. This guide outlines essential best practices to fortify your Ubuntu Server against common attacks and maintain data integrity.
1. Robust User Management:
- Dedicated Admin User: Create a separate administrative account for system administration, minimizing root user risks.
- Strong Password Policies: Enforce complex password requirements to thwart guessing attacks.
- SSH Key Authentication: Implement SSH key authentication for secure, passwordless logins, enhancing security and streamlining access.
2. Proactive System Updates & Patch Management:
- Regular Updates: Regularly apply security patches and updates.
- Automated Updates: Configure automatic updates for continuous security without manual intervention.
-
Unattended Upgrades: Leverage tools like
unattended-upgradesfor automated security update installation.
3. Impeccable Network Security:
- Firewall Configuration: Utilize a firewall (UFW or iptables) to control network traffic.
- Disable Unused Services: Deactivate unnecessary network services to reduce attack vectors.
- Fail2ban Implementation: Employ Fail2ban to detect and block brute-force login attempts.
4. Secure File System Management:
- Correct File Permissions: Maintain accurate file permissions and ownership to prevent unauthorized access.
- Access Control Lists (ACLs): Use ACLs for granular file and directory access control.
- File System Monitoring: Implement tools like AIDE to monitor for unauthorized file system modifications.
5. Comprehensive Monitoring & Auditing:
- System Monitoring: Use tools like Nagios for proactive system monitoring and early problem detection.
- Log Auditing: Employ Logwatch or similar tools to analyze system logs for suspicious activity.
- User Activity Monitoring: Utilize auditd to track user actions and identify unauthorized behavior.
6. Secure System Hardening:
- Disable Root Login: Disable direct root login to enhance security.
- GRUB Bootloader Security: Secure the GRUB bootloader to prevent unauthorized boot modifications.
- SELinux/AppArmor: Implement SELinux or AppArmor for robust access control and enhanced security.
7. Data Encryption & Protection:
- Data at Rest Encryption: Utilize LUKS for disk encryption to protect data from unauthorized access.
- Data in Transit Encryption: Employ SSL/TLS to encrypt data during transmission.
- Regular Backups: Implement regular backups using tools like Bacula for data recovery and disaster preparedness.
8. Ongoing Security Assessments:
- Vulnerability Assessments: Use OpenVAS or similar tools for regular vulnerability scans.
- Security Audits: Conduct periodic security audits to evaluate your security posture.
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of emerging security threats and best practices.
Conclusion:
Maintaining a robust security posture for your Ubuntu Server requires ongoing vigilance. By implementing these best practices and staying informed about evolving threats, you can create a resilient and secure server infrastructure. A proactive, security-first approach is crucial in today's dynamic threat landscape.
The above is the detailed content of Ubuntu Server Security Best Practices. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
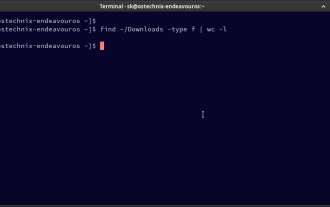 How To Count Files And Directories In Linux: A Beginner's Guide
Mar 19, 2025 am 10:48 AM
How To Count Files And Directories In Linux: A Beginner's Guide
Mar 19, 2025 am 10:48 AM
Efficiently Counting Files and Folders in Linux: A Comprehensive Guide Knowing how to quickly count files and directories in Linux is crucial for system administrators and anyone managing large datasets. This guide demonstrates using simple command-l
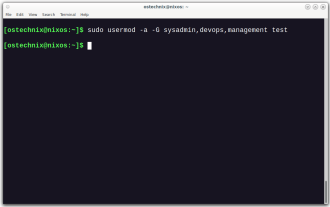 How To Add A User To Multiple Groups In Linux
Mar 18, 2025 am 11:44 AM
How To Add A User To Multiple Groups In Linux
Mar 18, 2025 am 11:44 AM
Efficiently managing user accounts and group memberships is crucial for Linux/Unix system administration. This ensures proper resource and data access control. This tutorial details how to add a user to multiple groups in Linux and Unix systems. We
 How To List Or Check All Installed Linux Kernels From Commandline
Mar 23, 2025 am 10:43 AM
How To List Or Check All Installed Linux Kernels From Commandline
Mar 23, 2025 am 10:43 AM
Linux Kernel is the core component of a GNU/Linux operating system. Developed by Linus Torvalds in 1991, it is a free, open-source, monolithic, modular, and multitasking Unix-like kernel. In Linux, it is possible to install multiple kernels on a sing
 How To Type Indian Rupee Symbol In Ubuntu Linux
Mar 22, 2025 am 10:39 AM
How To Type Indian Rupee Symbol In Ubuntu Linux
Mar 22, 2025 am 10:39 AM
This brief guide explains how to type Indian Rupee symbol in Linux operating systems. The other day, I wanted to type "Indian Rupee Symbol (₹)" in a word document. My keyboard has a rupee symbol on it, but I don't know how to type it. After
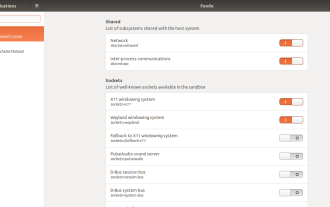 How To Easily Configure Flatpak Apps Permissions With Flatseal
Mar 22, 2025 am 09:21 AM
How To Easily Configure Flatpak Apps Permissions With Flatseal
Mar 22, 2025 am 09:21 AM
Flatpak application permission management tool: Flatseal User Guide Flatpak is a tool designed to simplify Linux software distribution and use. It safely encapsulates applications in a virtual sandbox, allowing users to run applications without root permissions without affecting system security. Because Flatpak applications are located in this sandbox environment, they must request permissions to access other parts of the operating system, hardware devices (such as Bluetooth, network, etc.) and sockets (such as pulseaudio, ssh-auth, cups, etc.). This guide will guide you on how to easily configure Flatpak with Flatseal on Linux
 What is the Linux best used for?
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:11 AM
What is the Linux best used for?
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Linux is best used as server management, embedded systems and desktop environments. 1) In server management, Linux is used to host websites, databases, and applications, providing stability and reliability. 2) In embedded systems, Linux is widely used in smart home and automotive electronic systems because of its flexibility and stability. 3) In the desktop environment, Linux provides rich applications and efficient performance.
 Linux Kernel 6.14 RC6 Released
Mar 24, 2025 am 10:21 AM
Linux Kernel 6.14 RC6 Released
Mar 24, 2025 am 10:21 AM
Linus Torvalds has released Linux Kernel 6.14 Release Candidate 6 (RC6), reporting no significant issues and keeping the release on track. The most notable change in this update addresses an AMD microcode signing issue, while the rest of the updates
 LocalSend - The Open-Source Airdrop Alternative For Secure File Sharing
Mar 24, 2025 am 09:20 AM
LocalSend - The Open-Source Airdrop Alternative For Secure File Sharing
Mar 24, 2025 am 09:20 AM
If you're familiar with AirDrop, you know it's a popular feature developed by Apple Inc. that enables seamless file transfer between supported Macintosh computers and iOS devices using Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. However, if you're using Linux and missing o




