 System Tutorial
System Tutorial
 LINUX
LINUX
 How To Create Interactive Bash Scripts With Yes, No, Cancel Prompt In Linux
How To Create Interactive Bash Scripts With Yes, No, Cancel Prompt In Linux
How To Create Interactive Bash Scripts With Yes, No, Cancel Prompt In Linux
Interactive shell scripts enhance system administration by offering user-friendly, efficient task management. This guide details creating interactive Bash scripts in Linux, incorporating "Yes," "No," and "Cancel" prompts to ensure user confirmation before execution, preventing accidental actions.
Table of Contents
- The
readCommand in Bash- Functionality
- Advantages
- Usage Examples
-
readCommand Basics
- Building Interactive Bash Scripts with Yes/No/Cancel Prompts
- Example 1: Debian System Update Script
- Example 2: Deleting Old Log Files
- Example 3: Copying Files Between Directories
- Conclusion
Introduction
Enhancing Bash scripts with user input significantly improves their utility and user experience. The read command facilitates this interactivity, prompting users for input and storing responses in variables. Combining read with conditional statements (e.g., if, case) enables dynamic script behavior based on user input. This tutorial covers:
- The
readcommand's purpose. - Capturing user input with
read. - Utilizing
ifandcasestatements for response handling. - Practical examples of interactive Bash scripts.
This guide equips you to create interactive Bash scripts that prompt users for confirmation, allowing them to proceed, abort, or cancel operations.
The read Command in Bash
Bash's read command reads a line of input (from the user or a file) and assigns it to one or more variables. It's crucial for interactive shell scripting and text file processing.
Functionality
read pauses script execution, awaiting user input followed by Enter. The entered text is stored in a specified variable.
Advantages
- Enables interactive scripts.
- Allows customized script behavior based on user input.
- Ideal for menus and confirmation prompts before critical actions.
Usage Examples
- Gathering user names for personalized messages.
- Obtaining yes/no confirmations before executing actions.
- Creating interactive menus with user-selectable options.
read Command Basics
1. Syntax:
read [options] variable_name
Options:
-
-r: Prevents backslash interpretation as escape characters. Example:read -r response -
-p: Displays a prompt message (eliminating the need forecho). Example:read -p "What's your name? " name -
-s: Hides user input (suitable for passwords). Example:read -s -p "Enter your password: " password -
-t: Sets a time limit for input. -
-n: Limits the number of characters accepted as input.
2. Reading User Input:
The primary use of read is prompting users for input during script execution.
Example:
echo "Please enter your name:" read name echo "Hello, $name!"

3. Using Prompts:
The -p option simplifies prompt display:
read -p "How old are you? " age echo "I am $age years old."

4. Multiple Variables:
Read multiple inputs into separate variables on a single line:
echo "Enter your first and last names:" read first_name last_name echo "Hello, $first_name $last_name!"

5. Default Values:
Provide default values if the user doesn't enter input:
read -p "Enter your favorite blog [OSTechNix]: " blog
blog=${blog:-OSTechNix}
echo "My favorite blog is $blog."
6. Time Limits:
Set input time limits with -t:
read -t 5 -p "Quick! Type your lucky number (5 seconds): " lucky_number echo "Your lucky number is $lucky_number"

7. Hidden Input (Passwords):
Use -s for sensitive data like passwords:
read -s -p "Enter a password: " password echo # Prints a newline echo "Password received (hidden for security)"
A sample read command snippet prompts for system update confirmation (Yes/No/Cancel):
prompt_for_input() {
while true; do
echo -n "Update system? (y/n/c): "
read -r response
case "$response" in
[Yy]* ) echo "Yes selected."; return 0 ;;
[Nn]* ) echo "No selected."; return 1 ;;
[Cc]* ) echo "Cancel selected."; return 2 ;;
* ) echo "Invalid input."; ;;
esac
done
}Building Interactive Bash Scripts with Yes/No/Cancel Prompts
Three example scripts illustrate interactive script creation using read and conditional statements.
Example 1: Debian System Update Script
This script prompts for confirmation before updating a Debian-based system.
(Script code would be inserted here, similar to the input but potentially improved for clarity and robustness)
Example 2: Deleting Old Log Files
This script warns the user and prompts for confirmation before deleting old log files. Caution: Test this thoroughly before using it on a production system. The script should specify the exact directory and age threshold for deletion.
(Script code would be inserted here, similar to the input but potentially improved for clarity and robustness, emphasizing safety precautions)
Example 3: Copying Files Between Directories
This script prompts for confirmation before copying files, warning about potential overwriting.
(Script code would be inserted here, similar to the input but potentially improved for clarity and robustness, highlighting file overwrite considerations)
Conclusion
This tutorial demonstrated creating interactive Bash scripts with Yes/No/Cancel prompts, using the read command and conditional statements for decision-making. While other methods exist, read offers simplicity and effectiveness. Remember to prioritize user safety and data integrity when creating interactive scripts.
The above is the detailed content of How To Create Interactive Bash Scripts With Yes, No, Cancel Prompt In Linux. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 Mastering Text Manipulation With the Sed Command
Mar 16, 2025 am 09:48 AM
Mastering Text Manipulation With the Sed Command
Mar 16, 2025 am 09:48 AM
The Linux command line interface provides a wealth of text processing tools, one of the most powerful tools is the sed command. sed is the abbreviation of Stream EDitor, a multi-functional tool that allows complex processing of text files and streams. What is Sed? sed is a non-interactive text editor that operates on pipeline inputs or text files. By providing directives, you can let it modify and process text in a file or stream. The most common use cases of sed include selecting text, replacing text, modifying original files, adding lines to text, or removing lines from text. It can be used from the command line in Bash and other command line shells. Sed command syntax sed
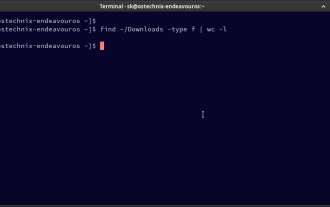 How To Count Files And Directories In Linux: A Beginner's Guide
Mar 19, 2025 am 10:48 AM
How To Count Files And Directories In Linux: A Beginner's Guide
Mar 19, 2025 am 10:48 AM
Efficiently Counting Files and Folders in Linux: A Comprehensive Guide Knowing how to quickly count files and directories in Linux is crucial for system administrators and anyone managing large datasets. This guide demonstrates using simple command-l
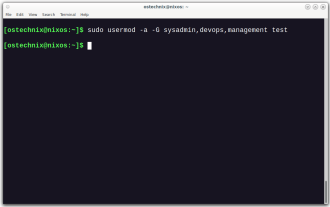 How To Add A User To Multiple Groups In Linux
Mar 18, 2025 am 11:44 AM
How To Add A User To Multiple Groups In Linux
Mar 18, 2025 am 11:44 AM
Efficiently managing user accounts and group memberships is crucial for Linux/Unix system administration. This ensures proper resource and data access control. This tutorial details how to add a user to multiple groups in Linux and Unix systems. We
 How To List Or Check All Installed Linux Kernels From Commandline
Mar 23, 2025 am 10:43 AM
How To List Or Check All Installed Linux Kernels From Commandline
Mar 23, 2025 am 10:43 AM
Linux Kernel is the core component of a GNU/Linux operating system. Developed by Linus Torvalds in 1991, it is a free, open-source, monolithic, modular, and multitasking Unix-like kernel. In Linux, it is possible to install multiple kernels on a sing
 How To Type Indian Rupee Symbol In Ubuntu Linux
Mar 22, 2025 am 10:39 AM
How To Type Indian Rupee Symbol In Ubuntu Linux
Mar 22, 2025 am 10:39 AM
This brief guide explains how to type Indian Rupee symbol in Linux operating systems. The other day, I wanted to type "Indian Rupee Symbol (₹)" in a word document. My keyboard has a rupee symbol on it, but I don't know how to type it. After
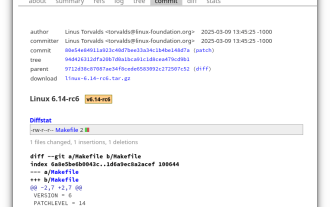 Linux Kernel 6.14 RC6 Released
Mar 24, 2025 am 10:21 AM
Linux Kernel 6.14 RC6 Released
Mar 24, 2025 am 10:21 AM
Linus Torvalds has released Linux Kernel 6.14 Release Candidate 6 (RC6), reporting no significant issues and keeping the release on track. The most notable change in this update addresses an AMD microcode signing issue, while the rest of the updates
 The 8 Best SSH Clients for Linux
Mar 15, 2025 am 11:06 AM
The 8 Best SSH Clients for Linux
Mar 15, 2025 am 11:06 AM
Recommended 8 best SSH clients for Linux system SSH (Secure Shell Protocol) is an encrypted network protocol used to securely run network services on an unsecure network. It is an important part of modern server management and provides secure remote access to the system. SSH clients (applications that utilize the SSH protocol) are an indispensable tool for system administrators, developers and IT professionals. Remote server management is common in the Linux world, and choosing the right SSH client is crucial. This article will discuss 8 best SSH clients for Linux. Selection criteria When choosing the best SSH client for Linux, the following factors must be considered: Performance: Speed and efficiency of SSH clients
 LocalSend - The Open-Source Airdrop Alternative For Secure File Sharing
Mar 24, 2025 am 09:20 AM
LocalSend - The Open-Source Airdrop Alternative For Secure File Sharing
Mar 24, 2025 am 09:20 AM
If you're familiar with AirDrop, you know it's a popular feature developed by Apple Inc. that enables seamless file transfer between supported Macintosh computers and iOS devices using Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. However, if you're using Linux and missing o



