The Sort Command: A Beginner's Guide to Using Linux's Best Organizer

sort command in Linux system is a powerful tool that can efficiently sort and organize data. Whether you are dealing with simple text files or complex datasets, mastering the details of sort commands can significantly improve your productivity. This article will explore the various functions and applications of sort commands and refer to multiple reliable sources.
The basics of sort commands: Getting started
The sort command is an essential utility in Linux for sorting file contents or standard input in ascending or descending order. It is based on line-by-line operations and offers many customization options.
Use the sort command to sort text files
Sort text files is one of the most common applications of sort command. By specifying the desired sorting criteria, you can easily sort rows in alphabetical or numerical order. The -t option allows you to define custom delimiters, while the -r option inverts the sort order.
Advanced sorting tips: Sort by fields and columns
When working with structured data, sorting by specific fields or columns is crucial. sort command provides flexibility in this regard. With the -k option, you can specify the field number or column range to sort. This feature is especially useful when processing CSV files, log files, or other tabular data.
Sort in complex scenarios: sorting with multiple keys
In the case where a single sorting criteria are insufficient, sort command allows you to sort with multiple keys. By combining the -k option and the -s option, you can sort data layer by layer, sort by primary and secondary keys. This approach can make complex data sets orderly and facilitate efficient data analysis.
Custom output sorting: Control sorting stability
By default, the sort command keeps the same keys in the original order. However, you can modify this behavior to achieve ordering stability or instability. The -s option ensures stable sorting, while the -u option removes duplicate rows. Understanding these options allows you to control the output accurately.
Sorting of large files: Handling memory limits
Sorting large files can require a lot of resources, especially when memory is limited. In this case, the sort command provides a solution. The -T option allows you to specify a temporary directory, allowing sort command to use disk space instead of memory, ensuring efficient sorting even if resources are limited.
sort command tips and tips: Improve efficiency
- Use the -n option: sort the values
- Combination sorting and filtering: Use pipelines and other command line tools
- Sort based on specific columns: master
-tand-koptions
in conclusion
Mastering the sort command in Linux will open up endless possibilities for efficient sorting and organizing data. From simple text files to complex datasets, the versatility of sort commands proves its valuable value in a variety of scenarios. By exploring insights from different sources and understanding the numerous options available, you can take full advantage of the potential of sort commands and increase your productivity in your Linux terminal. So, dig deeper, conduct experiments, and release the sort function of sort command.
The above is the detailed content of The Sort Command: A Beginner's Guide to Using Linux's Best Organizer. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 Mastering Text Manipulation With the Sed Command
Mar 16, 2025 am 09:48 AM
Mastering Text Manipulation With the Sed Command
Mar 16, 2025 am 09:48 AM
The Linux command line interface provides a wealth of text processing tools, one of the most powerful tools is the sed command. sed is the abbreviation of Stream EDitor, a multi-functional tool that allows complex processing of text files and streams. What is Sed? sed is a non-interactive text editor that operates on pipeline inputs or text files. By providing directives, you can let it modify and process text in a file or stream. The most common use cases of sed include selecting text, replacing text, modifying original files, adding lines to text, or removing lines from text. It can be used from the command line in Bash and other command line shells. Sed command syntax sed
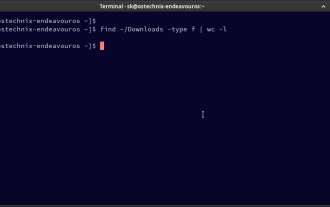 How To Count Files And Directories In Linux: A Beginner's Guide
Mar 19, 2025 am 10:48 AM
How To Count Files And Directories In Linux: A Beginner's Guide
Mar 19, 2025 am 10:48 AM
Efficiently Counting Files and Folders in Linux: A Comprehensive Guide Knowing how to quickly count files and directories in Linux is crucial for system administrators and anyone managing large datasets. This guide demonstrates using simple command-l
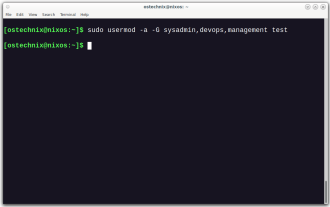 How To Add A User To Multiple Groups In Linux
Mar 18, 2025 am 11:44 AM
How To Add A User To Multiple Groups In Linux
Mar 18, 2025 am 11:44 AM
Efficiently managing user accounts and group memberships is crucial for Linux/Unix system administration. This ensures proper resource and data access control. This tutorial details how to add a user to multiple groups in Linux and Unix systems. We
 How To List Or Check All Installed Linux Kernels From Commandline
Mar 23, 2025 am 10:43 AM
How To List Or Check All Installed Linux Kernels From Commandline
Mar 23, 2025 am 10:43 AM
Linux Kernel is the core component of a GNU/Linux operating system. Developed by Linus Torvalds in 1991, it is a free, open-source, monolithic, modular, and multitasking Unix-like kernel. In Linux, it is possible to install multiple kernels on a sing
 How To Type Indian Rupee Symbol In Ubuntu Linux
Mar 22, 2025 am 10:39 AM
How To Type Indian Rupee Symbol In Ubuntu Linux
Mar 22, 2025 am 10:39 AM
This brief guide explains how to type Indian Rupee symbol in Linux operating systems. The other day, I wanted to type "Indian Rupee Symbol (₹)" in a word document. My keyboard has a rupee symbol on it, but I don't know how to type it. After
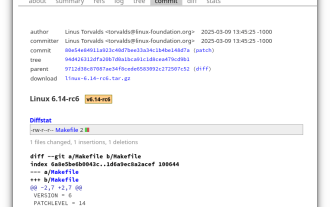 Linux Kernel 6.14 RC6 Released
Mar 24, 2025 am 10:21 AM
Linux Kernel 6.14 RC6 Released
Mar 24, 2025 am 10:21 AM
Linus Torvalds has released Linux Kernel 6.14 Release Candidate 6 (RC6), reporting no significant issues and keeping the release on track. The most notable change in this update addresses an AMD microcode signing issue, while the rest of the updates
 The 8 Best SSH Clients for Linux
Mar 15, 2025 am 11:06 AM
The 8 Best SSH Clients for Linux
Mar 15, 2025 am 11:06 AM
Recommended 8 best SSH clients for Linux system SSH (Secure Shell Protocol) is an encrypted network protocol used to securely run network services on an unsecure network. It is an important part of modern server management and provides secure remote access to the system. SSH clients (applications that utilize the SSH protocol) are an indispensable tool for system administrators, developers and IT professionals. Remote server management is common in the Linux world, and choosing the right SSH client is crucial. This article will discuss 8 best SSH clients for Linux. Selection criteria When choosing the best SSH client for Linux, the following factors must be considered: Performance: Speed and efficiency of SSH clients
 LocalSend - The Open-Source Airdrop Alternative For Secure File Sharing
Mar 24, 2025 am 09:20 AM
LocalSend - The Open-Source Airdrop Alternative For Secure File Sharing
Mar 24, 2025 am 09:20 AM
If you're familiar with AirDrop, you know it's a popular feature developed by Apple Inc. that enables seamless file transfer between supported Macintosh computers and iOS devices using Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. However, if you're using Linux and missing o




