How To Count Files And Directories In Linux: A Beginner's Guide
Efficiently Counting Files and Folders in Linux: A Comprehensive Guide
Knowing how to quickly count files and directories in Linux is crucial for system administrators and anyone managing large datasets. This guide demonstrates using simple command-line tools like find, wc, and ls to accurately determine the number of files and folders in Linux and Unix systems.
Table of Contents
- Counting Files in a Directory with
find - Counting Directories with
find - Advanced Counting with
find'smaxdepthandmindepthOptions- Counting Files within a Specific Depth Range
- Counting Directories at a Specific Depth
- Excluding the Top-Level Directory
- Counting Up to a Specific Depth
- Best Practices
- Counting Directories with
ls - Why
findandlsMight Produce Different Counts - Summary
Counting Files in a Directory with find
To count all files within a directory and its subdirectories, use find combined with wc -l:
find /path/to/your/directory -type f | wc -l
-
find /path/to/your/directory: Initiates the search. -
-type f: Specifies that only files should be found (not directories). -
|: Pipes thefindoutput towc -l. -
wc -l: Counts the lines (each line represents a file).
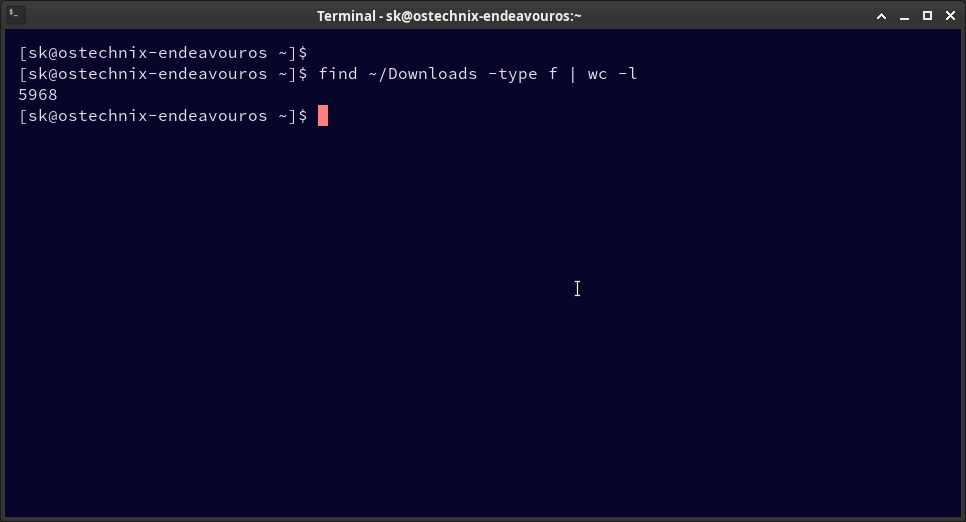
Example:
find ~/Downloads -type f | wc -l 5968
This indicates 5968 files in the Downloads directory.
Counting Directories with find
To count directories, use find with the -type d option:
find /path/to/the/directory -type d | wc -l
-
-type d: Specifies that only directories should be found.
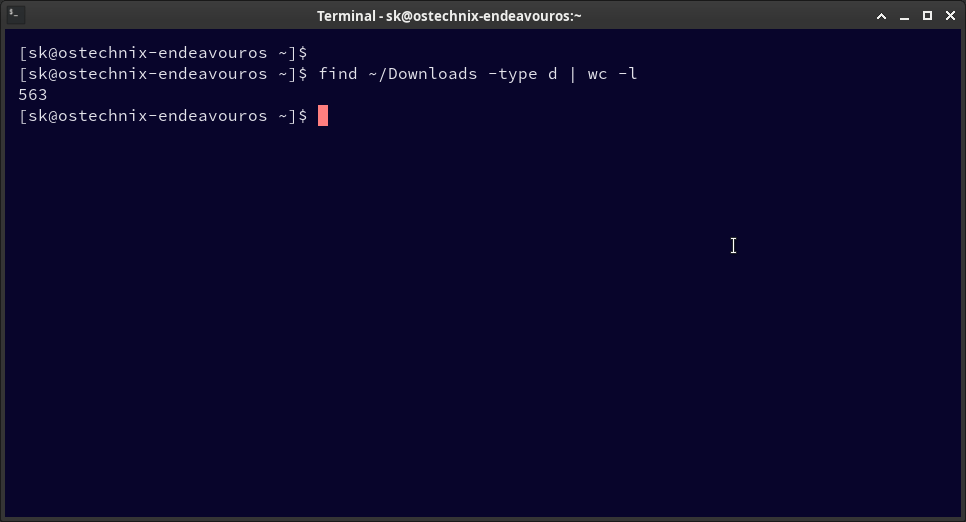
Example:
find ~/Downloads -type d | wc -l 563
This shows 563 directories (including the root directory) within ~/Downloads.
Remember to subtract 1 from the result if you need to exclude the root directory itself.
Advanced Counting with find's maxdepth and mindepth
The maxdepth and mindepth options provide fine-grained control over the search depth.
- Counting Files within a Specific Depth Range: Count files exactly two levels deep:
find /path/to/directory -mindepth 2 -maxdepth 2 -type f | wc -l
- Counting Directories at a Specific Depth: Count directories exactly three levels deep:
find /path/to/directory -mindepth 3 -maxdepth 3 -type d | wc -l
- Excluding the Top-Level Directory: Count files, excluding the top-level directory:
find /path/to/directory -mindepth 1 -type f | wc -l
- Counting Up to a Specific Depth: Count all files up to and including the second level:
find /path/to/directory -maxdepth 2 -type f | wc -l
Best Practices:
- Clearly define your target (files, directories, or both).
- Use
maxdepthandmindepthfor performance optimization in large directories. - Test your command on a small sample before running it on a large directory structure.
Counting Directories with ls
Another approach uses ls, grep, and wc:
ls -lR | grep ^d | wc -l
-
ls -lR: Lists all files and directories recursively with details. -
grep ^d: Filters for lines starting with "d" (directories). -
wc -l: Counts the lines.
This method might yield different results than find due to handling of hidden directories and the root directory.
Why find and ls Might Produce Different Counts
Discrepancies can arise because:
-
Hidden Directories:
findincludes hidden directories by default, whilelstypically doesn't (unless the-aoption is used). -
Root Directory Inclusion:
findincludes the root directory in its count, whilelsmay not, depending on interpretation.
Summary
Using find, ls, and wc, you can efficiently count files and directories in Linux. Understanding the nuances of each command and its options ensures accurate and efficient results, regardless of directory size or complexity. Remember to choose the method best suited to your specific needs and always test your command before applying it to a large directory structure.
The above is the detailed content of How To Count Files And Directories In Linux: A Beginner's Guide. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 Mastering Text Manipulation With the Sed Command
Mar 16, 2025 am 09:48 AM
Mastering Text Manipulation With the Sed Command
Mar 16, 2025 am 09:48 AM
The Linux command line interface provides a wealth of text processing tools, one of the most powerful tools is the sed command. sed is the abbreviation of Stream EDitor, a multi-functional tool that allows complex processing of text files and streams. What is Sed? sed is a non-interactive text editor that operates on pipeline inputs or text files. By providing directives, you can let it modify and process text in a file or stream. The most common use cases of sed include selecting text, replacing text, modifying original files, adding lines to text, or removing lines from text. It can be used from the command line in Bash and other command line shells. Sed command syntax sed
 How To Count Files And Directories In Linux: A Beginner's Guide
Mar 19, 2025 am 10:48 AM
How To Count Files And Directories In Linux: A Beginner's Guide
Mar 19, 2025 am 10:48 AM
Efficiently Counting Files and Folders in Linux: A Comprehensive Guide Knowing how to quickly count files and directories in Linux is crucial for system administrators and anyone managing large datasets. This guide demonstrates using simple command-l
 How To Add A User To Multiple Groups In Linux
Mar 18, 2025 am 11:44 AM
How To Add A User To Multiple Groups In Linux
Mar 18, 2025 am 11:44 AM
Efficiently managing user accounts and group memberships is crucial for Linux/Unix system administration. This ensures proper resource and data access control. This tutorial details how to add a user to multiple groups in Linux and Unix systems. We
 How To List Or Check All Installed Linux Kernels From Commandline
Mar 23, 2025 am 10:43 AM
How To List Or Check All Installed Linux Kernels From Commandline
Mar 23, 2025 am 10:43 AM
Linux Kernel is the core component of a GNU/Linux operating system. Developed by Linus Torvalds in 1991, it is a free, open-source, monolithic, modular, and multitasking Unix-like kernel. In Linux, it is possible to install multiple kernels on a sing
 How To Type Indian Rupee Symbol In Ubuntu Linux
Mar 22, 2025 am 10:39 AM
How To Type Indian Rupee Symbol In Ubuntu Linux
Mar 22, 2025 am 10:39 AM
This brief guide explains how to type Indian Rupee symbol in Linux operating systems. The other day, I wanted to type "Indian Rupee Symbol (₹)" in a word document. My keyboard has a rupee symbol on it, but I don't know how to type it. After
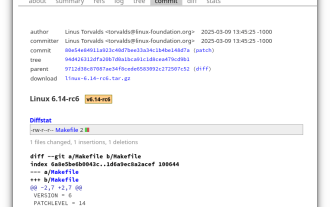 Linux Kernel 6.14 RC6 Released
Mar 24, 2025 am 10:21 AM
Linux Kernel 6.14 RC6 Released
Mar 24, 2025 am 10:21 AM
Linus Torvalds has released Linux Kernel 6.14 Release Candidate 6 (RC6), reporting no significant issues and keeping the release on track. The most notable change in this update addresses an AMD microcode signing issue, while the rest of the updates
 The 8 Best SSH Clients for Linux
Mar 15, 2025 am 11:06 AM
The 8 Best SSH Clients for Linux
Mar 15, 2025 am 11:06 AM
Recommended 8 best SSH clients for Linux system SSH (Secure Shell Protocol) is an encrypted network protocol used to securely run network services on an unsecure network. It is an important part of modern server management and provides secure remote access to the system. SSH clients (applications that utilize the SSH protocol) are an indispensable tool for system administrators, developers and IT professionals. Remote server management is common in the Linux world, and choosing the right SSH client is crucial. This article will discuss 8 best SSH clients for Linux. Selection criteria When choosing the best SSH client for Linux, the following factors must be considered: Performance: Speed and efficiency of SSH clients
 LocalSend - The Open-Source Airdrop Alternative For Secure File Sharing
Mar 24, 2025 am 09:20 AM
LocalSend - The Open-Source Airdrop Alternative For Secure File Sharing
Mar 24, 2025 am 09:20 AM
If you're familiar with AirDrop, you know it's a popular feature developed by Apple Inc. that enables seamless file transfer between supported Macintosh computers and iOS devices using Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. However, if you're using Linux and missing o




